Abstract
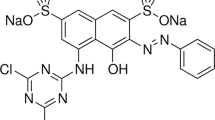
In this study, carbonized mandarin peel (CMP) was prepared and characterized and the adsorption behavior of the activated carbon for methylene blue (MB) and methyl orange (MO) removal was investigated. Adsorbent (CMP) was characterized by means of scanning electron microscopy (SEM-EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermo-gravimetric analyses (TGA), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). In the adsorption studies, the effects of initial dye concentration, solution pH, adsorbent dosage, and contact time on dye removal were investigated. In the same conditions, MB showed higher adsorption capacity than that of the MO. Therefore, the isotherms, kinetics, and thermo-dynamical adsorption studies were performed for MB. The appropriate adsorption isotherm for MB using CMP was determined as Langmuir isotherm. The kinetic values are well defined by the pseudo-second order kinetic model. The highest MB removal of 99.77% was obtained with CMP concentration of 5 g/L when the dye concentration was 5 mg/L at pH value of 6.9. After solvent regeneration, the adsorbent maintained 95.17% of its regeneration activity. The results show that CMP can be used as a low-cost and natural adsorbent to remove synthetic dye from the effluent of the textile wastewater.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul Khalil, H. P. S., Jawaid, M., Firoozian, P., Rashid, U., Islam, A., & Akil, H. M. (2013). Activated carbon from various agricultural wastes by chemical activation with KOH: preparation and characterization. Journal of Biobased Materials and Bioenergy, 7(6), 708–714.
Aboua, K. N., Yobouet, Y. A., Yao, K. B., Goné, D. L., & Trokourey, A. (2015). Investigation of dye adsorption onto activated carbon from the shells of Macoré fruit. Journal of Environmental Management, 156, 10–14.
Al-Hameedi, A. T. T., Alkinani, H. H., Dunn-Norman, S., Al-Alwani, M. A., Alshammari, A. F., Alkhamis, M. M., et al. (2020). Experimental investigation of environmentally friendly drilling fluid additives (mandarin peels powder) to substitute the conventional chemicals used in water-based drilling fluid. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 10(2), 407–417.
Almeida, C. A. P., Debacher, N. A., Downs, A. J., Cottet, L., & Mello, C. A. D. (2009). Removal of methylene blue from colored effluents by adsorption on montmorillonite clay. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 332(1), 46–53.
AlOthman, Z. A., Habila, M. A., Ali, R., Abdel Ghafar, A., & El-din Hassouna, M. S. (2014). Valorization of two waste streams into activated carbon and studying its adsorption kinetics, equilibrium isotherms and thermodynamics for methylene blue removal. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 7(6), 1148–1158.
Ateş, F., Şahin, S., İlbay, Z., & Kırbaşlar, I. (2019). A green valorisation approach using microwaves and supercritical CO2 for high-added value ingredients from mandarin (Citrus deliciosa Tenore) leaf waste. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 10(3), 533–546.
Azad, A. K. (2017). Biodiesel from mandarin seed oil: a surprising source of alternative fuel. Energies. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10111689.
Azharul Islam, M., Benhouria, A., Asif, M., & Hameed, B. H. (2015). Methylene blue adsorption on factory-rejected tea activated carbon prepared by conjunction of hydrothermal carbonization and sodium hydroxide activation processes. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 52, 57–64.
Azharul Islam, M., Ahmed, M. J., Khanday, W. A., Asif, M., & Hameed, B. H. (2017). Mesoporous activated coconut shell-derived hydrochar prepared via hydrothermal carbonization-NaOH activation for methylene blue adsorption. Journal of Environmental Management, 203, 237–244.
Banat, F., Al-Asheh, S., Al-Ahmad, R., & Bni-Khalid, F. (2007). Bench-scale and packed bed sorption of methylene blue using treated olive pomace and charcoal. Bioresource Technology, 98(16), 3017–3025.
Bazrafshan, E., Mostafapour, F., & Mahvi, A. H. (2014). Decolorization of reactive red 198 by adsorption onto ZnCl2 activated pistachio hull wastes. International Journal of Environmental Health Engineering, 2(6), 38–45.
Chakraborty, S., De, S., DasGupta, S., & Basu, J. K. (2005). Adsorption study for the removal of a basic dye: experimental and modeling. Chemosphere, 58(8), 1079–1086.
Chen, S., Zhang, J., Zhang, C., Yue, Q., Li, Y., & Li, C. (2010). Equilibrium and kinetic studies of methyl orange and methyl violet adsorption on activated carbon derived from Phragmites australis. Desalination, 252(1–3), 149–156.
