Abstract
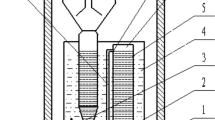
Real domestic wastewater was treated initially in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR), with partial nitrification achieved before the effluent was used as the influent for an anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) reactor (ASBR) system. The effects of three factors, hydraulic retention time (HRT), substrate (NO2−/NH4+) ratio, and the ratio of COD to NH4+ (C/N), on the removal of carbon and nitrogen by an anammox and denitrification process were investigated in the ASBR reactor at 24°C. The response surface methodology was used to explore the interactions of the three factors. The results indicated that the nitrogen and carbon removal efficiency was optimum when HRT, substrate ratio, and C/N ratio were 33 h, 1.4–1.6, and 3–5, respectively. The optimal removal rates of NH4+, NO2−, and COD were 96.30%, 97.79%, and 72.91%, respectively. The ΔNO2−/ΔNH4+ and ΔNO3−/ΔNH4+ ratios of the first two conditions were less than the theoretical anammox values of 1.32 and 0.26 due to heterotrophic denitrification. The optimum nitrogen and carbon removal efficiencies of the third condition could be realized by the synergistic effect of denitrification and the anammox process. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) results showed that when the HRT was 33.48 h, the substrate ratio was 1.46, and the C/N ratio was 4.28, the total nitrogen removal rate (TNR) was optimum (90.12 ± 0.1%), verified by parallel experiments.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Ahn YH, Hwang IS, Min KS (2004) Anammox and partial denitritation in anaerobic nitrogen removal from piggery waste. Water Sci Technol 49(5-6):145–153. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2004.0748
APHA (2007) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington
Banach-Wiśniewska A, Tomaszewski M, Cema G, Ziembińska-Buczyńska A (2020) Medium shift influence on nitrogen removal bacteria: ecophysiology and anammox process performance. Chemosphere 238:124597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124597
Cao S, Du R, Zhou Y (2020) Development of a denitrification system using primary sludge as solid carbon source-potential to couple with anammox process. Sci Total Environ 737:140315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140315
Chen H, Liu S, Yang F, Xue Y, Wang T (2009) The development of simultaneous partial nitrify-cation, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) process in a single reactor for nitrogen removal. Bioresour Technol 100(4):1548–1554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.09.003
Chen Y, Li B, Ye L, Peng Y (2015) The combined effects of COD/N ratio and nitrate recycling ratio on nitrogen and phosphorus removal in anaerobic/anoxic/aerobic (A2/O)-biological aerated filter (BAF) systems. Biochem Eng J 93:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2014.10.005
Chen R, Ji J, Chen Y, Takemura Y, Liu Y, Kubota K, Ma HY, Li YY (2019a) Successful opera-tion performance and syntrophic micro-granule in partial nitritation and anammox reactor treat-ing low-strength ammonia wastewater. Water Res 155:288–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.02.041
Chen Y, Zhao Z, Liu H, Ma Y, An F, Huang J, Shao Z (2019b) Achieving stable two-stage ma-instream partial-nitrification/anammox (PN/A) operation via intermittent aeration. Chemosphere 245:125650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125650
Gong X, Yu D, Wang X, Yuan M, Bi C, Du Y, Zhao J (2021) Feasibility of reinforced post-endogenous denitrification coupling with synchronous nitritation, denitrification and phosphorus removal for high-nitrate sewage treatment using limited carbon source in municipal wastewater. Chemosphere 269:128687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128687
Gut L, Plaza E, Trela J, Hultman B, Bosander J (2006) Combined partial nitritation/anammox system for treatment of digester supernatant. Water Sci Technol 53(12):149–159. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2006.417
Hamzaoui AH, Jamoussi B, M'nif A (2008) Lithium recovery from highly concentrated solutions: response surface methodology (RSM) process parameters optimization. Hydrometallurgy 90(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2007.09.005
Hellinga C, Schellen AAJC, Mulder JW, van Loosdrecht MCM, Heijnen JJ (1998) The SHARON process, an innovative method for nitrogen removal from ammonium-rich waste water. Water Sci Technol 37(9):135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00281-9
