Abstract
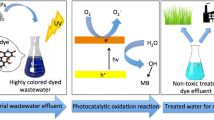
Photocatalytic degradation, as an advanced oxidation process (AOPs), offers a great advantage to target persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in water. RSM in the present study which is statistical means for optimizing processes like photocatalysis with minimum laboratory experimentation. RSM has a history of being a potent design experiment tool for creating new processes, modifying their designs, and optimizing their performances. Herein, a highly sought-after, easily preparable, visible-light active, copper bismuth oxide (CuBi2O4) is applied against a toxic emerging contaminant, 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) under an LED light source (viible light λ > 420 nm). A simple coprecipitation method was adopted to synthesize CuBi2O4 and later analyzed with FESEM, EDX, XRD, FTIR, and spectroscopy to determine its intrinsic properties. Principally, the photocatalytic degradation investigations were based on response surface methodology (RSM), which is a commanding tool in the optimization of the processes. The 2,4-DCP concentration (pollutant loading), CuBi2O4 dosage (catalyst dosge), contact time, and pH were the chosen as dependent factors, that were optimized. However, under optimal conditions, the CuBi2O4 nanoparticle showed a remarkable photocatalytic performance of 91.6% at pH = 11.0 with a pollutant concentration of 0.5 mg/L and a catalyst dose of 5 mg/L within 8 h. The obtained RSM model showed a satisfactory correlation between experimental and predicted values of 2,4-DCP removal, with an agreeable probability value (p) of 0.0069 and coefficient of regression (R2) of 0.990. It is therefore anticipated that the study may open up new possibilities for formulating a plan to specifically target these organic pollutants. In addition, CuBi2O4 possessed fair reusability for three-consequent cycles. Hence, the as-synthesized nanoparticles applied for photocatalysis foster a fit-for-purpose and reliable system in the decontamination of 2,4 DCP in environmental samples, and also the study highlights the efficient use of RSM for environmental remediation, particularly in AOP implementation.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Abdulkarem AM, Li J, Aref AA et al (2011) CuBi2O4 single crystal nanorods prepared by hydrothermal method : growth mechanism and optical properties. Mater Res Bull 46:1443–1450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2011.05.005
Adeem Ghaffar Rana and Mirjana Minceva (2021) Analysis of photocatalytic degradation of phenol with exfoliated graphitic carbon nitride and light-emitting diodes using response surface methodology. Catalysts 11:2–15https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11080898
Al-osta A, Saleh B, Nakate UT, Jadhav VV (2020) Microelectronic Engineering Electrodeposited spruce leaf-like structured copper bismuth oxide electrode for supercapacitor application. Microelectron Eng 229:111359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2020.111359
Ali M, Hashemi Z, Mohammadyan M, Fakhar M (2021) In vitro cytotoxicity against human cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and AGS), antileishmanial and antibacterial activities of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Scrophularia striata extract. Surfaces and Interfaces 23:100963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2021.100963
An W, Yang T, Liu C et al (2023) CuBi2O4 surface-modified three-dimensional graphene hydrogel adsorption and in situ photocatalytic Fenton synergistic degradation of organic pollutants. Appl Surf Sci 615:156396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.156396
Ashfaq M, Talreja N, Chauhan D, Adriana CAR (2022) A facile synthesis of CuBi2O4 hierarchical dumbbell ‑ shaped nanorod cluster : a promising photocatalyst for the degradation of caffeic acid. Environmental Science and pollutaion Research 53873–53883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19592-2
Balarak D, Mengelizadeh N, Rajiv P, Chandrika K (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin from aqueous solutions by titanium dioxide nanoparticles loaded on graphene oxide. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13525-1
Cao Y, He T, Li M et al (2022) A novel strategy to enhance the visible light driven photocatalytic activity of CuBi2O4 through its piezoelectric response. J Phys Chem Solids 167:110732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2022.110732
Chen F, Yang Q, Li X et al (2017) Hierarchical assembly of graphene-bridged Ag3PO4/Ag/BiVO4 (040) Z-scheme photocatalyst: an efficient, sustainable and heterogeneous catalyst with enhanced visible-light photoactivity towards tetracycline degradation under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B 200:330–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.07.021
Chen XT, Qiao H, Li XY, et al (2015) Electrical properties of Hg1-xCdxTe by different etching techniques. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2015.09.023
Choquette-Labbé M, Shewa WA, Lalman JA, Shanmugam SR (2014) Photocatalytic degradation of phenol and phenol derivatives using a Nano-TiO2 catalyst: integrating quantitative and qualitative factors using response surface methodology. Water (switzerland) 6:1785–1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6061785