Chen, H., Zhao, J., Wu, J., & Dai, G. (2011). Isotherm, thermodynamic, kinetics and adsorption mechanism studies of methyl orange by surfactant modified silkworm exuviae. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192(1), 246–254.
Choi, I. S., Lee, Y. G., Khanal, S. K., Park, B. J., & Bae, H. J. (2015). A low-energy, cost-effective approach to fruit and citrus peel waste processing for bioethanol production. Applied Energy, 140, 65–74.
Crini, G. (2006). Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresource Technology, 97(9), 1061–1085.
Dahmoune, F., Boulekbache, L., Moussi, K., Aoun, O., Spigno, G., & Madani, K. (2013). Valorization of Citrus limon residues for the recovery of antioxidants: evaluation and optimization of microwave and ultrasound application to solvent extraction. Industrial Crops and Products, 50, 77–87.
Dai, Y., Zhang, N., **ng, C., Cui, Q., & Sun, Q. (2019). The adsorption, regeneration and engineering applications of biochar for removal organic pollutants: a review. Chemosphere, 223, 12–27.
Demirbas, A. (2008). Heavy metal adsorption onto agro-based waste materials: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 157(2–3), 220–229.
Deng, H., Yang, L., Tao, G., & Dai, J. (2009). Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from cotton stalk by microwave assisted chemical activation-application in methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166(2–3), 1514–1521.
Djilani, C., Zaghdoudi, R., Djazi, F., Bouchekima, B., Lallam, A., Modarressi, A., & Rogalski, M. (2015). Adsorption of dyes on activated carbon prepared from apricot stones and commercial activated carbon. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 53, 112–121.
Dod, R., Banerjee, G., & Saini, S. (2012). Adsorption of methylene blue using green pea peels (Pisum sativum): a cost-effective option for dye-based wastewater treatment. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 17(4), 862–874.
Elmoubarki, R., Mahjoubi, F. Z., Tounsadi, H., Moustadraf, J., Abdennouri, M., Zouhri, A., et al. (2015). Adsorption of textile dyes on raw and decanted Moroccan clays: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Water Resources and Industry, 9, 16–29.
Feng, Y., Yang, F., Wang, Y., Ma, L., Wu, Y., Kerr, P. G., & Yang, L. (2011). Basic dye adsorption onto an agro-based waste material-Sesame hull (Sesamum indicum L.). Bioresource Technology, 102(22), 10280–10285.
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2010). Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chemical Engineering Journal, 156(1), 2–10.
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2012a). Coconut husk derived activated carbon via microwave induced activation: effects of activation agents, preparation parameters and adsorption performance. Chemical Engineering Journal, 184, 57–65.
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2012b). Potential of jackfruit peel as precursor for activated carbon prepared by microwave induced NaOH activation. Bioresource Technology, 112, 143–150.
Garg, V. K., Kumar, R., & Gupta, R. (2004). Removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution by adsorption using agro-industry waste: a case study of Prosopis cineraria. Dyes and Pigments, 62, 1–10.
Gopinathan, R., Bhowal, A., & Garlapati, C. (2017). Thermodynamic study of some basic dyes adsorption from aqueous solutions on activated carbon and new correlations. Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 107(2437), 182–188.
Gupta, N., Kushwaha, A. K., & Chattopadhyaya, M. C. (2016). Application of potato (Solanum tuberosum) plant wastes for the removal of methylene blue and malachite green dye from aqueous solution. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 9, 707–716.
Gusmão, K. A. G., Gurgel, L. V. A., Melo, T. M. S., & Gil, L. F. (2013). Adsorption studies of methylene blue and gentian violet on sugarcane bagasse modified with EDTA dianhydride (EDTAD) in aqueous solutions: kinetic and equilibrium aspects. Journal of Environmental Management, 118, 135–143.
Hameed, B. H., & El-Khaiary, M. I. (2008). Sorption kinetics and isotherm studies of a cationic dye using agricultural waste: broad bean peels. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 154(1–3), 639–648.
Hassan, W., Farooq, U., Ahmad, M., Athar, M., & Khan, M. A. (2017). Potential biosorbent, Haloxylon recurvum plant stems, for the removal of methylene blue dye. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 10, 1512–1522.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1998). Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chemical Engineering Journal, 70, 115–124.
Hu, Q. H., Qiao, S. Z., Haghseresht, F., Wilson, M. A., & Lu, G. Q. (2006). Adsorption study for removal of basic red dye using bentonite. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 45(2), 733–738.
