Abstract
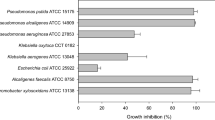
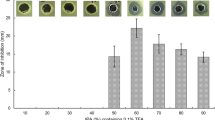
We studied a strain of Bacillus isolated from an artisanal tannery in Salta, Argentina. It was identified as Bacillus licheniformis B6 by 16 S phylogenetic analysis and MALDI TOF (GenBank accession code No. KP776730). The synthesis of lipopeptides by B6 and their antibacterial activity against clinical pathogenic strains was analyzed both in the cell-free supernatant (CFS) and in the crude fraction of lipopeptides (LF). Overall, the CFS did not significantly reduce the viability of the studied strains (Staphylococcus aureus 269 and ATCC 43,300, Escherichia coli 4591 and 25,922, Klebsiella sp. 1087 and 1101). However, LF at 9 mg/mL reduced the viability of those pathogenic strains by 2 and 3 log orders compared to those of the control. When the effects of LF and ampicillin were compared, they showed different sensitivity against pathogenic strains. For example, E. coli 4591 was the strain most resistant to ampicillin, requiring 250 mg/mL of antibiotic to achieve the same inhibitory effect as 9 mg/mL of B6 LF. SEM observations of the effect of LF on biofilm formation by E. coli 4591 and Klebsiella sp. 1087 clearly showed that biofilm structures were destabilized, these strains turning into weak biofilm formers. Signals in the CFS and LF corresponding to kurstakin and iturin were identified by MALDI TOF. Interestingly, surfactin was detected, rather than lichenysin, the expected lipopeptide in B. licheniformis species. Signals of bacitracin and fengycins were also found, the latter with a higher number of homologues and relative intensity in the LF than the other lipopeptides. These results show that the lipopeptides synthesized by B. licheniformis B6 have both potential antibacterial and anti-biofilm activity against pathogenic bacteria of health importance.
Highlights
Bacillus licheniformis B6 (Genbank accession code Nº KP776730, isolated from an artisanal tannery) synthesizes lipopeptides with biological activity.
The crude fraction of lipopeptides (LF) had antagonistic action against Staphylococcus aureus 269 and ATCC 43300, Escherichia coli 4591 and 25922, Klebsiella sp. 1087 and 1101.
9 mg/mL of B6 LF were effective to inhibit E. coli 4591, whereas 250 mg/mL of ampicillin were necessary to elicit a similar effect.
SEM observations of the effect of LF on biofilm formation by E. coli 4591 and Klebsiella sp. 1087 clearly showed that biofilm structures were destabilized.
Signals in the LF corresponding to kurstakins and iturin were identified by MALDI TOF; surfactin was detected instead of lichenysin.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audisio MC, Terzolo HR, Apella MC (2005) Bacteriocin from honeybee beebread Enterococcus avium, active against Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3373–3375. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.6.3373-3375.2005
Berić T, Stanković S, Draganić V et al (2014) Novel antilisterial bacteriocin licheniocin 50.2 from Bacillus licheniformis VPS50.2 isolated from soil sample. J Appl Microbiol 116:502–510. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12393
Bernlohrl W, Novell GD (1960) Some characteristics of bacitracin production by Bacillus licheniformis. Arch Biochem Biophys 87:232–238
Birarda G, Delneri A, Lagatolla C et al (2019) Multi-technique microscopy investigation on bacterial biofilm matrices: a study on Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical strains. Anal Bioanal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02111-7
Bonmatin J-M, Laprevote O, Peypoux F (2012) Diversity Among Microbial Cyclic Lipopeptides: Iturins and Surfactins. Activity-Structure Relationships to Design New Bioactive Agents. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 6:541–556. https://doi.org/10.2174/138620703106298716
Borucki MK, Peppin JD, White D et al (2003) Variation in Biofilm Formation among Strains of Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:7336–7342. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.12.7336-7342.2003
Cai D, Zhang B, Zhu J et al (2020) Enhanced Bacitracin Production by Systematically Engineering S-Adenosylmethionine Supply Modules in Bacillus licheniformis. 8:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00305
Carrillo C, Teruel A, Aranda FJ, Ortiz A (2003) Molecular mechanism of membrane permeabilization by the peptide antibiotic surfactin. 1611:91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2736(03)00029-4
Chen Y, Liu SA, Mou H et al (2017) Characterization of lipopeptide biosurfactants produced by Bacillus licheniformis MB01 from marine sediments. Front Microbiol 8:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00871
Chen YC, Chiang TJ, Liang TW et al (2012) Reclamation of squid pen by Bacillus licheniformis TKU004 for the production of thermally stable and antimicrobial biosurfactant. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 1:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2011.08.010
Chen YC, Yu YH (2020) Bacillus licheniformis-fermented products improve growth performance and the fecal microbiota community in broilers. Poult Sci 99:1432–1443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2019.10.061
Cladera-Olivera F, Caron GR, Brandelli A (2004) Bacteriocin-like substance production by Bacillus licheniformis strain P40. Lett Appl Microbiol 38:251–256. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2004.01478.x
