Abstract
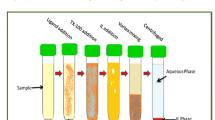
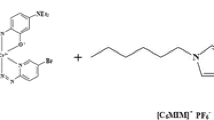
Several studies have reported that the chewing habit of smokeless tobacco (SLT) has been associated with oral cancer. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the trace levels of lead (Pb) in biological samples (blood, scalp hair) of oral cancer patients and referents of the same age group (range 30–60 years). As the concentrations of Pb are very low in biological samples, so a simple and efficient ionic liquid-based microextraction in a single syringe system has been developed, as a prior step to determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. In this procedure, the hydrophobic chelates of Pb with ammonium pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate (APDC) were extracted into fine droplets of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate [C4MIM][PF6] within a syringe while using Triton X-114 as a dispersant. Factors influencing the microextraction efficiency and determination, such as pH of the sample, volume of [C4MIM][PF6] and Triton X-114, ligand concentration, and incubation time, were studied. To validate the proposed method, certified reference materials were analyzed and the results of Pb2+ were in good agreement with certified values. At optimum experimental values of significant variables, detection limit and enhancement factor were found to be 0.412 μg/L and 80, respectively. The coexisting ions showed no obvious negative outcome on Pb preconcentration. The proposed method was applied satisfactorily for the preconcentration of Pb2+ in acid-digested SLT and biological samples of the study population. It was observed that oral cancer patients who consumed different SLT products have 2–3-fold higher levels of Pb in scalp hair and blood samples as compared to healthy referents (p < 0.001). While 31.4–50.8 % higher levels of Pb were observed in referents chewing different SLT products as compared to nonconsumers (p < 0.01).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdolmohammad-Zadeh H, Sadeghi G (2009) A novel microextraction technique based on 1-hexylpyridinium hexafluorophosphate ionic liquid for the preconcentration of zinc in water and milk samples. Anal Chim Acta 649:211–217
Accortt NA, Waterbor JW, Beall C, Howard G (2005) Cancer incidence among a cohort of smokeless tobacco users (United States). Cancer Causes Control 16:1107–1115
Alatise OI, Schrauzer GN (2010) Lead exposure: a contributing cause of the current breast cancer epidemic in Nigerian women. Biol Trace Elem Res 136:127–139
Alonso EV, Cordero MS, De Torres AG, Pavón JC (2006) Lead ultra-trace on-line preconcentration and determination using selective solid phase extraction and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry: applications in seawaters and biological samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 385:1178–1185
Arain SS, Kazi TG, Arain JB, Afridi HI, Brahman KD, Shah F, Arain S, Panhwar AH (2013) Simultaneous preconcentration of toxic elements in artificial saliva extract of smokeless tobacco product, mainpuri by cloud point extraction method. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 92:289–296
Arain SS, Kazi TG, Arain AJ, Afridi HI, Baig JA, Brahman KD, Arain SA (2015) Temperature-controlled ionic liquid-based ultrasound-assisted microextraction for preconcentration of trace quantity of cadmium and nickel by using organic ligand in artificial saliva extract of smokeless tobacco products. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 138:387–394
Baars AJ, Theelen RMC, Janssen PJCM, Hesse JM, Van Apeldoorn MEV, Van Meijerink MCM, Verdam L, Zeilmaker MJ (2001) Re-evaluation of human-toxicological maximum permissible risk levels. RIVM Report 711701025, p 297
Baghdadi M, Shemirani F (2008) Cold-induced aggregation microextraction: a novel sample preparation technique based on ionic liquids. Anal Chim Acta 613:56–63
Bai H, Zhou Q, **e G, **ao J (2010) Temperature-controlled ionic liquid–liquid-phase microextraction for the pre-concentration of lead from environmental samples prior to flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 80:1638–1642
Bhurgri Y, Bhurgri A, Hassan SH, Zaidi S, Rahim A, Sankaranarayanan R, Parkin DM (2000) Cancer incidence in Karachi, Pakistan: first results from Karachi cancer registry. Int J Cancer 85:325–329
Bhurgri Y, Bhurgri A, Nishter S, Ahmed A, Usman A, Pervez S, Kayani N, Ahmed R, Hassan SH, Riaz A, Bhurgri H, Bashir I (2006) Pakistan-country profile of cancer and cancer control 1995–2004. J Pak Med Assoc 56:124–130
Bouquot J (1991) Reviewing oral leukoplakia: clinical concepts for the 1990s. J Am Dent Assoc 122:80–82 (1939)
Boyle P, Ferlay J (2005) Cancer incidence and mortality in Europe, 2004. Ann Oncol 16:481–488
Calabrese EJ, Baldwin LA (1992) Lead-induced cell proliferation and organ-specific tumorigenicity. Drug Metab Rev 24:409–416
Citak D, Tuzen M (2010) A novel preconcentration procedure using cloud point extraction for determination of lead, cobalt and copper in water and food samples using flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem Toxicol 48:1399–1404
