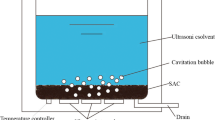
Abstract
Activated carbon adsorption technology is widely used in wastewater treatment, however, efficient regeneration of spent granular activated carbon (SGAC) at low energy consumption has become a challenge in this technology area. In this study, the thermal + ozone oxidation regeneration (LTO) was proposed for the first time. Technical feasibility is explored and mechanisms are analyzed in detail. According to the analysis of the LTO test, when the regeneration temperature was 350℃, the time was 1 h, the ozone addition time as 40 min, the SGAC regeneration efficiency was as high as 95%, which was 34% higher than thermal regeneration. The regeneration efficiency of SGAC decreased slightly after the three adsorption-regeneration cycles, but it was still able to reach 81.8% almost no carbon loss. During the low-thermal regeneration stage, phenol could desorb physically by the change of temperature and opened the pores for ozone to enter the inside of GAC. In the ozone regeneration phase, the chemisorbed phenol is desorbed and oxidized through the oxidizing power of ozone itself and hydroxyl radicals. This study helps to reduce the regeneration temperature for conventional thermal regeneration and the amount of oxidant used for ozone regeneration, which has practical engineering implications.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abrouki, Y., Mabrouki, J., Anouzla, A., Rifi, S. K., Zahiri, Y., Nehhal, S., & Souabi, S. (2021). Optimization and modeling of a fixed-bed biosorption of textile dye using agricultural biomass from the Moroccan Sahara. Desalination and Water Treatment, 240, 144–151.
Alvárez’, P. M., Beltrán, F. J., Masa, F. J., & Pocostales, J. P. (2009). A comparison between catalytic ozonation and activated carbon adsorption/ozone-regeneration processes for wastewater treatment. Applied Catalysis B, Environmental, 92(3–4), 393–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.08.019
Bakar, H. H. A., Yusop, H. M., & Samah, N. A. (2022). Adsorption behavior of heavy metal ions by hybrid inulin-TEOS for water treatment. Civil Engineering Journal, 37(6), 1868–1876. https://doi.org/10.28991/CEJ-2022-08-09-03
Bao, M., & Li, Q. B. (2023). Molecular transformation of dissolved organic matter in reverse osmosis concentrated leachate during a tight-ultrafiltration membrane combined with an O3/GAC system. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 11(2), 109428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.109428
Benítez, P. M. A., Chica, A. F., & MartínCaballero, M. A. (2020). Evaluating the thermal regeneration process of massively generated granular activated carbons for their reuse in wastewater treatments plants. Powder Technology, 366(15), 132685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132685
Berenguer, R., Marco-Lozar, J. P., Quijada, C., Cazorla-Amorós, D., & Morallón, E. (2010). Comparison among chemical, thermal, and electrochemical regeneration of phenol-saturated activated carbon. Energy & Fuels, 24(6), 3366–3372.
Changmai, M., & Purkait, M. K. (2017). Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic study of phenol adsorption using NiFe2O4 nanoparticles aggregated on PAC. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 16, 90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.12.011
Costa, L. R. C., Ribeiro, L. M., Hidalgo, G. E. N., & Féris, L. A. (2022). Evaluation of efficiency and capacity of thermal, chemical and ultrasonic regeneration of tetracycline exhausted activated carbon. Environmental Technology., 43(6), 910. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2020.1811391
Du, M. H., Zhang, W., Ling, L. P., Zhang, Y. Z., & Sun, X. M. (2023). Study on the performance of O3-PAC-ceramic membrane coupling technology for phenol wastewater treatment. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 13(1), 240. https://doi.org/10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210610
Gamal, M. E., Mousa, H. A., EL-Naas, M. H., Zacgarua, R., & Judd, S. (2018). Bio-regeneration of activated carbon: A comprehensive review. Separation and Purification Technology, 197, 345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.01.015
He, X., Elkouz, M., Inyang, M., Dickenson, E., Wert, E. C. (2017). Ozone regeneration of granular activated carbon for trihalomethane control. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 326(15), 101-109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.12.016
Jian, X. P., Xu, W., Hou, X. L., & Liu, S. (2020). Research progress on activated carbon modification technology. Biomass Chemical Engineering, 54(5), 66–72. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2020.05.009
