Abstract
Contamination of water by toxic dyes is a serious environmental problem. Adsorbents prepared by an environmentally safe route have stood out for application in pollutant removal. Herein, iron oxide–based nanomaterial composed of Fe(III)-OOH and Fe(II/III) bound to proanthocyanidins, with particles in the order of 20 nm, was prepared by green synthesis assisted by extract of açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) berry seeds from an agro-industrial residue. The nanomaterial was applied in the adsorption of cationic dyes. Screening tests were carried out for methylene blue (MB), resulting in an outstanding maximum adsorption capacity of 531.8 mg g−1 at 343 K, pH 10, 180 min. The kinetics followed a pseudo-second-order model and the isotherm of Fritz-Schülnder provided the best fit. Thermodynamic data show an endothermic process with entropy increase, typical of chemisorption. The proposed mechanism is based on the multilayer formation over a heterogeneous adsorbent surface, with chemical and electrostatic interactions of MB with the iron oxide nanoparticles and with the proanthocyanidins. The high adsorption efficiency was attributed to the network formed by the polymeric proanthocyanidins that entangled and protected the iron oxide nanoparticles, which allowed the reuse of the nanomaterial for seven cycles without loss of adsorption efficiency.
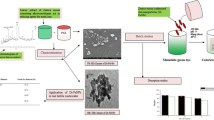
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aljerf L (2018) High-efficiency extraction of bromocresol purple dye and heavy metals as chromium from industrial effluent by adsorption onto a modified surface of zeolite: Kinetics and equilibrium study. J Environ Manage 225:120–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.07.048
Ayawei N, Ebelegi AN, Wankasi D (2017) Modelling and interpretation of adsorption isotherms. J Chem 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3039817
Bano S, Nazir S, Nazir A et al (2016) Microwave-assisted green synthesis of superparamagnetic nanoparticles using fruit peel extracts: surface engineering, T2relaxometry, and photodynamic treatment potential. Int J Nanomed 11:3833–3848. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S106553
Bensedira A, Haddaoui N, Doufnoune R et al (2022) Study of methylene blue dye elimination from water using polyaniline (PANI) and PANI/SiO2 composite. Polym Polym Compos 30:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/09673911221141747
Bolade OP, Williams AB, Benson NU (2020) Green synthesis of iron-based nanomaterials for environmental remediation: a review. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 13:100279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2019.100279
Bollinger JC, Tran HN, Lima EC (2022) Comments on “removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution using citric acid modified apricot stone”. Chem Eng Commun 0:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2022.2111556
Bonilla-Petriciolet A, Mendoza-Castillo DI, Reynel-Ávila HE (2017) Adsorption processes for water treatment and purification. Springer International Publishing AG. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-58136-1
Carvalho SSF, Carvalho NMF (2017) Dye degradation by green heterogeneous Fenton catalysts prepared in presence of Camellia sinensis. J Environ Manage 187:82–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.11.032
Corrêa BS, Costa MS, Cabrera-Pasca GA et al (2020) High-saturation magnetization in small nanoparticles of Fe3O4 coated with natural oils. Journal of Nanoparticle Research 22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-4761-5
Cui K, Yan B, **e Y et al (2018) Regenerable urchin-like Fe3O4@PDA-Ag hollow microspheres as catalyst and adsorbent for enhanced removal of organic dyes. J Hazard Mater 350:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.02.011
da Fonseca Machado AP, Geraldi MV, do Nascimento RD et al (2021) Polyphenols from food by-products: an alternative or complementary therapy to IBD conventional treatments. Food Res Int 140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.110018
De Bem GF, Costa CA, Santos IB et al (2018) Antidiabetic effect of euterpe oleracea mart. (açaí) extract and exercise training on high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: A positive interaction. PLoS One 13:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199207
De Oliveira PRB, Da Costa CA, De Bem GF et al (2015) Euterpe oleracea Mart.-derived polyphenols protect mice from diet-induced obesity and fatty liver by regulating hepatic lipogenesis and cholesterol excretion. PLoS One 10:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143721
De Souza APN, Licea YE, Colaço MV et al (2021) Green iron oxides/amino-functionalized MCM-41 composites as adsorbent for anionic azo dye: kinetic and isotherm studies. J Environ Chem Eng 9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105062
Dotto GL, Costa JAV, Pinto LAA (2013a) Kinetic studies on the biosorption of phenol by nanoparticles from Spirulina sp. LEB 18. J Environ Chem Eng 1:1137–1143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.08.029