Desai NN, Soraganvi VS, Madabhavi VK (2020) Solar photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants in landfill leachate using TiO2 nanoparticles by RSM and ANN. Nature Environ Pollut Technol 19:651–662. https://doi.org/10.46488/NEPT.2020.V19I02.019
Elaziouti A (2015) Preparation and characterization of p – n heterojunction CuBi2O4/CeO2 and its photocatalytic activities under UVA light irradiation. 120–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2014.08.002
Gao H, Wang F, Wang S, et al (2019) Photocatalytic activity tuning in a novel Ag2S/CQDs/CuBi2O4 composite : synthesis and photocatalytic mechanism. 115:140–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.03.021
Gnanasekaran L, Rajendran S, Priya AK, et al (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol using bio-green assisted TiO2–CeO2 nanocomposite system. Environ Res 195:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.110852
Govindan K, Suresh AK, Sakthivel T, et al (2019) Effect of peroxomonosulfate, peroxodisulfate and hydrogen peroxide on graphene oxide photocatalytic performances in methyl orange dye degradation. Chemosphere 237:124479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124479
Hao D, Yang Y, Xu B, Cai Z (2018) Bifunctional fabric with photothermal effect and photocatalysis for highly efficient clean water generation bifunctional fabric with photothermal effect and photocatalysis for highly efficient clean water generation. ACS publications 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02094
Hashemi Z, Mizwari ZM, Mohammadi-aghdam S (2022) Sustainable green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Sambucus ebulus phenolic extract (AgNPs @ SEE) : optimization and assessment of photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange and their in vitro antibacterial and anticancer activity. Arab J Chem 15:103525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103525
Heidari Z, Pelalak R, EshaghiMalekshah R et al (2022) A new insight into catalytic ozonation of sulfasalazine antibiotic by plasma-treated limonite nanostructures: experimental, modeling and mechanism. Chem Eng J 428:131230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131230
Jiangtian Li, Mark Griep, YuSong Choi and DC (2018) Photoelectrochemical overall water splitting with textured CuBi2O4 as photocathode. The Royal Society of Chemistry 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CC09041B
Jones KC, Voogt P De (1999) Persistent organic pollutants (POPs): state of the science. Environ Pollut 100:209–221. S0269-7491(99)00098-6
Karaca M, Kiranşan M, Karaca S et al (2016) Sonocatalytic removal of naproxen by synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles on montmorillonite. Ultrason Sonochem 31:250–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.01.009
Kaur M, Noonia A, Dogra A, Thind PS (2021) Optimising the parameters affecting degradation of Cypermethrin in an aqueous solution using TiO2/H2O2 mediated UV photocatalysis : RSM-BBD, kinetics, isotherms and reusability. Int J Environ Anal Chem 00:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1872066
Khormali K, Mizwari ZM, Masoumeh S et al (2021) Bioorganic Chemistry Novel Dy2O3/ZnO-Au ternary nanocomposites : green synthesis using pomegranate fruit extract, characterization and their photocatalytic and antibacterial properties. Bioorg Chem 115:105204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105204
Kidd KA, Blanchfield PJ, Mills KH et al (2007) Collapse of a fish population after exposure to a synthetic estrogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:8897–8901. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0609568104
Körbahti BK, Rauf MA (2008) Response surface methodology (RSM) analysis of photoinduced decoloration of toludine blue. Chem Eng J 136:25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.03.007
Li S, Ma X, Liu L, Cao X (2015) Degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol in wastewater by low temperature plasma coupled with TiO2 photocatalysis. RSC Adv 5:1902–1909. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra10797g
Lin Y, Yang C, Wu S et al (2020) Construction of built-in electric field within silver phosphate photocatalyst for enhanced removal of recalcitrant organic pollutants. Adv Func Mater 2002918:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202002918
Liu C, Min Y, Zhang A et al (2019) Electrochemical treatment of phenol-containing wastewater by facet- tailored TiO2: efficiency, characteristics and mechanisms. Water Research 165:114980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.114980
Mahy JG, Lejeune L, Haynes T, et al (2021) Crystalline ZnO photocatalysts prepared at ambient temperature: Influence of morphology on p-nitrophenol degradation in water. Catalysts 11:. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11101182
Ming T, Gong T, De RRK et al (2016) Freshwater generation from a solar chimney power plant. Energy Convers Manage 113:189–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.01.064
Mohammad MS, Ebrahimzadeh A, Mortazavi-derazkola ANS (2020) Novel NiFe/Si/Au magnetic nanocatalyst : Biogenic synthesis, efficient and reusable catalyst with enhanced visible light photocatalytic degradation and antibacterial activity. 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5467
Naghizadeh A, Mizwari ZM, Masoumeh S (2021) Environmental Technology & Innovation Biogenic and eco-benign synthesis of silver nanoparticles using jujube core extract and its performance in catalytic and pharmaceutical applications : Removal of industrial contaminants and in-vitro antibacterial and. Environ Technol Innov 23:101560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101560