Cogliano V, Straif K, Baan R, Grosse Y, Secretan B, Ghissassi FE (2004) Smokeless tobacco and tobacco-related nitrosamines. Lancet Oncol 5:708
Comitre ALD, Reis BF (2005) Automatic flow procedure based on multicommutation exploiting liquid–liquid extraction for spectrophotometric lead determination in plant material. Talanta 65:846–852
Cruz-Vera M, Lucena R, Cárdenas S, Valcarcel M (2009) One-step in-syringe ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J Chromatogr A 1216:6459–6465
Fang Z-L, Liu Z-S, Shen Q (1997) Combination of flow injection with capillary electrophoresis. Part I. The basic system. Anal Chim Acta 346:135–143
Ferlay J, Pisani P, Parkin DM (2004) Cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide. IARC Cancer Base (2002 estimates). IARC Press, Lyon
Gama EM, da Silva Lima A, Lemos VA (2006) Preconcentration system for cadmium and lead determination in environmental samples using polyurethane foam/Me-BTANC. J Hazard Mater 136:757–762
Ghaedi M, Niknam K, Taheri K, Hossainian H, Soylak M (2010) Flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of copper, zinc and manganese after solid-phase extraction using 2,6-dichlorophenyl-3,3-bis (indolyl) methane loaded on Amberlite XAD-16. Food Chem Toxicol 48:891–897
Ghaedi M, Tashkhourian J, Montazerozohori M, Soylak M (2013) Silver nanoparticle loaded on activated carbon and activated carbon modified with 2-(4-isopropylbenzylideneamino) thiophenol (IPBATP) as new sorbents for trace metal ions enrichment. Int J Environ Anal 93:386–400
Godwin HA (2001) The biological chemistry of lead. Curr Opin Chem Biol 5:223–227
Golia E, Dimirkou A, Mitsios I (2007) Accumulation of metals on tobacco leaves (primings) grown in an agricultural area in relation to soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:158–162
Gundogdu A, Ozdes D, Duran C, Bulut VN, Soylak M, Senturk HB (2009) Biosorption of Pb (II) ions from aqueous solution by pine bark (Pinus brutia Ten.). Chem Eng J 153:62–69
Gupta PC, Ray CS (2003) Smokeless tobacco and health in India and South Asia. Respirology 8:419–431
Gwini S, MacFarlane E, Del Monaco A, McLean D, Pisaniello D, Benke GP, Sim MR (2012) Cancer incidence, mortality, and blood lead levels among workers exposed to inorganic lead. Ann Epidemiol 22:270–276
Haixia S, Zaijun L, Ming L (2007) Ionic liquid 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate as a solvent for extraction of lead in environmental water samples with detection by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchim Acta 159:95–100
Heintz A (2005) Recent developments in thermodynamics and thermophysics of non-aqueous mixtures containing ionic liquids. A review. J Chem Thermodyn 37:525–535
International Agency for Research on Cancer (2007) Smokeless tobacco and tobacco-specific nitrosamines. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, vol 89. IARC Scientific Publications, Lyon
Jaffe EK, Martins J, Li J, Kervinen J, Dunbrack RL (2001) The molecular mechanism of lead inhibition of human porphobilinogen synthase. J Biol Chem 276:1531–1537
Johnson N (2001) Tobacco use and oral cancer: a global perspective. J Dent Educ 65:328–339
Kazi TG, Wadhwa SK, Afridi HI, Kazi N, Kandhro GA, Baig JA, Shah AQ, Kolachi NF, Arain MB (2010a) Interaction of cadmium and zinc in biological samples of smokers and chewing tobacco female mouth cancer patients. J Hazard Mater 176:985–991
Kazi TG, Wadhwa SK, Afridi HI, Kazi N, Kandhro GA, Baig JA, Shah AQ, Kolachi NF, Khan S (2010b) Evaluation of cadmium and zinc in biological samples of tobacco and alcohol user male mouth cancer patients. Hum Exp Toxicol 29:221–230
Khandekar S, Bagdey P, Tiwari R (2006) Oral cancer and some epidemiological factors: a hospital based study. Indian J Community Med 31:157–159
Kingsley K, O’Malley S, Ditmyer M, Chino M (2008) Analysis of oral cancer epidemiology in the US reveals state-specific trends: implications for oral cancer prevention. BMC Public Health 8:87
Liu R, Liu JF, Yin YG, Hu XL, Jiang GB (2009) Ionic liquids in sample preparation. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:871–883
Łuczak J, Hupka J, Thoming J, Jungnickel C (2008) Self-organization of imidazolium ionic liquids in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 329:125–133
Lustberg M, Silbergeld E (2002) Blood lead levels and mortality. Arch Intern Med 162:2443–2449
Marsh K, Boxall J, Lichtenthaler R (2004) Room temperature ionic liquids and their mixtures—a review. Fluid Phase Equilib 219:93–98
Martinis EM, Wuilloud RG (2010) Cold vapor ionic liquid-assisted headspace single-drop microextraction: a novel preconcentration technique for mercury species determination in complex matrix samples. J Anal At Spectrom 25:1432–1439
Martinis EM, Olsina RA, Altamirano JC, Wuilloud RG (2008) Sensitive determination of cadmium in water samples by room temperature ionic liquid-based preconcentration and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 628:41–48
