Abstract
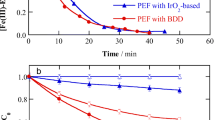
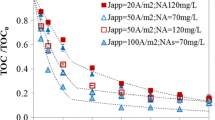
This work explores the role of electrode material and the oxidation ability of electrochemical advanced oxidation processes (EAOPs), such as electro-oxidation (EO) with or without H2O2 production, electro-Fenton (EF), and UVA photoelectron-Fenton (PEF), in the degradation of metolachlor. The performance of the EAOPs using Boron-doped diamond (BDD) or Pt as anode has been compared from the analysis of decay kinetics, mineralization profile, and energy consumption using small undivided batch cell. Metolachlor concentration always decays following a pseudo-first-order kinetics. Using the Pt anode, none of the processes reaches 30% mineralization, including PEF. In contrast, the BDD anode showed a higher mineralization rate allowing almost total mineralization in PEF due to the synergetic action of UVA light and oxidant hydroxyl radicals formed in the bulk from Fenton’s reaction, as well as in the BDD, which has large reactivity to oxidize the pollutants. The increase in current density and decrease in metolachlor concentration accelerated the mineralization in PEF, although lower current efficiency and higher energy consumption was obtained. The GC-MS and HPLC analysis allowed the identification of up to 17 aromatics intermediates and 7 short-chain carboxylic acids. Finally, a reaction pathway for metolachlor mineralization by EAOPs is proposed. PEF with BDD allowed total removal of the herbicide in real water matrix and a high mineralization (83.82%).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
© World Health Organization (1993) Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality - WHO 1993. 1:11. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
Almeida LC, Garcia-Segura S, Arias C, Bocchi N, Brillas E (2012) Electrochemical mineralization of the azo dye acid red 29 (Chromotrope 2R) by photoelectro-Fenton process. Chemosphere 89:751–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.07.007
Anglada A, Urtiaga A, Ortiz I (2009) Contributions of electrochemical oxidation to waste-water treatment: fundamentals and review of applications. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84:1747–1755. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2214
Barra Caracciolo A, Giuliano G, Grenni P, Guzzella L, Pozzoni F, Bottoni P, Fava L, Crobe A, Orrù M, Funari E (2005) Degradation and leaching of the herbicides metolachlor and diuron: a case study in an area of northern Italy. Environ Pollut 134:525–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.08.014
Boye B, Dieng MM, Brillas E (2003) Electrochemical degradation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid in aqueous medium by peroxi-coagulation. Effect of pH and UV light. Electrochim Acta 48:781–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(02)00747-8
Brillas E, Martínez-Huitle CA (2015) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An updated review. Appl Catal B Environ 166–167:603–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.11.016
Brillas E, Boye B, Sirés I, Garrido JA, Rodrı́guez RḾ, Arias C, Cabot PĹ, Comninellis C (2004) Electrochemical destruction of chlorophenoxy herbicides by anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton using a boron-doped diamond electrode. Electrochim Acta 49:4487–4496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2004.05.006
Brillas E, Sirés I, M a O (2009) Electro-Fenton process and related electrochemical technologies based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Chem Rev 109:6570–6631. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr900136g
Chaplin BPP (2014) Critical review of electrochemical advanced oxidation processes for water treatment applications. Environ Sci Process Impacts 16:1182–1203. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00679D
Coffinet S, Rifai A, Genty C, Souissi Y, Bourcier S, Sablier M, Bouchonnet S (2012) Characterization of the photodegradation products of metolachlor: structural elucidation, potential toxicity and persistence. J Mass Spectrom 47:1582–1593. https://doi.org/10.1002/jms.3121
Coria G, Sirés I, Brillas E, Nava JL (2016) Influence of the anode material on the degradation of naproxen by Fenton-based electrochemical processes. Chem Eng J 304:817–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.012
Daneshvar N, Aber S, Vatanpour V, Rasoulifard MH (2008) Electro-Fenton treatment of dye solution containing Orange II: influence of operational parameters. J Electroanal Chem 615:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2007.12.005
Dirany A, Sirés I, Oturan N, Özcan A, Oturan MA (2012) Electrochemical treatment of the antibiotic sulfachloropyridazine: kinetics, reaction pathways, and toxicity evolution. Environ Sci Technol 46:4074–4082. https://doi.org/10.1021/es204621q
El-Ghenymy A, Rodríguez RM, Brillas E et al (2014) Electro-Fenton degradation of the antibiotic sulfanilamide with Pt/carbon-felt and BDD/carbon-felt cells. Kinetics, reaction intermediates, and toxicity assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8368–8378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2773-3
Feng L, van Hullebusch ED, Rodrigo MA, Esposito G, Oturan MA (2013) Removal of residual anti-inflammatory and analgesic pharmaceuticals from aqueous systems by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. A review. Chem Eng J 228:944–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.061
Friedman CL, Lemley AT, Hay A (2006) Degradation of chloroacetanilide herbicides by anodic Fenton treatment. J Agric Food Chem 54:2640–2651. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0523317
Garcia-Segura S, Brillas E (2016) Combustion of textile monoazo, diazo and triazo dyes by solar photoelectro-Fenton: decolorization, kinetics and degradation routes. Appl Catal B Environ 181:681–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.08.042