Nakada N, Shinohara H, Murata A et al (2007) Removal of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) during sand filtration and ozonation at a municipal sewage treatment plant. Water Res 41:4373–4382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.06.038
Nguyen VH, Smith SM, Wantala K, Kajitvichyanukul P (2020) Photocatalytic remediation of persistent organic pollutants (POPs): a review. Arab J Chem 13:8309–8337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.04.028
Oturan MA, Aaron JJ (2014) Advanced oxidation processes in water/wastewater treatment: principles and applications. A review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44:2577–2641. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2013.829765
Padmanabhan PVA, Sreekumar KP, Thiyagarajan TK et al (2006) Nano-crystalline titanium dioxide formed by reactive plasma synthesis. Vacuum 80:1252–1255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2006.01.054
Rakshitha R, Gurupadayya B, Devi SHK, Pallavi N (2022a) Coprecipitation aided synthesis of bimetallic silver tungstate: a response surface simulation of sunlight-driven photocatalytic removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20062-y
Rakshitha R, Gurupadayya B, Haridass S et al (2022b) Coprecipitation aided synthesis of bimetallic silver tungstate : a response surface simulation of sunlight ‑ driven photocatalytic removal of 2 , 4 ‑ dichlorophenol. Environmental Science and Pollution Researchhttps://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20062-y
Ray S, Lalman JA, Biswas N (2009) Using the Box-Benkhen technique to statistically model phenol photocatalytic degradation by titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 150:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.11.039
Sabonian M, Behnajady MA (2015) Artificial neural network modeling of Cr(VI) photocatalytic reduction with TiO2-P25 nanoparticles using the results obtained from response surface methodology optimization. Desalin Water Treat 56:2906–2916. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.963161
Santhosh Kumar R, Govindan K, Ramakrishnan S et al (2021) Fe3O4 nanorods decorated on polypyrrole/reduced graphene oxide for electrochemical detection of dopamine and photocatalytic degradation of acetaminophen. Appl Surf Sci 556:149765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149765
Shirzadi-ahodashti M, Mizwari ZM, Hashemi Z (2021) Environmental Technology & Innovation Discovery of high antibacterial and catalytic activities of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using C. fruticosu s ( CF-AgNPs ) against multi-drug resistant clinical strains and hazardous pollutants. Environ Technol Innov 23:101607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101607
Sokhansanj A, Haghighi M, Shabani M (2023) Macroporous flowerlike Bi2O2CO3-CuBi2O4 nanoheterojunction photocatalyst for high concentrated malachite green degradation: influence of nanocomposite composition and sonication approach. J Mol Liq 371:121024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.121024
Toe ED, Kurniawan W, Andrews EM et al (2021) All-solid-state Z-scheme plasmonic Si@Au nanoparticles on CuBi2O4/BiVO4 for efficient photocatalytic activity. Adv Powder Technol 32:4330–4342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2021.09.040
Yashas SR, Shivaraju HP, McKay G et al (2021) Designing bi-functional silver delafossite bridged graphene oxide interfaces: Insights into synthesis, characterization, photocatalysis and bactericidal efficiency. Chem Eng J 426:131729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131729
Zhu L, Chen B, Tao S, Chiou CT (2003) Interactions of organic contaminants with mineral-adsorbed surfactants. Environ Sci Technol 37:4001–4006. https://doi.org/10.1021/es026326k
Zulfiqar M, Samsudin MFR, Sufian S (2019) Modelling and optimization of photocatalytic degradation of phenol via TiO2 nanoparticles: an insight into response surface methodology and artificial neural network. J Photochem Photobiol A: Chem 384:112039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112039
Acknowledgements
R., Rakshitha gratefully acknowledges the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, New Delhi, India, for giving financial help via the “National Fellowship and Scholarship for Higher Education of S.T. Students,” broad Award No. 202021-NFST-KAR-00004. The JSS Academy of Higher Education and Research, Mysuru, provided a laboratory facility to the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RR executed the experiments, analyzed the obtained results, and prepared first draft of manuscript. CR supported in experimentation and curation of data. BMG and SHKD assisted in the interpretations of the results and validated th methodology for the study. NP hypothesized and supervised the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ricardo A. Torres-Palma
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rakshitha, R., Rajesh, C., Gurupadayya, B. et al. A response surface modeling and optimization of photocatalytic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol in water using hierarchical nano-assemblages of CuBi2O4 particles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 75655–75667 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27774-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27774-9