Abstract
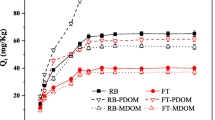
In recent years, the accumulation ability of heavy metals in sediment has become a key indicator for sediment pollution prevention and control. The adsorption-desorption processes of typical heavy metal pollutants in sediments under different conditions were explored and relied in this article. In addition, different binary competitive adsorption systems were designed to study the competitive adsorption properties of heavy metal contaminants, The quasi-secondary kinetic model simulated the adsorption kinetic process. The sediment adsorption rates for heavy metals were (in descending order) Cu, Pb, Cd, Zn. The Elovich equation simulated the desorption kinetics process better, and the sediment desorption rates for heavy metals were (in descending order) Cd, Cu, Zn, Pb. The average free adsorption energy E of heavy metals was within the range of 8–16 kJ∙mol−1. After the removal of organic matter, the ability of the sediment to sequester heavy metals decreases, The binary competitive adsorption results showed that the presence of interfering ions had the greatest effect on Cd and the least effect on Pb. The adsorption and desorption of the four heavy metals by the sediments in the submerged zone increased with the increase of temperature, and the ratio of desorption to adsorption also increased therewith: the adsorptions of heavy metals by the sediments were all spontaneous processes (under heat absorption reactions). The presence of organic matter can increase the ability of the sediment to sequester Cd, Pb, Cu, and Zn. Additionally, heavy metals exhibited significant selective adsorption properties.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Arias M, Perez-Novo C, Lopez E, Soto B (2006) Competitive adsorption and desorption of copper and zinc in acid soils. Geoderma 133(3-4):151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.07.002
Atkinson CA, Jolley DF, Simpson SL (2007) Effect of overlying water pH, dissolved oxygen, salinity and sediment disturbances on metal release and sequestration from metal contaminated marine sediments. Chemosphere 69(9):1428–1437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.04.068
Baghenejad M, Javaheri F, Moosavi AA (2016) Adsorption isotherms of some heavy metals under conditions of their competitive adsorption onto highly calcareous soils of southern Iran. Arch Agron Soil Sci 62(10):1462–1473. https://doi.org/10.1080/036503402016.1147647
Campillo-Cora C, Conde-Cid M, Arias-Estevez M, Fernandez-Calvino D, Alonso-Vega F (2020) Specific adsorption of heavy metals in soils: individual and competitive experiments. Basel, Switz 10(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10081113
Cela-Dablanca R, Barreiro A, Ferreira-Coelho G, Campillo-Cora C, Perez-Rodriguez P, Arias-Estevez M, Nunez-Delgado A, Alvarez-Rodriguez E, Fernandez-Sanjurjo MJ (2022) Cu and As(V) adsorption and desorption on/from different soils and bio-adsorbents. Materials 15(14). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15145023
Cerqueira B, Covelo EF, Andrade L, Vega FA (2011) The influence of soil properties on the individual and competitive sorption and desorption of Cu and Cd. Geoderma 162(1-2):20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.08.013
Chen ZF, Ding YF, Jiang XY, Duan HJ, Ruan XL, Li ZH, Li YP (2022) Combination of UNMIX, PMF model and Pb-Zn-Cu isotopic compositions for quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in suburban agricultural soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113369
Conde-Cid M, Ferreira-Coelho G, Fernandez-Calvino D, Nunez-Delgado A, Fernandez-Sanjurjo MJ, Arias-Estevez M, Alvarez-Rodriguez E (2020) Single and simultaneous adsorption of three sulfonamides in agricultural soils: effects of pH and organic matter content. Sci Total Environ 744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140872
Covelo EF, Vega FA, Andrade ML (2007) Simultaneous sorption and desorption of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in acid soils I. selectivity sequences. J Hazard Mater 147(3):852–861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.123
Cranswick RH, Cook PG, Lamontagne S (2014) Hyporheic zone exchange fluxes and residence times inferred from riverbed temperature and radon data. J Hydrol 519:1870–1881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.09.059
Das B, Mondal NK, Bhaumik R, Roy P (2014) Insight into adsorption equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics of lead onto alluvial soil. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(4):1101–1114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0279-z
Datry T, Larned ST, Scarsbrook MR (2007) Responses of hyporheic invertebrate assemblages to large-scale variation in flow permanence and surface-subsurface exchange. Freshwater Biol (8):52, 1452–1462. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2007.01775.x