Jioui, I., Abrouki, Y., AboulHrouz, S., Sair, S., Dânoun, K., & Zahouily, M. (2023). Efficient removal of Cu2+ and methylene blue pollutants from an aqueous solution by applying a new hybrid adsorbent based on alginate-chitosan and HAP derived from Moroccan rock phosphate. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(49), 107790–107810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29890-y
Jr, O. F. C., Gómez, I. G., Rodríguez-Reinoso, F., Silvestre-Albero, J., Rambo, C. R., Martínez-Escandell, M. (2023). Activated carbons with high micropore volume obtained from polyurethane foams for enhanced CO2 adsorption. Chemical Engineering Science, 273(5), 118671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2023.118671
Kalombo, M. L., Adeniyi, A., Nomadolo, N., Setshedi, K., Madito, M. J., Manyala, N., & Mbaya, R. K. (2021). Preparation and characterization of polypyrrole nanoparticles for enhancement of granular activated carbon (GAC) as adsorbent. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 129, 264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2021.10.004
Karimi, S., Yaraki, M. T., & Karri, R. R. (2019). A comprehensive review of the adsorption mechanisms and factors influencing the adsorption process from the perspective of bioethanol dehydration. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 107, 535–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.03.025
Khanday, W. A., Ahmed, M. J., Okoye, P. U., Hummadi, E. H., & Hameed, B. H. (2019). Single-step pyrolysis of phosphoric acid-activated chitin for efficient adsorption of cephalexin antibiotic. Bioresource Technology, 280, 255–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.003
Li, Q., Qi, Y., & Gao, C. (2015). Chemical regeneration of spent powdered activated carbon used in decolorization of sodium salicylate for the pharmaceutical industry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 86, 424–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.08.008
Liu, S., Xue, H., Qiu, D., Feng, X., & Wang, N. (2021). Research and prospect on activated carbon regeneration technology. Sintering and Pelletizing, 46(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.13403/j.sjqt.2021.01.005
Lobata-Peralta, D. R., Duque-Brito, E., Ayala-Cortés, A., Arias, D. M., Longria, A., Cuentas-Gallegos, A. K., Sebastian, P. J., & Okoye, P. U. (2021). Advances in activated carbon modification, surface heteroatom configuration, reactor strategies, and regeneration methods for enhanced wastewater treatment. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(4), 2213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105626
Lu, Y., Li, J. F., Li, H. X., **n, X., Shi, X. W., Liu, Z., & Cheng, J. P. (2018). Experimental and characteristic analysis on pyrolysis regeneration of waste powdered activated carbon. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 37(1), 389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.109428
Maroto-Valer, M., Dranca, I., Clifford, D., Lupascu, T., Nastas, R., Carlos, A., & Leon y Leon, C. A. (2006). Thermal regeneration of activated carbons saturated with ortho - and meta -chlorophenols. Thermochimica Acta, 2, 148–156.
Marques, S. C. R., Marcuzzo, J. M., Baldan, M. R., Mestre, A. S., & Carvalho, A. P. (2017). Pharmaceuticals removal by activated carbons: Role of morphology on cyclic thermal regeneration. Chemical Engineering Journal, 321, 233–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.101
Matatovmeytal, Y., Sheintuch, M., Shter, G. E., & Grader, G. S. (2019). Enhanced treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater by combining three-dimensional electrochemical process with ozonation to in situ regenerate granular activated carbon particle electrodes. Separation and Purification Technology, 208, 12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.06.030
Mustafa, M., Kozyatnyk, I., Gallampois, C., Oesterle, P., Östman, M., & Tysklind, M. (2021). Regeneration of saturated activated carbon by electro-peroxone and ozonation: Fate of micropollutants and their transformation products. Science of the Total Environment, 776, 145723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145723
Nieto-Sandoval, J., Morabet, F. E., Munoz, M., Loperz-Arago, N., Pedro, Z. M., & Casas, J. A. (2023). In-situ regeneration of a novel Fe3O4/GAC adsorbent for micropollutants removal in a continuous fixed-bed. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances, 10, 100267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2023.100267
Nistratov, A., Klimenko, N. N., Pustynnikov, I. V., & Vu, L. K. (2022). Thermal regeneration and reuse of carbon and glass fibers from waste composites. Emerging Science Journal, 6(5), 967–984. https://doi.org/10.28991/ESJ-2022-06-05-04
Rachiq, T., Abrouki, Y., Mabrouki, J., Samghouli, N., Fersi, C., Rahal, S., & El Hajjaji, S. (2021). Evaluation of the efficiency of different materials to remove specific pollutants from landfill leachate. Desalination and Water Treatment, 238, 240–250.