Dotto GL, Moura JM, Cadaval TRS, Pinto LAA (2013b) Application of chitosan films for the removal of food dyes from aqueous solutions by adsorption. Chemical Engineering Journal 214:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.10.027
Ebrahiminezhad A, Zare-Hoseinabadi A, Sarmah AK et al (2018) Plant-mediated synthesis and applications of iron nanoparticles. Mol Biotechnol 60:154–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-017-0053-4
Franco RT, Silva AL, Licea YE et al (2021) Green synthesis of iron oxides and phosphates via thermal treatment of iron polyphenols synthesized by a Camellia sinensis extract. Inorg Chem 60:5734–5746. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c03794
Fu C, Yan M, Wang Z et al (2023) New insights into the degradation and detoxification of methylene blue using heterogeneous-Fenton catalyzed by sustainable siderite. Environ Res 216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114819
Gallori S, Bilia AR, Bergonzi MC et al (2004) Polyphenolic constituents of fruit pulp of Euterpe oleracea Mart. (Açai palm). Chromatographia 59:739–743. https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-004-0305-x
Gironés-Vilaplana A, Baenas N, Villaño D et al (2014) Evaluation of Latin-American fruits rich in phytochemicals with biological effects. J Funct Foods 7:599–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2013.12.025
Gordon A, Cruz APG, Cabral LMC et al (2012) Chemical characterization and evaluation of antioxidant properties of açaí fruits (Euterpe oleraceae Mart.) during ripening. Food Chem 133:256–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.11.150
Gorjian H, Raftani Amiri Z, Mohammadzadeh Milani J, Ghaffari Khaligh N (2021) Preparation and characterization of the encapsulated myrtle extract nanoliposome and nanoniosome without using cholesterol and toxic organic solvents: a comparative study. Food Chem 342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128342
Greenwood NN, Gibb TC (1971) Mössbauer spectroscopy. Chapman and Hall Ltd., London
Guo M, Weng X, Wang T, Chen Z (2017) Biosynthesized iron-based nanoparticles used as a heterogeneous catalyst for the removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol. Sep Purif Technol 175:222–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.11.042
Hamdaoui O, Naffrechoux E (2007) Modeling of adsorption isotherms of phenol and chlorophenols onto granular activated carbon. Part II. Models with more than two parameters. J Hazard Mater 147:401–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.023
Hossain A, Ngo HH, Guo W (2013) Introductory of Microsoft Excel SOLVER function - spreadsheet method for isotherm and kinetics modelling of metals biosorption in water and wastewater. J Water Sustain 3:223–237
Huang L, Weng X, Chen Z et al (2014) Synthesis of iron-based nanoparticles using oolong tea extract for the degradation of malachite green. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 117:801–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.09.054
Hutin A (2022) Difference between isoelectric point (IEP), point of zero charge (PZC), and isoionic point (IIP). In The little corner of science: Vol. Application Notes φ - χ : Theory (1.0). Zenodo:1–5. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.634686
Katata-Seru L, Moremedi T, Aremu OS, Bahadur I (2018) Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera extracts and their applications: removal of nitrate from water and antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli. J Mol Liq 256:296–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.11.093
Khaghani S, Ghanbari D, Khaghani S (2017) Green synthesis of iron oxide-palladium nanocomposites by pepper extract and its application in removing of colored pollutants from water. J Nanostruct 7:175–182. https://doi.org/10.22052/jns.2017.03.002
Kilmartin PA, Hsu CF (2003) Characterisation of polyphenols in green, oolong, and black teas, and in coffee, using cyclic voltammetry. Food Chem 82:501–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(03)00066-9
Krishna Moorthy A, Govindarajan Rathi B, Shukla SP et al (2021) Acute toxicity of textile dye methylene blue on growth and metabolism of selected freshwater microalgae. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2020.103552
Liu Y (2009) Is the free energy change of adsorption correctly calculated? J Chem Eng Data 54:1981–1985. https://doi.org/10.1021/je800661q
Machado S, Pacheco JG, Nouws HPA et al (2015) Characterization of green zero-valent iron nanoparticles produced with tree leaf extracts. Sci Total Environ 533:76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.091
Markova Z, Novak P, Kaslik J et al (2014) Iron(II,III)-polyphenol complex nanoparticles derived from green tea with remarkable ecotoxicological impact. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:1674–1680. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc5001435
Mondal P, Anweshan A, Purkait MK (2020) Green synthesis and environmental application of iron-based nanomaterials and nanocomposite: a review. Chemosphere 259:127509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127509