Garcia-Segura S, Brillas E, Cornejo-Ponce L, Salazar R (2016) Effect of the Fe3+/Cu2+ ratio on the removal of the recalcitrant oxalic and oxamic acids by electro-Fenton and solar photoelectro-Fenton. Sol Energy 124:242–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2015.11.033
Garcia-Segura S, Ocon JD, Chong MN (2018) Electrochemical oxidation remediation of real wastewater effluents—a review. Process Saf Environ Prot 113:48–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.09.014
Gozzi F, Sirés I, Thiam A, de Oliveira SC, Junior AM, Brillas E (2017) Treatment of single and mixed pesticide formulations by solar photoelectro-Fenton using a flow plant. Chem Eng J 310:503–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.026
Gozzi F, Sirés I, de Oliveira SC, Machulek A Jr, Brillas E (2018) Influence of chelation on the Fenton-based electrochemical degradation of herbicide tebuthiuron. Chemosphere 199:709–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.060
Guinea E, Garrido JA, Rodríguez RM, Cabot PL, Arias C, Centellas F, Brillas E (2010) Degradation of the fluoroquinolone enrofloxacin by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes based on hydrogen peroxide electrogeneration. Electrochim Acta 55:2101–2115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.11.040
Isarain-Chávez E, Arias C, Cabot PL, Centellas F, Rodríguez RM, Garrido JA, Brillas E (2010) Mineralization of the drug β-blocker atenolol by electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton using an air-diffusion cathode for H2O2 electrogeneration combined with a carbon-felt cathode for Fe2+ regeneration. Appl Catal B Environ 96:361–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.02.033
Kimmel EC, Casida JE, Ruzo LO (1986) Formamidine insecticides and chloroacetanilide herbicides: disubstituted anilines and nitrosobenzenes as mammalian metabolites and bacterial mutagens. J Agric Food Chem 34:157–161. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00068a002
Lanzarini-Lopes M, Garcia-Segura S, Hristovski K, Westerhoff P (2017) Electrical energy per order and current efficiency for electrochemical oxidation of p-chlorobenzoic acid with boron-doped diamond anode. Chemosphere 188:304–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.145
Li D, Gao Q, Xu L, Pang S, Liu Z, Wang C, Tan W (2016) Characterization of glutathione S-transferases in the detoxification of metolachlor in two maize cultivars of differing herbicide tolerance. Pestic Biochem Physiol 143:265–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2016.12.003
Liu H, Huang R, **e F, Zhang S, Shi J (2012) Enantioselective phytotoxicity of metolachlor against maize and rice roots. J Hazard Mater 217–218:330–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.03.037
Malato S, Fernández-Ibáñez P, Maldonado MI, Blanco J, Gernjak W (2009) Decontamination and disinfection of water by solar photocatalysis: recent overview and trends. Catal Today 147:1–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2009.06.018
Martínez-Huitle CA, Rodrigo MA, Sirés I, Scialdone O (2015) Single and coupled electrochemical processes and reactors for the abatement of organic water pollutants: a critical review. Chem Rev 115:13362–13407. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00361
Mendy A, Thiaré DD, Sambou S, Khonté A, Coly A, Gaye-Seye MD, Delattre F, Tine A (2016) New method for the determination of metolachlor and buprofezin in natural water using orthophthalaldehyde by thermochemically-induced fluorescence derivatization (TIFD). Talanta 151:202–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.01.036
Moreira FC, Garcia-Segura S, Vilar VJP, Boaventura RAR, Brillas E (2013) Decolorization and mineralization of sunset yellow FCF azo dye by anodic oxidation, electro-Fenton, UVA photoelectro-Fenton and solar photoelectro-Fenton processes. Appl Catal B Environ 142–143:877–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.03.023
Moreira FC, Boaventura RAR, Brillas E, Vilar VJP (2017) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: a review on their application to synthetic and real wastewaters. Appl Catal B Environ 202:217–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.037
Nidheesh PV, Zhou M, Oturan MA (2018) An overview on the removal of synthetic dyes from water by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 197:210–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.195
Orge CA, Pereira MFR, Faria JL (2017) Photocatalytic-assisted ozone degradation of metolachlor aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 318:247–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.136
Oturan N, Hamza M, Ammar S, Abdelhédi R, Oturan MA (2011) Oxidation/mineralization of 2-nitrophenol in aqueous medium by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes using Pt/carbon-felt and BDD/carbon-felt cells. J Electroanal Chem 661:66–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2011.07.017
Oturan N, Brillas E, Oturan MA (2012) Unprecedented total mineralization of atrazine and cyanuric acid by anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton with a boron-doped diamond anode. Environ Chem Lett 10:165–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-011-0337-z
Özcan A, Oturan MA, Oturan N, Şahin Y (2009) Removal of acid Orange 7 from water by electrochemically generated Fenton’s reagent. J Hazard Mater 163:1213–1220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.088
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2009) Electro-Fenton degradation of synthetic dyes. Water Res 43:339–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.10.028