Ding ZH, Wan YS, Hu X, Wang SS, Zimmerman AR, Gao B (2016) Sorption of lead and methylene blue onto hickory biochars from different pyrolysis temperatures: importance of physicochemical properties. J Ind Eng Chem 37:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.03.035
Dong WH, Shen XF, Wan YY, Cao ZP, Wei YJ, Liu Y (2022) Adsorption/desorption of naphthalene and phenanthrene in a binary competitive system in the riparian zone. Environ Geochem Health 44(11):3875–3890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01147-y
Erses AS, Fazal MA, Onay TT, Craig WH (2005) Determination of solid waste sorption capacity for selected heavy metals in landfills. J Hazard Mater 121(1-3):223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.02.011
Fan Q, He J, Xue H, Lü C, Liang Y, Saruli Sun Y, Shen L (2007) Competitive adsorption, release and speciation of heavy metals in the Yellow River sediments, China. Environ Geol 53(2):239–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0638-5
Fu J, Sheng S, Wen T, Zhang ZM, Wang Q, Hu QX, Li QS, An SQ, Zhu HL (2011) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of the Jialu River. Ecotoxicology 20(5):940–950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0622-4
Fu J, Zhao CP, Luo YP, Liu CS, Kyzas GZ, Luo Y, Zhao DY, An SQ, Zhu HL (2014) Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: their relations to environmental factors. J Hazard Mater 270:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.044
Futalan CM, Phatai P, Kim J, Maulana AY, Yee JJ (2019) Treatment of soil washing wastewater via adsorption of lead and zinc using graphene oxide. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(17):17292–17304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05010-7
Helios-Rybicka E, Wojcik R (2012) Competitive sorption/desorption of Zn, Cd, Pb, Ni, Cu, and Cr by clay-bearing mining wastes. Appl Clay Sci:65, 6–66, 13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2012.06.006
Hsieh CH, Lo SL, Kuan WH, Chen CL (2006) Adsorption of copper ions onto microwave stabilized heavy metal sludge. J Hazard Mater 136(2):338–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.026
Huang LM, ** Q, Tandon P, Li AM, Shan AD, Du JJ (2018) High-resolution insight into the competitive adsorption of heavy metals on natural sediment by site energy distribution. Chemosphere 197:411–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.056
Huang Y, Fu C, Li Z, Fang F, Ouyang WJ, Guo JS (2019) Effect of dissolved organic matters on adsorption and desorption behavior of heavy metals in a water-level-fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China, Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109695
Kong XS, Tian K, Jia YY, He ZH, Song SY, He XB, **ang CG, An SQ, Tian XJ (2020) Ecological improvement by restoration on the Jialu River: water quality, species richness and distribution. Mar Freshwater Res 71(12):1602–1615. https://doi.org/10.1071/mf19262
Li YK, Liu F, **ao DY, Zhou XJ, Zhu PF, Wang X, Zhang LC, Sun CY (2017) Thermodynamic test on antimony adsorption performance of modified activated carbon. Fresenius Environ Bull 26(3):2271–2276
Li Z, Li XZ, Wang SH, Che FF, Zhang Y, Yang PJ, Zhang JB, Liu YX, Guo HC, Fu ZH (2023) Adsorption and desorption of heavy metals at water sediment interface based on Bayesian model. J Environ Manage 329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117035
Li ZY, Ma ZW, van der Kuijp TJ, Yuan ZW, Huang L (2014) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: pollution and health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 468:843–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.090
Liao LX, Selim HM (2009) Competitive sorption of nickel and cadmium in different soils. Soil Sci 174(10):549–555. https://doi.org/10.1097/SS.0b013e3181bbbd27
Liu J, Liu YJ, Liu Y, Liu Z, Zhang AN (2018a) Quantitative contributions of the major sources of heavy metals in soils to ecosystem and human health risks: a case study of Yulin, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 164:261–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.030
Liu Y, Yan YB, Seshadri B, Qi FJ, Xu YL, Bolan N, Zheng FL, Sun XY, Han WQ, Wang LJ (2018b) Immobilization of lead and copper in aqueous solution and soil using hydroxyapatite derived from flue gas desulphurization gypsum. J Geochem Explor 184:239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.08.006
Lu SG, Xu QF (2009) Competitive adsorption of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn by different soils of Eastern China. Environ Geol 57(3):685–693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1347-4
Ma FJ, Wan Y, Yuan GX, Meng LP, Dong ZM, Hu JY (2012a) Occurrence and source of nitrosamines and secondary amines in groundwater and its adjacent Jialu River Basin, China. Environ Sci Technol 46(6):3236–3243. https://doi.org/10.1021/es204520b
Ma FJ, Yuan GX, Meng LP, Oda Y, Hu JY (2012b) Contributions of flumequine and nitroarenes to the genotoxicity of river and ground waters. Chemosphere 88(4):476–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.02.080