Monje DS, Mercado DF, Mesa GAP, Valencia GC (2022a) Carbon dots decorated magnetite nanocomposite obtained using yerba mate useful for remediation of textile wastewater through a photo-Fenton treatment: Ilex paraguariensis as a platform of environmental interest—part 2. Environ Sci Pollut Res 3070–3087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22405-1
Monje DS, Ruiz OS, Valencia GC, Mercado DF (2022b) Iron oxide nanoparticles embedded in organic microparticles from Yerba Mate useful for remediation of textile wastewater through a photo-Fenton treatment: Ilex paraguariensis as a platform of environmental interest – part 1. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:57127–57146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19744-4
Mozaffari Majd M, Kordzadeh-Kermani V, Ghalandari V et al (2022) Adsorption isotherm models: a comprehensive and systematic review (2010−2020). Sci Total Environ 812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151334
Nakamura T, Silva FS, da Silva DX et al (2013) Determinação da atividade antioxidante e do teor total de polifenol em amostras de chá de ervas comercializadas em sachets. ABCS Health Sci 38:8–16. https://doi.org/10.7322/abcshs.v38i1.3
Nebaghe KC, El Boundati Y, Ziat K et al (2016) Comparison of linear and non-linear method for determination of optimum equilibrium isotherm for adsorption of copper(II) onto treated Martil sand. Fluid Phase Equilib 430:188–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2016.10.003
Oladoye PO, Ajiboye TO, Omotola EO, Oyewola OJ (2022) Methylene blue dye: toxicity and potential elimination technology from wastewater. Results Eng 16:100678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2022.100678
Ovchinnikov OV, Evtukhova AV, Kondratenko TS et al (2016) Manifestation of intermolecular interactions in FTIR spectra of methylene blue molecules. Vib Spectrosc 86:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2016.06.016
Pan Z, Lin Y, Sarkar B et al (2019) Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using red peanut skin extract: synthesis mechanism, characterization and effect of conditions on chromium removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 558:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.09.106
Perrotti TC, Freitas NS, Alzamora M et al (2019) Green iron nanoparticles supported on amino-functionalized silica for removal of the dye methyl orange. J Environ Chem Eng 7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103237
Pessôa TS, de Lima Ferreira LE, da Silva MP et al (2019) Açaí waste beneficing by gasification process and its employment in the treatment of synthetic and raw textile wastewater. J Clean Prod 240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118047
Prasad C, Gangadhara S, Venkateswarlu P (2016) Bio-inspired green synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using watermelon rinds and their catalytic activity. Appl Nanosci (Switzerland) 6:797–802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-015-0485-8
Priya N, Kaur K, Sidhu AK (2021) Green synthesis: an eco-friendly route for the synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles. Front Nanotechnol 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnano.2021.655062
Raji F, Saraeian A, Pakizeh M, Attarzadeh F (2015) Removal of Pb(ii) from aqueous solution by mesoporous silica MCM-41 modified by ZnCl2: kinetics, thermodynamics, and isotherms. RSC Adv 5:37066–37077. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra01192b
Rashid R, Shafiq I, Akhter P et al (2021) A state-of-the-art review on wastewater treatment techniques: the effectiveness of adsorption method. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:9050–9066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12395-x
Saharan P, Kumar V, Kaushal I et al (2023) A comprehensive review on the metal-based green valorized nanocomposite for the remediation of emerging colored organic waste. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25998-3
Sandford SA, Bernstein MP, Materese CK (2013) The infrared spectra of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with excess peripheral H atoms (H n -PAHs) and their relation to the 3.4 and 6.9 μm pah emission features. Astrophysical J Supplement Series 205. https://doi.org/10.1088/0067-0049/205/1/8
Schauss AG, Wu X, Prior RL et al (2006) Phytochemical and nutrient composition of the freeze-dried amazonian palm berry, Euterpe oleraceae Mart. (Acai). J Agric Food Chem 54:8598–8603. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf060976g
Shalaby SM, Madkour FF, El-Kassas HY et al (2021) Green synthesis of recyclable iron oxide nanoparticles using Spirulina platensis microalgae for adsorptive removal of cationic and anionic dyes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:65549–65572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15544-4
Sharma B, Kumari N, Mathur S, Sharma V (2022) A systematic review on iron-based nanoparticle-mediated clean-up of textile dyes: challenges and prospects of scale-up technologies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:312–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16846-3