Panizza M, Oturan MA (2011) Degradation of alizarin red by electro-Fenton process using a graphite-felt cathode. Electrochim Acta 56:7084–7087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.05.105
Pipi ARF, Sirés I, De Andrade AR, Brillas E (2014) Application of electrochemical advanced oxidation processes to the mineralization of the herbicide diuron. Chemosphere 109:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.03.006
Poyatos JM, Muñio MM, Almecija MC, Torres JC, Hontoria E, Osorio F (2010) Advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: state of the art. Water Air Soil Pollut 205:187–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0065-1
Pratap K, Lemley AT (1994) Electrochemical peroxide treatment of aqueous herbicide solutions. J Agric Food Chem 42:209–215. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00037a038
Pratap K, Lemley AT (1998) Fenton electrochemical treatment of aqueous atrazine and metolachlor. J Agric Food Chem 46:3285–3291. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9710342
Restivo J, órfão JJM, Armenise S et al (2012) Catalytic ozonation of metolachlor under continuous operation using nanocarbon materials grown on a ceramic monolith. J Hazard Mater 239–240:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.08.073
Restivo J, Garcia-Bordejé E, Órfão JJM, Pereira MFR (2016) Carbon nanofibers doped with nitrogen for the continuous catalytic ozonation of organic pollutants. Chem Eng J 293:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.055
Ruiz EJ, Arias C, Brillas E, Hernández-Ramírez A, Peralta-Hernández JM (2011) Mineralization of acid yellow 36 azo dye by electro-Fenton and solar photoelectro-Fenton processes with a boron-doped diamond anode. Chemosphere 82:495–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.11.013
Salazar R, Brillas E, Sirés I (2012) Finding the best Fe2+/Cu2+ combination for the solar photoelectro-Fenton treatment of simulated wastewater containing the industrial textile dye disperse blue 3. Appl Catal B Environ 115–116:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.12.026
Sirés I, Garrido JA, Rodríguez RM, Brillas E, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2007) Catalytic behavior of the Fe3+/Fe2+ system in the electro-Fenton degradation of the antimicrobial chlorophene. Appl Catal B Environ 72:382–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2006.11.016
Sirés I, Brillas E, Oturan MA, Rodrigo MA, Panizza M (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: today and tomorrow. A review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8336–8367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2783-1
Skoumal M, Arias C, Cabot PL, Centellas F, Garrido JA, Rodríguez RM, Brillas E (2008) Mineralization of the biocide chloroxylenol by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 71:1718–1729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.12.029
Skoumal M, Rodríguez RM, Cabot PL, Centellas F, Garrido JA, Arias C, Brillas E (2009) Electro-Fenton, UVA photoelectro-Fenton and solar photoelectro-Fenton degradation of the drug ibuprofen in acid aqueous medium using platinum and boron-doped diamond anodes. Electrochim Acta 54:2077–2085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2008.07.014
Sopaj F, Oturan N, Pinson J, Podvorica F, Oturan MA (2016) Effect of the anode materials on the efficiency of the electro-Fenton process for the mineralization of the antibiotic sulfamethazine. Appl Catal B Environ 199:331–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.06.035
Steter JR, Brillas E, Sirés I (2018) Solar photoelectro-Fenton treatment of a mixture of parabens spiked into secondary treated wastewater effluent at low input current. Appl Catal B Environ 224:410–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.10.060
Thiam A, Zhou M, Brillas E, Sirés I (2014) Two-step mineralization of tartrazine solutions: study of parameters and by-products during the coupling of electrocoagulation with electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Appl Catal B Environ 150–151:116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.12.011
Thiam A, Brillas E, Garrido JA, Rodríguez RM, Sirés I (2016) Routes for the electrochemical degradation of the artificial food azo-colour Ponceau 4R by advanced oxidation processes. Appl Catal B Environ 180:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.06.039
Vasudevan S, Oturan MA (2014) Electrochemistry: as cause and cure in water pollution—an overview. Environ Chem Lett 12:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0434-2
Villegas-Guzman P, Hofer F, Silva-Agredo J, Torres-Palma RA (2017) Role of sulfate, chloride, and nitrate anions on the degradation of fluoroquinolone antibiotics by photoelectro-Fenton. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:28175–28189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0404-5
White PM, Potter TL, Culbreath AK (2010) Fungicide dissipation and impact on metolachlor aerobic soil degradation and soil microbial dynamics. Sci Total Environ 408:1393–1402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.11.012
Wilson RI, Mabury SA (2000) Photodegradation of metolachlor: isolation, identification, and quantification of monochloroacetic acid. J Agric Food Chem 48:944–950. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf990618w
Acknowledgments
CONICYT (Chile) provided the financial support under FONDECYT postdoctorado projects no. 3160753, Fondecyt Iniciación no. 11170882, and Fondecyt regular no. 1170352.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thiam, A., Salazar, R. Fenton-based electrochemical degradation of metolachlor in aqueous solution by means of BDD and Pt electrodes: influencing factors and reaction pathways. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 2580–2591 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3768-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3768-2