Mai NTH, Postma D, Trang PTK, Jessen S, Viet PH, Larsen F (2014) Adsorption and desorption of arsenic to aquifer sediment on the Red River floodplain at Nam Du, Vietnam. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 142:587–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2014.07.014
Miranda LS, Ayoko GA, Egodawatta P, Goonetilleke A (2022) Adsorption-desorption behavior of heavy metals in aquatic environments: influence of sediment, water and metal ionic properties. J Hazard Mater 421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126743
Miranda LS, Wijesiri B, Ayoko GA, Egodawatta P, Goonetilleke A (2021) Water-sediment interactions and mobility of heavy metals in aquatic environments. Water Res 202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117386
Mishra SR, Chandra R, Kaila AJ, Darshi BS (2017) Kinetics and isotherm studies for the adsorption of metal ions onto two soil types. Environ Technol Innovation 7:87–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2016.12.006
Ottosen LM, Hansen HK, Jensen PE (2009) Relation between pH and desorption of Cu, Cr, Zn, and Pb from industrially polluted soils. Water, Air, Soil Pollut 201(1-4):295–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9945-z
Otunola BO, Ololade OO (2020) A review on the application of clay minerals as heavy metal adsorbents for remediation purposes. Environ Technol Innovation 18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100692
Qu JH, Tian X, Jiang Z, Cao B, Akindolie MS, Hu Q, Feng CC, Feng Y, Meng XL, Zhang Y (2020a) Multi -component adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) onto microwave-functionalized cellulose: kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics, mechanisms and application for electroplating wastewater purification. J Hazard Mater 387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat2019.121718
Qu M, Chen J, Huang B, Zhao Y (2020b) Enhancing apportionment of the point and diffuse sources of soil heavy metals using robust geostatistics and robust spatial receptor model with categorical soil-type data. Environ Pollut 265(Pt A):114964
Saeedi M, Hosseinzadeh M, Rajabzadeh M (2011) Competitive heavy metals adsorption on natural bed sediments of Jajrood River, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 62(3):519–527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0544-0
Sangiumsak N, Punrattanasin P (2014) Adsorption behavior of heavy metals on various soils. Pol J Environ Stud 23(3):853–865
Serrano S, Garrido F, Campbell CG, Garcia-Gonzalez MT (2005) Competitive sorption of cadmium and lead in acid soils of Central Spain. Geoderma 124(1-2):91–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.04.002
Shaheen SM, Tsadilas CD (2010) Influence of fly ash and sewage sludge application on cadmium and lead sorption by an acidic alfisol. Pedosphere 20(4):436–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1002-0160(10)60033-1
Sharifipour F, Hojati S, Landi A, Cano F (2015) Kinetics and thermodynamics of lead adsorption from aqueous solutions onto Iranian sepiolite and zeolite. Int J Environ Res 9(3):1001–1010
Song JX, Yang XG, Zhang JL, Long YQ, Zhang Y, Zhang TF (2015) Assessing the variability of heavy metal concentrations in liquid-solid two-phase and related environmental risks in the Weihe River of Shaanxi Province, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12(7):8243–8262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120708243
Sun J, Zhang R, Qin L, Zhu HX, Huang Y, Xue YG, An SQ, **e XC, Li AM (2017) Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity reduction of the polluted urban river after ecological restoration: a field-scale study of Jialu River in northern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(7):6715–6723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8352-z
Uygur V, Karaduman MA, Kececi M, Sukusu E, Mujdeci M (2017) Competitive adsorption of heavy metals in different soils. Fresenius Environ Bull 26(10):6205–6211
Valett HM, Hakenkamp CC, Boulton AJ (1993) Perspectives on the hyporheic zone - integrating hydrology and biology - introduction. J N Am Benthol Soc 12(1):40–43. https://doi.org/10.2307/1467683
Wan Y, Bao YY, Zhou QX (2010) Simultaneous adsorption and desorption of cadmium and tetracycline on cinnamon soil. Chemosphere 80(7):807–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.04.066
Wang HF, Luo PC (2020) Preparation, kinetics, and adsorption mechanism study of microcrystalline cellulose-modified bone char as an efficient Pb (II) adsorbent. Water, Air, Soil Pollut 231(7). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04687-8
Wang L, Dong K, Geng CY, Li JR, Yu LJ, Xu C, Zhu HL (2015) Effects of do on nitrogen release and transition from sediments to water of the Jialu River. Fresenius Environ Bull 24(6B):2009–2016
Wang WL, Gao JQ, Guo X, Li WC, Tian XY, Zhang RQ (2012) Long-term effects and performance of two-stage baffled surface flow constructed wetland treating polluted river. Ecol Eng 49:93–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.08.016