Deleu M, Paquot M, Nylander T (2005) Fengycin interaction with lipid monolayers at the air – aqueous interface — implications for the effect of fengycin on biological membranes. 283:358–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.09.036
Deleu M, Paquot M, Nylander T (2008) Effect of Fengycin, a Lipopeptide Produced by Bacillus subtilis, on Model Biomembranes. Biophys J 94:2667–2679. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.107.114090
Desai JD, Banat IM (1997) Microbial production of surfactants and their commercial potential. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61:47–64. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.61.1.47-64.1997
Donelli G, Vuotto C (2014) Biofilm-based infections in long-term care facilities. Future Microbiol 9:175–188. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb.13.149
EFSA (2021) Safety and efficacy of the feed additive consisting of Bacillus licheniformis DSM 28710 (B-Act®) for laying hens, minor poultry species for laying, poultry species for breeding purposes and ornamental birds (HuvePharma N.V.). EFSA J 19. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6449
FAO (2011) 74th JECFA - Chemical and Technical Assessment (CTA), 2011 © FAO 2011. 1–6
Flemming HC, Wingender J, Szewzyk U et al (2016) Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:563–575. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.94
Fux CA, Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Stoodley P (2005) Survival strategies of infectious biofilms. Trends Microbiol 13:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2004.11.010
Giri SS, Ryu EC, Sukumaran V, Park SC (2019) Antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-adhesive activities of biosurfactants isolated from Bacillus strains. Microb Pathog 132:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.04.035
Gomaa EZ (2012) Antimicrobial activity of a biosurfactant produced by Bacillus licheniformis strain M104 grown on whey. 6:4396–4403. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR11.463
He L, Chen W (2006) Synergetic activity of nisin with cell-free supernatant of Bacillus licheniformis ZJU12 against food-borne bacteria. Food Res Int 39:905–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2006.05.008
Høiby N, Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M et al (2010) Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int J Antimicrob Agents 35:322–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2009.12.011
Hu L, Bin, Shi ZQ, Zhang T, Yang ZM (2007) Fengycin antibiotics isolated from B-FS01 culture inhibit the growth of Fusarium moniliforme Sheldon ATCC 38932. FEMS Microbiol Lett 272:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00743.x
Ibarguren C, Vivas L, Alejandra Bertuzzi M et al (2010) Edible films with anti-Listeria monocytogenes activity. Int J Food Sci Technol 45:1443–1449. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2010.02286.x
Joshi SJ, Geetha SJ, Desai AJ (2015) Characterization and Application of Biosurfactant Produced by Bacillus licheniformis R2. 346–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1746-4
Lautenbach E, Patel JB, Bilker WB et al (2001) Extended spectrum beta lactamase producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae: Risk factors for infection and impact of resistance on outcomes. J Assoc Physicians India 58:41–44
Lawrance A, Balakrishnan M, Cheriath T et al (2014) Functional and molecular characterization of a lipopeptide surfactant from the marine sponge-associated eubacteria Bacillus licheniformis NIOT-AMKV06 of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. Mar Pollut Bull 82:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.03.018
Lin J, Lin L, Zheng Q et al (2020) Isolation and Characterization of Fengycins Produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens JFL21 and Its Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Potential Against Multidrug-Resistant Foodborne Pathogens. 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.579621
Lin LL, Chyau CC, Hsu WH (1998) Production and properties of a raw-starch-degrading amylase from the thermophilic and alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. TS-23. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 28:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1470-8744.1998.tb00513.x
Merritt JH, Kadour DE, O’Toole GA (1947) Gold therapy at the Arthritis Clinic, Boston Dispensary. Bull New Engl Med Cent 9:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780471729259.mc01b01s00.Growing
Moryl M, Spętana M, Dziubek K et al (2015) Antimicrobial, antiadhesive and antibiofilm potential of lipopeptides synthesised by Bacillus subtilis, on uropathogenic bacteria Acta Biochim Pol. 62:725–732. https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2015_1120
Muslim SN, AL-Kadmy IMS, Hussein NH et al (2016) Chitosanase purified from bacterial isolate Bacillus licheniformis of ruined vegetables displays broad spectrum biofilm inhibition. Microb Pathog 100:257–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2016.10.001
Newell DG, Koopmans M, Verhoef L et al (2010) Food-borne diseases - The challenges of 20years ago still persist while new ones continue to emerge. Int J Food Microbiol 139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.01.021
O’Toole GA, Kolter R (1998) Initiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple, convergent signalling pathways: A genetic analysis. Mol Microbiol 28:449–461. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00797.x