Ji J, Peng Y, Li X, Zhang Q, Liu X (2020a) A novel partial nitrification-synchronous anammox and endogenous partial denitrification (PN-SAEPD) process for advanced nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater at ambient temperatures. Water Res 175:115690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115690
Ji J, Peng Y, Wang B, Li X, Zhang Q (2020b) A novel SNPR process for advanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal from mainstream wastewater based on anammox, endogenous partial-denitrification and denitrifying dephosphatation. Water Res 170:115363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115363
** RC, **ng BS, Yu JJ, Qin TY, Chen SX (2013) The importance of the substrate ratio in the operation of the anammox process in upflow biofilter. Ecol Eng 53(3):130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.12.027
Kosugi Y, Matsuura N, Liang Q, Yamamoto-Ikemoto R (2019) Nitrogen flow and microbial com-munity in the anoxic reactor of “sulfate reduction, denitrification/anammox and partial nitri-fication” process. Biochem Eng J 151:107304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2019.107304
Kraiem K, Wahab MA, Kallali H, Fra-vazquez A, Pedrouso A, Mosquera-Corral A, Jedidi N (2018) Effects of short-and long-term exposures of humic acid on the anammox activity and mi-crobial community. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:19012–19024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2786-4
Laureni M, Falås P, Robin O, Wick A, Weissbrodt DG, Nielsen JL, Ternes TA, Morgenroth E, Joss A (2016) Mainstream partial nitritation and anammox: long-term process stability and effluent quality at low temperatures. Water Res 101:628–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.005
Li Y, Huang Z, Ruan W, Ren H, Zhao M (2015) Anammox performance, granulation, and microbial response under COD disturbance. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 90(1):139–148. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4298
Li B, Wang Y, Li J, Yang L, Li X, Zhou Z, Li Y, Chen X, Wu L (2019) The symbiosis of an-aerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria and heterotrophic denitrification bacteria in a size-fractioned single-stage partial nitrification/anammox reactor. Biochem Eng J 151:107353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2019.107353
Li Z, Peng Y, Gao H (2020) Enhanced long-term advanced denitrogenation from nitrate wastewa-ter by anammox consortia: dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) coupling wi-th anammox in an upflow biofilter reactor equipped with EDTA-2Na/Fe(II) ratio and pH cont-rol. Bioresour Technol 305:123083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123083
Lovric M (2011) International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science. Springer, Berlin, pp 1037–1039
Miao Y, Peng Y, Zhang L, Li B, Li X, Wu L, Wang S (2018) Partial nitrification-anammox (PNA) treating sewage with intermittent aeration mode: effect of influent C/N ratios. Chem Eng J 334:664–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.072
Michaelis M, Leopold CS (2015) A measurement system analysis with design of experiments: investigation of the adhesion performance of a pressure sensitive adhesive with the probe tack test. Int J Pharm 496:448–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.09.061
Mirazimi SMJ, Rashchi F, Saba M (2013) Vanadium removal from roasted LD converter slag: optimization of parameters by response surface methodology (RSM). Sep Purif Technol 116:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.05.032
Ni SQ, Ni JY, Hu DL, Sung SW (2012) Effect of organic matter on the performance of granularanammox process. Bioresour Technol 110:701–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.066
Pathak KB, Kazama F, Saiki Y, Sumino T (2007) Presence and activity of anammox and denitrification process in low ammonium-fed bioreactors. Bioresour Technol 98(11):2201–2206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.08.014
Phanwilai S, Piyavorasakul S, Noophan P, Daniels KD, Snyder SA (2020) Inhibition of anaerobicammonium oxidation (anammox) bacteria by addition of high and low concentrations of chlor-amphenicol and comparison of attached-and suspended-growth. Chemosphere 238:124570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124570
Qu T, Niu S, Zhang X, Han K, Lu C (2021) Preparation of calcium modified Zn-Ce/Al2O3 heter-ogeneous catalyst for biodiesel production through transesterification of palm oil with methan-ol optimized by response surface methodology. Fuel 284:118986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118986
