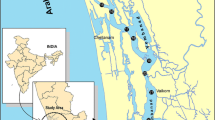
Abstract
The mercury content in the seafloor sediments and benthic flathead fish collected from the offshore regions of Leizhou Peninsula was analyzed, and related mercury contamination was assessed. The results show that mercury content of seafloor sediments ranged from 0.005 to 0.359 mg kg−1 with an average of 0.081 mg kg−1. As a whole, the mercury content in the seafloor sediments of the eastern offshore region of Leizhou Peninsula was higher than that of southern and western offshore regions. Mercury content in fish organs of the branchial, muscle, and liver was in the range of 0.032 ~ 0.034 mg kg−1, 0.065 ~ 0.080 mg kg−1, and 0.228 ~ 0.270 mg kg−1, respectively, and displayed a mercury content order of the liver > muscle > branchial and a significant liver accumulation preference. The pollution assessment suggested that there is an ecological risk of mercury contamination in the eastern offshore region of Leizhou Peninsula, while the southern and western regions are in low risk of mercury pollution. Although the mercury content of the benthic fish is generally consistent with the mercury contamination level of seafloor sediments where the fish is captured, there is no clear correlation between the fish size and their mercury contents which may imply that there is low risk of mercury bioaccumulation in these benthic fish.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Atta, A., Voegborlo, R. B., & Agorku, E. S. (2012). Total mercury distribution in different tissues of six species of freshwater fish from the Kpong hydroelectric reservoir in Ghana. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 3259–3265.
Bin, T. H. W. (1999). Artificial seedling technology points of Platycephalus indicus in Japan. Journal of Fujian Fisheries, 1, 63–65.
Cai, R. B., Yang, L. K., Zhu, N., et al. (2015). Evaluation and content of various heavy metals found in the water and fish collected from Bohai Bay (Section in Hebei) during the autumn. Journal of Hebei University (natural Science Edition), 35(4), 371–378.
Chen, W. Q., & Zhao, W. Q. (1986). A preliminary study on age and growth of Chrysalis pupa in the Yellow Sea. Journal of Fisheries of China, 10(3), 289–304.
Chen, Z. J., Lu, S. L., Lu, L. Y., et al. (2021). Community structure of macrobenthic crustacean with the relationship of affected factors in the east coastal of Leizhou Peninsula. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 41(01), 17–25.
Cui, Y., Chen, B. J., Song, Y. L., et al. (1997). Heavy metals content in sea water and marine organisms at Jiaozhou Bay. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 8(3), 650–654.
Cui, Z. M., Huang, J. W., Wang, H. Y., et al. (2018). Classification and distribution of oysters in eastern coast of Leizhou Peninsula, China. Oceanologia Et Limnologia Sinica, 49(6), 1.350-1.357.
Cunningham, P. A., Sullivan, E. E., Everett, K. H., et al. (2019). Assessment of metal contamination in Arabian/Persian Gulf fish: A review. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 143, 264–283.
Dai, Y., Wu, S. J., Shu, L. Q., et al. (2018). Studies on antioxidant activity of hydrolysates derived from protein of Platycephalus indicus. Food Research and Development, 39(3), 35–40.
EPA USA. (1997). Mercury study report to congress. In Volume 4. An assessment of exposure to mercury in the United States. Research Triangle Park, NC: Ralergh: Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards.
Feng, Y. T., Zhao, H., & Shi, Y. Z. (2019). The concentration of nutrients and chlorophyll a in the offshore of Leizhou Peninsula in autumn spatial distribution and their relationship. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 39(2), 75–82.
General Administration of Quality Supervision. (2001). Inspection and quarantine of the People's Republic of China. In Safety and quality of agricultural products-Part 4: Safety requirements for non-pollution aquatic products: GB 18406.4 —2001 (vol. 5). Bei**g: China Agriculture Press.
General Administration of Quality Supervision. (2002). Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. In Marine Sediment Quality of the People's Republic of China: GB 18668—2002 (vol. 3). Bei**g: China Standards Press.
Hosseini, M., Nabavi, S. M. B., & Parsa, Y. (2013). Bioaccumulation of trace mercury in trophic levels of benthic, benthopelagic, pelagic fish species, and sea birds from Arvand River. Iran. Biological Trace Element Research, 156, 175–180.
Juresa, D., & Blanusa, M. (2003). Mercury, arsenic, lead and cadmium in fish and shellfish from the Adriatic Sea. Food Additives and Contaminants, 20, 241–246.
La, C. N. S., Botte, S. E., Oliva, A. L., et al. (2017). Tracing Cr, Pb, Fe and Mn occurrence in the Bahia Blanca estuary through commercial fish species. Chemosphere, 175, 286–293.
Li, X. Y., Sun, X. L., Zhang, Y. B., et al. (2014). Characteristics of oil-hydrocarbon distribution in coastal waters of Leizhou Peninsula during summer season. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(12), 138–142.
Li, J., Zhou, Q., Yuan, G., et al. (2015). Mercury bioaccumulation in the food web of Three Gorges Reservoir (China): Tempo-spatial patterns and effect of reservoir management. Science of the Total Environment, 527, 203–210.
Li, Y. Y., Yang, L. F., & Li, R. (2018a). Analysis and aesthetic implication of Leizhou Peninsula’s yearly feast. Journal of Nanning Polytechnic, 23(2), 11–15.
Li, Y. L., Liu, X. Z., Ji, G., et al. (2018). Structure and genetic diversity of mtDNA D-loop sequences of sand gurnard Platycephalus s. 1 inhabiting Liaoning Coast. Fishery Science, 37(6), 1003–1111.
Liu, J. L., Xu, X. R., Ding, Z. H., et al. (2013a). Heavy metals contamination in fish from coral reef ecosystem and ecology risk evaluation. Marine Environmental Science, 32(2), 262–266.
