Abstract
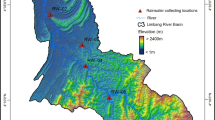
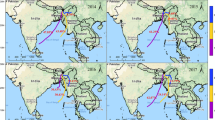
Rainwater chemistry was investigated at a semi-rural site in Ya’an, Sichuan basin with rain samples collected from May 2013 to July 2014. The rainwater pH values ranged from 3.25 to 6.86, with an annual volume-weighted mean (VWM) of 4.38, and the acid rain frequency was 74 %. Such severe acidification, 15 % of the total events showed a pH below 4.0, attributed to the deficiency of Ca2+, significant anthropogenic pollution contribution, and rainy pattern to this area. The annual VWM of total ions concentration was 477.19 μeq/L. NH4 + was the most abundant ionic species, followed by SO4 2−, NO3 −, Ca2+, Cl−, Na+, K+, Mg2+, and F− in a descending order. The total ionic concentrations presented a seasonal trend of lower values in autumn and summer but higher ones in winter and spring. Based on enrichment factor, correlation analysis and principle component analysis, three factors were identified: factor 1 (NH4 +, SO4 2−, NO3 −, K+, and Cl−, 47.45 % of the total variance) related to anthropogenic sources (coal/fuel combustion, biomass burning and agriculture), factor 2 (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, and Cl−, 34.01 % of the total variance) associated with natural sources, and factor 3 (H+, 11.78 % of the total variance) related to free acidity. Back trajectory analysis indicates that the rainwater chemistry in Ya’an was mainly affected by regional air masses from Sichuan basin. Long-range transported air masses from southwest with heavy anthropogenic pollution increased the total ion concentration and acidity of rainwater. Considering its special topography, anthropogenic emissions from regional and long-range transport (especially from southwest) must be controlled effectively to improve the acid rain condition of non-urban areas in Sichuan basin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas W, Shao M, ** L, Larssen T, Zhao D, **ang R, Zhang J, **ao J, Duan L (2007) Air concentrations and wet deposition of major inorganic ions at five non-urban sites in China, 2001–2003. Atmos Environ 41:1706–1716
Al-Khashman OA (2009) Chemical characteristics of rainwater collected at a western site of Jordan. Atmos Res 91:53–61
Baez A, Belmont R, García R, Padilla H, Torres MC (2007) Chemical composition of rainwater collected at a southwest site of Mexico City, Mexico. Atmos Res 86:61–75
Balasubramanian R, Victor T, Begum R (1999) Impact of biomass burning on rainwater acidity and composition in Singapore. J Geophys Res 104(26):881–890
Budhavant KB, Rao PSP, Safai PD, Ali K (2011) Influence of local sources on rainwater chemistry over Pune region, India. Atmos Res 100:121–131
Celle-Jeanton H, Travi Y, Loÿe-Pilot MD, Huneau F, Bertrand G (2009) Rainwater chemistry at a Mediterranean inland station (Avignon, France): local contribution versus long-range supply. Atmos Res 91:118–126
Charlson RJ, Rodhe H (1982) Factors controlling the acidity of natural rainwater. Nature 295:683–685
Chen XY, Mulder J (2007) Atmospheric deposition of nitrogen at five subtropical forested sites in South China. Sci Total Environ 378:317–330
Chhabra SK, Chhabra P, Rajpal S, Gupta RK (2001) Ambient air pollution and chronic respiratory morbidity in Delhi. Arch Environ Health Int J 56(1):58–64
Coelho CH, Allen AG, Fornaro A, Orlando EA, Grigoletto TL, Campos MLA (2011) Wet deposition of major ions in a rural area impacted by biomass burning emissions. Atmos Environ 45:5260–5265
Fan H (2002) On worldwide acid rain research. J Fujian Coll For 22:71–375 (in Chinese)
Feng ZW, Huang YZ, Feng YW, Ogura N, Zhang FZ (2001) Chemical composition of precipitation in Bei**g area, northern China. Water Air Soil Pollut 125:345–356
Gioda A, Mayol-Bracero OL, Scatena FN, Weathers KC, Mateus VL, McDowell WH (2013) Chemical constituents in clouds and rainwater in the Puerto Rican rainforest: potential sources and seasonal drivers. Atmos Environ 68:208–220
Goyer RA, Bachmann J, Clarkson TW, Ferris BG Jr, Graham J, Mushak P, Perl DP, Rall DP, Schlesinger R, Sharpe W, Wood JM (1985) Potential human health effects of acid rain: report of a workshop. Environ Health Perspect 60:355–368
Han G, Tang Y, Wu Q, Tan Q (2010) Chemical and strontium isotope characterization of rainwater in karst virgin forest, Southwest China. Atmos Environ 44:174–181
Hu GP, Balasubramanian R, Wu CD (2003) Chemical characterization of rainwater at Singapore. Chemosphere 51:747–755
Huang Y, Wang YL, Zhang LP (2008a) Long-term trend of chemical composition of wet atmospheric precipitation during 1986–2006 at Shenzhen City, China. Atmos Environ 42:3740–3750