Sheng S, Liu B, Hou X, Liang Z, Sun X, Du L, Wang D (2018) Effects of different carbon so-urces and C/N ratios on the simultaneous anammox and denitrification process. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 127:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.11.002
Simate GS, Ndlovu S, Gericke M (2009) Bacterial leaching of nickel laterites using chemolithotr-ophic microorganisms: process optimisation using response surface methodology and central c-omposite rotatable design. Hydrometallurgy 98:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2009.05.007
Strous M, Heijnen JJ, Kuenen JG, Jetten MSM (1998) The sequencing batch reactor as a power-ful tool for the study of slowly growing anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:589–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051340
Strous M, Kuenen JG, Jetten MSM (1999) Key physiology of anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(7):3248–3250. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.65.7.3248-3250.1999
Tang CJ, Zheng P, Hu BL, Chen JW, Wang CH (2010) Influence of substrates on nitrogen rem-oval performance and microbiology of anaerobic ammonium oxidation by operating two UASB reactors fed with different substrate levels. J Hazard Mater 181(1-3):19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.04.015
Tomar S, Gupta SK (2016) Investigating the role of co-substrate-substrate ratio and filter media on the performance of anammox hybrid reactor treating nitrogen rich wastewater. J Biosci Bioeng 121(3):310–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2015.07.005
Tsushima I, Ogasawara Y, Kindaichi T, Satoh H, Okabe S (2007) Development of high-rate an-aerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) biofilm reactors. Water Res 41(8):1623–1634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.01.050
Wang B, Peng Y, Guo Y, Yuan Y, Zhao M, Wang S (2016) Impact of partial nitritation degree and C/N ratio on simultaneous sludge fermentation, denitrification and anammox process. Bioresour Technol 219:411–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.114
Wang C, Liu S, Xu X, Zhang C, Wang D, Yang F (2018) Achieving mainstream nitrogen remo-val through simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification process in an integ-rated fixed film activated sludge reactor. Chemosphere 203:457–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.016
Wang W, Pang C, Sierra JM, Hu Z, Ren X (2019) Performance and recovery of a completely s-eparated partial nitritation and anammox process treating phenol-containing wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:33917–33926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2701-z
Yang Y, Liu Y, Yang T, Lv Y (2017) Characterization of a microbial consortium capable of het-erotrophic nitrifying under wide C/N range and its potential application in phenolic and coki-ng wastewater. Biochem Eng J 120:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2016.12.008
Yang S, Xu S, Mohammed A, Ashbolt NJ, Liu Y (2019) Improving nitrogen removal in an IFAS nitritation-anammox reactor treating lagoon supernatant by manipulating biocarrier filling rat-io and hydraulic retention time. Biochem Eng J 152:107365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2019.107365
Zhao J, Wang XX, Li XY, Jia SY, Peng YZ (2018) Advanced nutrient removal from ammonia and domestic wastewaters by a novel process based on simultaneous partial nitrification-anammox and modified denitrifying phosphorus removal. Chem Eng J 354:589–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.21
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51668033) and the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province (18JR3RA126).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YC contributed to the conception and modification of the study. ZY performed the experiment and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. YM contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation. FA helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions. AL analyzed the data with the response surface methodology. HL helped perform the experiment. ZZ modified the content of the study. JM sorted out and summarized the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, ., Yuan, Z., Ma, Y. et al. Simultaneous carbon and nitrogen removal by anaerobic ammonium oxidation and denitrification under different operating strategies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 65462–65473 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15531-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15531-9