Liu, J. L., Xu, X. R., Chen, L. G., et al. (2013b). Mercury and methylmercury contamination in fish from Yongxing Island and human health risk evaluation. Marine Environmental Science, 32(6), 867–870.
Monteiro, D. A., Rantin, F. T., & Kalinin, A. L. (2010). Inorganic mercury exposure: Toxicological effects, oxidative stress biomarkers and bioaccumulation in the tropical freshwater fish matrinxã, Brycon amazonicus (Spix and Agassiz, 1829). Ecotoxicology, 19, 105–123.
Olmedo, P. P. A., Hernández, A. F., Barbier, F., et al. (2013). Determination of toxic elements (mercury, cadmium, lead, tin and arsenic) in fish and shellfish samples. Risk assessment for the consumers. Environment International, 59, 63–72.
Peng, X., Liu, F., & Wang, W. X. (2016). Organ-specific accumulation, transportation, and elimination of methylmercury and inorganic mercury in a low Hg accumulating fish. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 35, 2074–2083.
Peterson, S. A., Van Sickle, J., Herlihy, A. T., et al. (2007). Mercury concentration in fish from streams and rivers through out the western United States. Environmental Science & Technology., 41(1), 58–65.
Qin, H. (2017). Research on heavy metals from marine sediments, large yellow croaker and sea bass near Ningbo and Zhoushan. Zhejiang Ocean University.
Qin, Y., & Gao, T. X. (2012). Fishery biology and resource abundance of Platycephalus indicus in coastal water of Dongying. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 42(7/8), 106–111.
Safiur, R. M., Solaiman, H. M., Ahmed, M. K., et al. (2019). Assessment of heavy metals contamination in selected tropical marine fish species in Bangladesh and their impact on human health. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 11, 232–241.
Sandraq, G., Iseia, L., & Carlos, B. (2008). Mercury removal from contaminated water by ultrasound -promoted reduction/vaporization in a microscale reactor. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 15, 212–216.
Saudith, B., Amado, N., José, M., et al. (2017). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals in the Cispata Bay, Colombia: A marine tropical ecosystem. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 120, 379–386.
Suo, Q. S. (2014). Mercury and other heavy metals in fishes from **aolangdi Reservoir and health risk assessment. Henan Polytechnic University.
Tetsuya, E., Hideki, O., Moriaki, H., et al. (2017). Correlations between mercury concentration, and stable isotope ratios of carbon and nitrogen of amino acids in scalp hair from whale meat eaters and heavy fish eaters. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 31, 745–752.
The Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China. (2006). Non-pollution food limit of toxic and harmful substances in aquatic products: NY 5073—2006 (vol. 2). Bei**g: China Agriculture Press.
Tuzen, M. (2009). Toxic and essential trace elemental contents in fish species from the Black Sea. Turkey. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 47(8), 1785–1790.
Wang, H. Q., Jia, X. P., & Lin Y. T. (1984). A preliminary discussion on some criteria for evaluation of marine biological pollution//Office of Leading Group for Comprehensive Survey of Coastal Zone and Tideland Resources of Guangdong Province. In Survey and study of coastal zone and tideland resources in the Pearl River estuary (vol. 2, pp. 132–141). Guangzhou: Guangdong Science and Technology Press.
WHO (World Health Organization). (1989). Heavy metals - environmental aspects. Environment Health Criteria: No. 85[S]. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO.
Wiener, J. G., Spry, D. J. (1996). Toxicological significance of mercury in freshwater fish. In W. N. Beyer, G. H. Heinz, & A. W. Redmon-Norwood (Eds.), Larger Work Title: Environmental Contaminants in Wildlife: Interpreting Tissue Concentrations (pp. 297–340). Publisher: Lewis Publishers.
Xu, Q. Q. (2019). Distribution characteristics of mercury and organophosphorus ester in water, soil/sediment and fish in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Southwest University.
Xu, Q., Zhao, L., Wang, Y., et al. (2018). Bioaccumulation characteristics of mercury in fish in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environmental Pollution, 243, 115–126.
Yang, G. H., Sun, X. L., & Song, Z. G. (2020). Trophic level and heavy metal pollution of Sardinella albella in Liusha Bay, Beibu Gulf of the South China Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 156, 1–8.
Ye, Y. T., Luo, C. B., Yang, K. M., et al. (2019). Evaluation of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk of soil in Leizhou Peninsula. Anhui Agriculture Science Bulletin, 25(14), 95–98.
Zhan, J. Z., Yang, Q., & Zhan, Y. Q. X. (2015). Complete fishing techniques (Revised Edition). Science and Technology Press.
Zhang, Z. S., Sun, W., & Zhou, Y. Z. (2008). Quantitatively assessment of eco-environmental vulnerability in tropic coastal arid area: A case study of Leizhou Peninsula. Journal of Desert Research, 28(1), 125–130.
Zhang, C. X., Gong, Y. Y., Sun, X. L., et al. (2014). Zooplankton community in the coastal zone of Leizhou Peninsula in summer 2010. Acta Oceanologica Sinica (in Chinese), 36(4), 91–99.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Project of Marine Geochemistry and Climate Change of Guangdong Ocean University (No. 002026002004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• The mercury content in the seafloor sediments of the eastern peninsula was higher than that of the southern and western regions.
• The mercury contents of flathead fish samples showed the regularity of the liver > muscle > gill.
• The mercury content level in flathead fish is generally consistent with that of sediments.
• The mercury bioaccumulation risk is low in these benthic flathead fish.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, G., Gao, Y., Song, Z. et al. Environmental Significance of Mercury Content in Seafloor Sediments and Benthic Fish from the Offshores of Leizhou Peninsula, China. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 539 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06559-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06559-3