Huang K, Zhuang G, Xu C, Wang Y, Tang A (2008b) The chemistry of the severe acidic precipitation in Shanghai, China. Atmos Res 89:149–160
Huang DY, Xu YG, Peng PA, Zhang HH, Lan JB (2009) Chemical composition and seasonal variation of acid deposition in Guangzhou, South China: comparison with precipitation in other major Chinese cities. Environ Pollut 157:35–41
Huang XF, Li X, He LY, Feng N, Hu M, Niu YW, Zeng LW (2010) 5-Year study of rainwater chemistry in a coastal mega-city in South China. Atmos Res 97:185–193
Huang J, Sun S, Xue Y, Li J, Zhang J (2014) Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation and dryness/wetness during 1961–2008 in Sichuan province, west China. Water Resour Manag 28:1655–1670
Huo M, Sun Q, Bai Y, Li J, **e P, Liu Z, Wang X (2012) Influence of airborne particles on the acidity of rainwater during wash-out process. Atmos Environ 59:192–201
Jawad Al Obaidy AHM, Joshi H (2006) Chemical composition of rainwater in a tropical urban area of northern India. Atmos Environ 40:6886–6891
Laouali D, Galy-Lacaux C, Diop B, Delon C, Orange D, Lacaux JP, Akpo A, Lavenu F, Gardrat E, Castera P (2012) Long term monitoring of the chemical composition of precipitation and wet deposition fluxes over three Sahelian savannas. Atmos Environ 50:314–327
Larssen T, Seip HM, Semb A, Mulder J, Muniz IP, Vogt RD, Lydersen E, Angell V, Tang D, Eilertsen O (1999) Acid deposition and its effects in China: an overview. Environ Sci Pol 2:9–24
Lee BK, Hong SH, Lee DS (2000) Chemical composition of precipitation and wet deposition of major ions on the Korean peninsula. Atmos Environ 34:563–575
Lei HC, Tanner PA, Huang MY, Shen ZL, Wu YX (1997) The acidification process under the cloud in southwest China: observation results and simulation. Atmos Environ 31:851–861
Li Y, Yu X, Cheng H, Lin W, Tang J, Wang S (2010) Chemical characteristics of precipitation at three Chinese regional background stations from 2006 to 2007. Atmos Res 96:173–183
Liu X, Zhang Y, Han W, Tang A, Shen J, Cui Z, Vitousek P, Erisman JW, Goulding K, Christie P, Fangmeier A, Zhang F (2013) Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 494:459–462
Lu Z, Streets DG, Zhang Q, Wang S, Carmichael GR, Cheng YF, Wei C, Chin M, Diehl T, Tan Q (2010) Sulfur dioxide emissions in China and sulfur trends in East Asia since 2000. Atmos Chem Phys 10:6311–6331
Lu X, Li LY, Li N, Yang G, Luo D, Chen J (2011) Chemical characteristics of spring rainwater of **’an city, NW China. Atmos Environ 45:5058–5063
Lu QM, Zhao L, Li L, Yang FM, Yang QL, Wei SQ, He KB, Cheng GC (2013) Chemical composition of precipitation and its spatiotemporal variations in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Acta Sci Circum 33(6):1682–1689 (in Chinese)
Lynch JA, Bowersox VC, Grimm JW (2000) Changes in sulfate deposition in eastern USA following implementation of Phase I of Title IV of the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990. Atmos Environ 34:1665–1680
Moreda-Piñeiro J, Alonso-Rodríguez E, Moscoso-Pérez C, Blanco-Heras G, Turnes-Carou I, López-Mahía P, Muniategui-Lorenzo S, Prada-Rodríguez D (2014) Influence of marine, terrestrial and anthropogenic sources on ionic and metallic composition of rainwater at a suburban site (northwest coast of Spain). Atmos Environ 88:30–38
Mouli PC, Mohan SV, Reddy SJ (2005) Rainwater chemistry at a regional representative urban site: influence of terrestrial sources on ionic composition. Atmos Environ 39:999–1008
Niu H, He Y, Zhu G, **n H, Du J, Pu T, Lu X, Zhao G (2013) Environmental implications of the snow chemistry from Mt. Yulong, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Quatern Int 313:168–178
Niu H, He Y, Lu XX, Shen J, Du J, Zhang T, Tao P, **n H, Chang L (2014) Chemical composition of rainwater in the Yulong Snow Mountain region, Southwestern China. Atmos Res 144:195–206
Okuda T, Iwase T, Ueda H, Suda Y, Tanaka S, Dokiya Y, Fushimi K, Hosoe M (2005) Long-term trend of chemical constituents in precipitation in Tokyo metropolitan area, Japan, from 1990 to 2002. Sci Total Environ 339:127–141
Qiao X, **ao W, Jaffe D, Kota SH, Ying Q, Tang Y (2015) Atmospheric wet deposition of sulfur and nitrogen in Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve, Sichuan Province, China. Sci Total Environ 511:28–36
Sharma M, Maloo S (2005) Assessment of ambient air PM10 and PM2.5 and characterization of PM10 in the city of Kanpur, India. Atmos Environ 39:6015–6026