Pathak KV, Keharia H, Gupta K et al (2012) Lipopeptides from the banyan endophyte, Bacillus subtilis K1: Mass spectrometric characterization of a library of fengycins. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 23:1716–1728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-012-0437-4
Pecci Y, Rivardo F, Martinotti MG, Allegrone G (2010) LC/ESI-MS/MS characterisation of lipopeptide biosurfactants produced by the Bacillus licheniformis V9T14 strain. J Mass Spectrom 45:772–778. https://doi.org/10.1002/jms.1767
Price NPJ, Rooney AP, Swezey JL et al (2007) Mass spectrometric analysis of lipopeptides from Bacillus strains isolated from diverse geographical locations. FEMS Microbiol Lett 271:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00702.x
Ramasubburayan R, Titus S, Verma PK et al (2014) Isolation, screening and optimization of culture conditions for enhanced antibacterial activity by a marine epibiotic bacterium Bacillus flexus APGI against fouling bacterial strains. J Pure Appl Microbiol 8:2909–2920
Rivardo F, Martinotti MG, Turner RJ, Ceri H (2011) Synergistic effect of lipopeptide biosurfactant with antibiotics against Escherichia coli CFT073 biofilm. Int J Antimicrob Agents 37:324–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.12.011
Sabaté DC, Carrillo L, Audisio MC (2009) Inhibition of Paenibacillus larvae and Ascosphaera apis by Bacillus subtilis isolated from honeybee gut and honey samples. Res Microbiol 160:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2009.03.002
Sabaté DC, Gonzaléz MJ, Porrini MP et al (2012) Synergistic effect of surfactin from Bacillus subtilis C4 and Achyrocline satureioides extracts on the viability of Paenibacillus larvae. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:1415–1422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0941-x
Shobharani P, Padmaja RJ, Halami PM (2015) Diversity in the antibacterial potential of probiotic cultures Bacillus licheniformis MCC2514 and Bacillus licheniformis MCC2512. Res Microbiol 166:546–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2015.06.003
Stepanović S, Ćirković I, Ranin L, Švabić-Vlahović M (2004) Biofilm formation by Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes on plastic surface. Lett Appl Microbiol 38:428–432. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2004.01513.x
Suthar H, Nerurkar A (2016) Characterization of Biosurfactant Produced by Bacillus licheniformis TT42 Having Potential for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 248–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2096-6
Torres MJ, Brandan CP, Petroselli G et al (2016) Antagonistic effects of Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis and B. amyloliquefaciens against Macrophomina phaseolina: SEM study of fungal changes and UV-MALDI-TOF MS analysis of their bioactive compounds. Microbiol Res 182:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2015.09.005
Torres MJ, Petroselli G, Audisio MC et al (2015) Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis CBMDC3f with antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive foodborne pathogenic bacteria: UV-MALDI-TOF MS analysis of its bioactive compounds. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 929–940. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1847-9
Van Houdt R, Michiels CW (2010) Biofilm formation and the food industry, a focus on the bacterial outer surface. J Appl Microbiol 109:1117–1131. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04756.x
Vater J, Kablitz B, Wilde C et al (2002) Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry of lipopeptide biosurfactants in whole cells and culture filtrates of Bacillus subtilis C-1 isolated from petroleum sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:6210–6219. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.12.6210-6219.2002
Youssef NH, Duncan KE, Nagle DP et al (2004) Comparison of methods to detect biosurfactant production by diverse microorganisms. J Microbiol Methods 56:339–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2003.11.001
Zhao H, Shao D, Jiang C et al (2017) Biological activity of lipopeptides from Bacillus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:5951–5960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8396-0
Zhao H, Shao D, Jiang C, et al (2017) Biological activity of lipopeptides from Bacillus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:5951–5960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8396-0
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funds from the University of Buenos Aires (Argentina; UBACyT 20020170100110BA), and the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCYT) (Argentina, PICT2016-00130; PICT2015-00640). The Ultraflex II TOF/TOF mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonics) was supported by a grant from ANPCYT (PME2003 No.125, CEQUIBIEM, DQB, FCEN, University of Buenos Aires). Audisio M.C., Erra-Basells R., Petroselli G. and Torres M.J. are Research Members at Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Tecnológicas (CONICET, Argentina). Díaz P.R. was supported by doctoral fellowships from ANPCyT and CONICET (Argentina).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz, P.R., Torres, M.J., Petroselli, G. et al. Antibacterial activity of Bacillus licheniformis B6 against viability and biofilm formation of foodborne pathogens of health importance. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 181 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03377-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03377-3