Wang Y, Tang XW, Chen YM, Zhan LT, Li ZZ, Tang Q (2009) Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Cd(II) on loess soil from China. J Hazard Mater 172(1):30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.121
Wei X, Han LF, Gao B, Zhou HD, Lu J, Wan XH (2016) Distribution, bioavailability, and potential risk assessment of the metals in tributary sediments of Three Gorges Reservoir: the impact of water impoundment. Ecol Indic 61:667–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.10.018
Wu LJ, Yue WF, Zheng NZ, Guo MS, Teng YG (2022a) Assessing the impact of different salinities on the desorption of Cd, Cu and Zn in soils with combined pollution. Sci Total Environ 836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155725
Wu YF, Li X, Yu L, Wang TQ, Wang JN, Liu TT (2022b) Review of soil heavy metal pollution in China: spatial distribution, primary sources, and remediation alternatives. Resour, Conserv Recycl 181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106261
Yang L, Song X, Zhang Y, Han D, Zhang B, Long D (2012) Characterizing interactions between surface water and groundwater in the Jialu River basin using major ion chemistry and stable isotopes. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16(11):4265–4277. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-16-4265-2012
Yin YJ, Impellitteri CA, You SJ, Allen HE (2002) The importance of organic matter distribution and extract soil : solution ratio on the desorption of heavy metals from soils. Sci Total Environ 287(1-2):107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(01)01000-2
Zhang FJ, Ou XX, Chen S, Ran CQ, Quan X (2012a) Competitive adsorption and desorption of copper and lead in some soil of North China. Front Environ Sci Eng 6(4):484–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-012-0423-x
Zhang, H., Gao, M., Song, A.M., Zhao, J.J. and Song, M.W. 2012b Ecological risk of heavy metals pollution in sediments of Beijiang River, pp. 1137-+, Hohhot, PEOPLES R CHINA
Zhang KZ, Shen JQ, Han H, Jia YZ (2019) Urban river health analysis of the Jialu River in Zhengzhou City using the improved fuzzy matter-element extension model. Water 11(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061190
Zhang MK, Fang LP, Huang CY (2006) Competitive adsorption and mobility sequence of heavy metals in urban soils of southeastern China. J Environ Sci 18(2):329–333
Zhang YZ, Song XF, Kondoh A, **a J, Tang CY (2011) Behavior, mass inventories and modeling evaluation of xenobiotic endocrine-disrupting chemicals along an urban receiving wastewater river in Henan Province, China. Water Res 45(1):292–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.07.057
Zhao CP, Zhou XJ, Dong K, Fu J, Zhu DD, An SQ, Zhu HL (2017) Potential ecological risk and speciation analysis of heavy metals in sediments from the Jialu River, China. Int J Environ Pollut 61(1):72–88. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijep.2017.082700
Zheng XM, Dou JF, Yuan J, Qin W, Hong XX, Ding AZ (2017) Removal of Cs+ from water and soil by ammonium-pillared montmorillonite/Fe3O4 composite. J Environ Sci 56:12–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.08.019
Zhou YF, Haynes RJ (2012) A comparison of water treatment sludge and red mud as adsorbents of As and Se in aqueous solution and their capacity for desorption and regeneration. Water, Air, Soil Pollut 223(9):5563–5573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1296-0
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41402225 and 41972261), the Key Scientific Research in Universities in Henan Province (Grant No. 21A170014), and Key Research and Development and Promotion Program of Henan Province in 2022 (Key Science and Technology).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Furong Yu and Yangkun Li; sample collection, Furong Yu; experiment and analysis, Yangkun Li; writing—original draft preparation, Yuekun Ji; data curation, Furong Yu; chart drawing: Yue Meng and Yangkun Li; writing—review and editing, Furong Yu and Yuekun Ji; visualization, Yuekun Ji; project administration, Furong Yu and Zhi** Li; funding acquisition, Furong Yu and Zhi** Li. All the authors have read and approved the manuscript. All authors agree to the publication of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
This article has not been published before and has not been considered for publication elsewhere. Its publication has been approved by all co-authors and relevant institutions.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Luke Mosley
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 6962 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, ., Ji, Y., Li, Z. et al. Adsorption-desorption characteristics of typical heavy metal pollutants in submerged zone sediments: a case study of the Jialu section in Zhengzhou, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 96055–96074 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29059-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29059-7