Silveira C, Shimabuku QL, Fernandes Silva M, Bergamasco R (2018) Iron-oxide nanoparticles by the green synthesis method using Moringa oleifera leaf extract for fluoride removal. Environ Technol (United Kingdom) 39:2926–2936. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1369582
Thakare Y, Kore S, Sharma I, Shah M (2022) A comprehensive review on sustainable greener nanoparticles for efficient dye degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:55415–55436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20127-y
Thomas JM (1961) Textbook errors, 29 the existence of endothermic adsorption guest author. J Chem Educ 38:138–139. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed038p138
Trotte NSF, Alzamora M, Sánchez DR, Carvalho NMF (2018) Removal of methyl orange by heterogeneous Fenton catalysts prepared using glycerol as green reducing agent. Environ Technol (United Kingdom) 39:2822–2833. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1367038
Valencia-Hernandez LJ, Wong-Paz JE, Ascacio-Valdés JA et al (2021) Procyanidins: from agro-industrial waste to food as bioactive molecules. Foods 10:1–33. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123152
Vidovix TB, Januário EFD, Araújo MF et al (2022) Investigation of two new low-cost adsorbents functionalized with magnetic nanoparticles for the efficient removal of triclosan and a synthetic mixture. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:46813–46829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19187-x
Wang J, Guo X (2020) Adsorption isotherm models: classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 258:127279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127279
Wang T, ** X, Chen Z et al (2014) Green synthesis of Fe nanoparticles using eucalyptus leaf extracts for treatment of eutrophic wastewater. Sci Total Environ 466–467:210–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.07.022
Wu Y, Zhang M, Zhao H et al (2014) Functionalized mesoporous silica material and anionic dye adsorption: MCM-41 incorporated with amine groups for competitive adsorption of Acid Fuchsine and Acid Orange II. RSC Adv 4:61256–61267. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra11737a
Yang J, Qiu K (2010) Preparation of activated carbons from walnut shells via vacuum chemical activation and their application for methylene blue removal. Chem Eng J 165:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.09.019
Zhou X, Yu X, Hao J, Liu H (2022) Comments on the calculation of the standard equilibrium constant using the Langmuir model in Journal of Hazardous Materials 422 (2022) 126863. J Hazard Mater 429:128407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128407
Zhou X, Zhou X (2020) Comments on ‘“Removal of uranium (VI) from aqueous solution by adsorption of hematite”’, by X. Shuibo, Z. Chun, Z. **nghuo, Y. **g, Z. **aojian, W. **gsong. J Environ Radioact 213:2019–2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2019.106106
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Laboratório de Cristalografia e Difração de Raio-X (CBPF), LACES (UFRJ) for thermogravimetric analyses, and Laboratório Multiusuário de Caracterização de Materiais for zeta potential measurements (LAMATE-UFF).
Funding
This work was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico – CNPq [PQ-2/2021: 316550/2021-3], Fundação Carlos Chagas de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro – FAPERJ [JCNE 2018: E-26/203.023/2018; JCNE 2019: E-26/202.755/2019; CNE 2021: E-26/200.416/2023; Emergentes 2019: E-26/010.002171/2019; E-26/010.002212/2019; Agrárias 2022: SEI-260003/001750/2023], and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior – Brasil (CAPES) [Financing code 001].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ana P. N. Souza: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, data curation, writing — original draft, visualization. Mariella Alzamora: investigation, formal analysis, writing — review and editing. Dalber R. Sánchez: investigation; formal analysis; writing — review and editing. Marcos V. Colaço: methodology, writing — review and editing. Marcelo A. V. Souza: methodology, writing - review and editing. Jefferson S. Gois: methodology, writing — review and editing. Jaqueline D. Senra: formal analysis; writing — review and editing, supervision. Nakédia M. F. Carvalho: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, resources, writing — review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme Luiz Dotto
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 7960 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
De Souza, A.P.N., Sánchez, D.R., Alzamora, M. et al. Outstanding adsorption capacity of iron oxide synthesized with extract of açaí berry residue: kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic study for dye removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 109423–109437 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29872-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29872-0