Matoso E, Kubota L, Cadore S (2003) Use of silica gel chemically modified with zirconium phosphate for preconcentration and determination of lead and copper by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 60:1105–1111
Mazahir S et al (2006) Socio-demographic correlates of betel, areca and smokeless tobacco use as a high risk behavior for head and neck cancers in a squatter settlement of Karachi, Pakistan. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy 1:10
Menke A, Muntner P, Batuman V, Silbergeld EK, Guallar E (2006) Blood lead below 0.48 μmol/L (10 μg/dL) and mortality among US adults. Circulation 114:1388–1394
Minami T, Sohrin Y, Ueda J (2005) Determination of chromium, copper and lead in river water by graphite-furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after coprecipitation with terbium hydroxide. Anal Sci 21:1519–1522
Naeemullah, Tuzen M, Kazi TG, Citak D, Soylak M (2013) Pressure-assisted ionic liquid dispersive microextraction of vanadium coupled with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 28:1441–1445
Naseri MT, Hosseini MRM, Assadi Y, Kiani A (2008) Rapid determination of lead in water samples by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 75:56–62
Nowak B, Chmielnicka J (2000) Relationship of lead and cadmium to essential elements in hair, teeth, and nails of environmentally exposed people. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 46:265–274
Oji C, Chukwuneke Fn (2007) Oral cancer in Enugu, Nigeria, 1998–2003. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 45:298–301
Panhwar AH, Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Shaikh HR, Arain SA, Arain SS, Brahman KD (2013) Evaluation of calcium and magnesium in scalp hair samples of population consuming different drinking water: risk of kidney stone. Biol Trace Elem Res 156:67–73
Pasha Q, Malik SA, Shaheen N, Shah MH (2010) Investigation of trace metals in the blood plasma and scalp hair of gastrointestinal cancer patients in comparison with controls. Clin Chim Acta 411:531–539
Prozialeck WC, Edwards JR, Nebert DW, Woods JM, Barchowsky A, Atchison WD (2008) The vascular system as a target of metal toxicity. Toxicol Sci 102:207–218
Qidwai W, Saleheen D, Saleem S, Andrades M, Azam S (2002) Are our people health conscious? Results of a patients survey in Karachi, Pakistan. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 15:10–13
Quintanilla-Vega B, Hoover D, Bal W, Silbergeld EK, Waalkes MP, Anderson LD (2000) Lead effects on protamine–DNA binding. Am J Ind Med 38:324–329
Rodu B, Cole P (2002) Smokeless tobacco use and cancer of the upper respiratory tract. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 93:511–515
Rodushkin I, Axelsson MD (2000) Application of double focusing sector field ICP-MS for multielemental characterization of human hair and nails. Part II. A study of the inhabitants of northern Sweden. Sci Total Environ 262:21–36
Shah F, Yilmaz E, Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Soylak M (2012) Vortex-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction coupled to flame atomic absorption spectrometry for lead determination: ionic liquid based microextraction using Triton X-100 as dispersant. Anal Methods 4:4091–4095
Silbergeld EK (2003) Facilitative mechanisms of lead as a carcinogen. Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech 533:121–133
Silbergeld EK, Waalkes M, Rice JM (2000) Lead as a carcinogen: experimental evidence and mechanisms of action. Am J Ind Med 38:316–323
Stepanov I, Hecht SS (2005) Tobacco-specific nitrosamines and their pyridine-N-glucuronides in the urine of smokers and smokeless tobacco users. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers 14:885–891
Van Wijngaarden E, Dosemeci M (2006) Brain cancer mortality and potential occupational exposure to lead: findings from the National Longitudinal Mortality Study, 1979–1989. Int J Cancer 119:1136–1144
Vaziri N, Khan M (2007) Interplay of reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of experimental lead-induced hypertension. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 34:920–925
Yakub M, Iqbal MP (2010) Association of blood lead (Pb) and plasma homocysteine: a cross sectional survey in Karachi, Pakistan. PLoS One 5:11706
Yousefi SR, Shemirani F (2010) Development of a robust ionic liquid–based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction against high concentration of salt for preconcentration of trace metals in saline aqueous samples: application to the determination of Pb and Cd. Anal Chim Acta 669:25–31
Zhao FQ, Li J, Zeng BZ (2008) Coupling of ionic liquid-based headspace single-drop microextraction with GC for sensitive detection of phenols. J Sep Sci 31:3045–3049
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arain, S.S., Kazi, T.G., Arain, A.J. et al. Estimation of lead in biological samples of oral cancer patients chewing smokeless tobacco products by ionic liquid-based microextraction in a single syringe system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 12396–12406 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4536-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4536-1