Real, F. J., Acero, J. L., Benitez, F. J., & Matamoros, E. (2022). Elimination of neonicotinoids by ozone-based advanced oxidation processes: Kinetics and performance in real water matrices. Separation and Purification Technology, 301, 121975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121975
Ren, D., Li, D., Huang, Z., Shi, H., & Chen, Q. (2021). Regeneration of spent powdered activated carbon from adsorption of dyestuff wastewater by hydrothermal Carbonization. Research of Environmental Science, 34(02), 365–371. https://doi.org/10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.08.05
Ren, M. Z., Wang, J., Wang, Z. Y., Sun, S. H., Qiu, J. K., Shi, Y. C., Wang, Z. J., & **e, Y. B. (2022). Activated carbon adsorption coupled with ozonation regeneration for efficient removal of chlorobenzene. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(2), 107319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107319
Santos, D. H. S., Santos, J. P. T. S., Duarte, J. L. S., Oliveira, L. M. T. M., Tonholo, J., Meili, L., & Zanta, C. L. P. S. (2022). Regeneration of activated carbon adsorbent by anodic and cathodic electrochemical process. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 159, 1150–1163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.01.083
Sivarasan, G., Manikandan, V., Periyasamy, S., Alsalhi, M. S., Devanesan, S., Kumarf, P. S. M., Pasupuleti, R., Liu, X. H., & Lo, H. (2023). Iron-engineered mesoporous biocarbon composite and its adsorption, activation, and regeneration approach for removal of paracetamol in water. Environmental Research, 227, 115723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115723
Thom, D. T., Manh, D. V., & Tuyen, T. V. (2020). Nano-catalysts in ozone-based advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment. Current Pollution Reports, 6(3), 217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-020-00147-3
Wang, R. K., Ma, Q. Q., Zhao, Z., Ye, X. M., Zhao, Z. H., & Liu, J. (2019). Adsorption of Surfactants on coal surfaces in the coking wastewater environment: Kinetics and effects on the slurring properties of coking wastewater–coal slurry. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 58(28), 12825–12834. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b01829
Wang, T., Song, Y. Q., Ding, H. J., Liu, Z., Baldwin, A., Wong, I., Li, H., & Zhao, C. (2020). Insight into synergies between ozone and in-situ regenerated granular activated carbon particle electrodes in a three-dimensional electrochemical reactor for highly efficient nitrobenzene degradation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 394, 124852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124852
Wang, Y. Q., Lin, C. Y., Liu, T. X., Ren, W. B., Huang, X. K., He, M., & Wei, O. Y. (2021). Efficient removal of acetochlor pesticide from water using magnetic activated carbon: Adsorption performance, mechanism, and regeneration exploration. Science of the Total Environment, 778, 146353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146353
Wang, B., Wang, Q., Zhu, K., Peng, A., Wang, D., & Guan, J. (2023a). Adsorption characteristics of coffee grounds activated carbon for methylene blue. Industrial Water & Wastewater, 54(3), 16–20.
Wang, Y., Huang, Y., & Ma, L. (2023b). The special mechanisms of quasi-complexation and enhanced effect of “·OH action zone” in activated carbon combined ozonation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 11(3), 110094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.110094
Yuan, H., Ye, J., Yang, J., Wang, H., Ni, X., Li, D., & Chen, Y. (2023). Green regeneration of spent activated carbon from antibiotics purification as remarkable absorbent for aqueous Cd2+ removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances, 12, 100361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2023.100361
Zanella, O., Bilibio, D., Priamo, W. L., Tessaro, L. C., & Feris, L. A. (2017). Electrochemical regeneration of phenol-saturated activated carbon proposal of a reactor. Environmental Technology Letters, 38(5–8), 551. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1202327
Zhang, J., Huang, G. Q., Liu, C., Zhang, R. N., Chen, X. X., & Zhang, L. (2018). Synergistic effect of microbubbles and activated carbon on the ozonation treatment of synthetic dyeing wastewater. Separation and Purification Technology, 201, 10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.02.003
Zhong, C. X. (2021). Pilot-scale Study on advanced treatment of wastewater treatment plant by ozone and activated carbon process. Technology of Water Treatment, 47(10), 117–120. https://doi.org/10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.2021.10.025
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the funding from Doctoral Research Startup Fund of the North China University of science and technology (28409899).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, W., Tang, C. et al. Effective Combination of Low-Thermal and Ozone as a Method for Regenerating Spent GAC Saturated with Phenol. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 344 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07130-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07130-4