Shen Z, Zhang L, Cao J, Tian J, Liu L, Wang G, Zhao Z, Wang X, Zhang R, Liu S (2012) Chemical composition, sources, and deposition fluxes of water-soluble inorganic ions obtained from precipitation chemistry measurements collected at an urban site in northwest China. J Environ Monitor 14:3000–3008
Song F, Gao Y (2009) Chemical characteristics of precipitation at metropolitan Newark in the US East Coast. Atmos Environ 43:4903–4913
Sopauskiene D, Jasineviciene D (2006) Changes in precipitation chemistry in Lithuania for 1981–2004. J Environ Monitor 8:347–352
State Environmental Protection Administration of China (2004) Technical specifications for acid deposition monitoring. Bei**g (In Chinese)
Streets DG, Waldhoff ST (2000) Present and future emissions of air pollutants in China: SO2, NOx, and CO. Atmos Environ 34:363–374
Tang A, Zhuang G, Wang Y, Yuan H, Sun Y (2005) The chemistry of precipitation and its relation to aerosol in Bei**g. Atmos Environ 39:3397–3406
Tørseth K, Aas W, Breivik K, Fjæraa AM, Fiebig M, Hjellbrekke AG, Myhre L, Solberg S, Yttri KE (2012) Introduction to the European Monitoring and Evaluation Programme (EMEP) and observed atmospheric composition change during 1972–2009. Atmos Chem Phys 12:5447–5481
Tu J, Wang H, Zhang Z, ** X, Li W (2005) Trends in chemical composition of precipitation in Nan**g, China, during 1992–2003. Atmos Res 73:283–298
Vet R, Artz RS, Carou S, Shaw M, Ro CU, Aas W, Baker A, Bowersox VC, Dentener F, Galy-Lacaux C, Hou A, Pienaar JJ, Gillett R, Forti CM, Gromov S, Hara H, Khodzherm T, Mahowald NM, Nickovic S, Rao PSP, Reid NW (2014) A global assessment of precipitation chemistry and deposition of sulfur, nitrogen, sea salt, base cations, organic acids, acidity and pH, and phosphorus. Atmos Environ 93:3–100
Wang H, Han G (2011) Chemical composition of rainwater and anthropogenic influences in Chengdu, Southwest China. Atmos Res 99:190–196
Wang G, Li J, Cheng C, Hu S, **e M, Gao S, Zhou B, Dai W, Cao J, An Z (2011) Observation of atmospheric aerosols at Mt. Hua and Mt. Tai in central and east China during spring 2009–Part 1: EC, OC and inorganic ions. Atmos Chem Phys 11:4221–4235
Wu Q, Han G, Tao F, Tang Y (2012) Chemical composition of rainwater in a karstic agricultural area, Southwest China: the impact of urbanization. Atmos Res 111:71–78
Xu Z, Han G (2009) Chemical and strontium isotope characterization of rainwater in Bei**g, China. Atmos Environ 43:1954–1961
Xu Z, Tang Y, Ji J (2012) Chemical and strontium isotope characterization of rainwater in Bei**g during the 2008 Olympic year. Atmos Environ 107:115–125
Xu Z, Wu Y, Liu WJ, Liang CS, Ji J, Zhao T, Zhang X (2015) Chemical composition of rainwater and the acid neutralizing effect at Bei**g and Chizhou city, China. Atmos Res 164–165:278–285
Yang FM, He KB, Lei Y, Ma YL, Yu XC, Tanaka S, Okuda T, Iwase T (2004) Chemical characters of atmospheric precipitation in Bei**g in years of 2001–2003. China Environ Sci 24(5):538–541 (in Chinese)
Yang R, Hayashi K, Zhu B, Li F, Yan X (2010) Atmospheric NH3 and NO2 concentration and nitrogen deposition in an agricultural catchment of Eastern China. Sci Total Environ 408:4624–4632
Yao X, Zhang L (2012) Chemical processes in sea-salt chloride depletion observed at a Canadian rural coastal site. Atmos Environ 46:189–194
Zhang M, Wang S, Wu F, Yuan X, Zhang Y (2007) Chemical compositions of wet precipitation and anthropogenic influences at a develo** urban site in southeastern China. Atmos Res 84:311–322
Zhang X, Jiang H, Zhang Q, Zhang X (2012) Chemical characteristics of rainwater in northeast China, a case study of Dalian. Atmos Res 116:151–160
Zhao D, **ong J, Xu Y, Chan W (1988) Acid rain in southwestern China. Atmos Environ 22:349–358
Zhao M, Li L, Liu Z, Chen B, Huang J, Cai J, Deng S (2013) Chemical composition and sources of rainwater collected at a semi-rural site in Ya’an, Southwestern China. Atmos Clim Sci 3:486–496
Zhou ZY, Chen DR, Ying J, Zhang WL (2003) The chemical composition of precipitation analysis in Chongqing city. Chongqing Environ Sci 25(11):112–114 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (41205095) and (21305097) of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerhard Lammel
Yun-Chun Li and Meng Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 579 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YC., Zhang, M., Shu, M. et al. Chemical characteristics of rainwater in Sichuan basin, a case study of Ya’an. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 13088–13099 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6363-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6363-4