Jawad, A. H., Rashid, R. A., Ishak, M. A. M., & Wilson, L. D. (2016). Adsorption of methylene blue onto activated carbon developed from biomass waste by H2SO4 activation: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(52), 25194–25206.
Jawad, A. H., Razuan, R., Appaturi, J. N., & Wilson, L. D. (2019). Adsorption and mechanism study for methylene blue dye removal with carbonized watermelon (Citrullus lanatus)rind prepared via one-step liquid phase H2SO4 activation. Surfaces and Interfaces, 16, 76–84.
Kadirvelu, K., Kavipriya, M., Karthika, C., Radhika, M., Vennilamani, N., & Pattabhi, S. (2003). Utilization of various agricultural wastes for activated carbon preparation and application for the removal of dyes and metal ions from aqueous solutions. Bioresource Technology, 87(1), 129–132.
Kim, I., Saif Ur Rehman, M., & Han, J. I. (2014). Fermentable sugar recovery and adsorption potential of enzymatically hydrolyzed rice straw. Journal of Cleaner Production, 66, 555–561.
Koyuncu, F., Güzel, F., & Sayğılı, H. (2018). Role of optimization parameters in the production of nanoporous carbon from mandarin shells by microwave-assisted chemical activation and utilization as dye adsorbent. Advanced Powder Technology, 29(9), 2108–2118.
Kumar, K. V., & Porkodi, K. (2006). Relation between some two- and three-parameter isotherm models for the sorption of methylene blue onto lemon peel. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 138(3), 633–635.
Kumar, K. V., Ramamurthi, V., & Sivanesan, S. (2005). Modeling the mechanism involved during the sorption of methylene blue onto fly ash. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 284, 14–21.
Lim, L. B. L., Priyantha, N., Tennakoon, D. T. B., Chieng, H. I., Dahri, M. K., & Suklueng, M. (2017). Breadnut peel as a highly effective low-cost biosorbent for methylene blue: equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 10, 3216–3228.
Malekbala, M. R., Hosseini, S., Kazemi Yazdi, S., Masoudi Soltani, S., & Malekbala, M. R. (2012). The study of the potential capability of sugar beet pulp on the removal efficiency of two cationic dyes. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 90(5), 704–712.
Marković, S., Stanković, A., Lopičić, Z., Lazarević, S., Stojanović, M., & Uskoković, D. (2015). Application of raw peach shell particles for removal of methylene blue. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3(2), 716–724.
Mittal, A., Malviya, A., Kaur, D., Mittal, J., & Kurup, L. (2007). Studies on the adsorption kinetics and isotherms for the removal and recovery of methyl orange from wastewaters using waste materials. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 148(1–2), 229–240.
Nguyen, C. H., Fu, C. C., & Juang, R. S. (2018). Degradation of methylene blue and methyl orange by palladium-doped TiO2 photocatalysis for water reuse: efficiency and degradation pathways. Journal of Cleaner Production, 202, 413–427.
Nigiz, F. U. (2019). Synthesis of a novel graphene–kaolin–alginate adsorbent for dye removal, and optimization of the adsorption by response surface methodology. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 45(7), 3739–3753.
Ofomaja, A. E., & Ho, Y. S. (2008). Effect of temperatures and pH on methyl violet biosorption by Mansonia wood sawdust. Bioresource Technology, 99(13), 5411–5417.
Pathak, P. D., Mandavgane, S. A., & Kulkarni, B. D. (2017). Fruit peel waste: characterization and its potential uses. Current Science, 113(3), 444–454.
Pathania, D., Sharma, S., & Singh, P. (2017). Removal of methylene blue by adsorption onto activated carbon developed from Ficus carica bast. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 10, 1445–1451.
Pavan, F. A., Lima, E. C., Dias, S. L. P., & Mazzocato, A. C. (2008). Methylene blue biosorption from aqueous solutions by yellow passion fruit waste. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 150(3), 703–712.
Ponnusami, V., Gunasekar, V., & Srivastava, S. N. (2009). Kinetics of methylene blue removal from aqueous solution using gulmohar (Delonix regia) plant leaf powder: multivariate regression analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 169(1–3), 119–127.
Postai, D. L., Demarchi, C. A., Zanatta, F., Melo, D. C. C., & Rodrigues, C. A. (2016). Adsorption of rhodamine B and methylene blue dyes using waste of seeds of Aleurites moluccana, a low cost adsorbent. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 55(2), 1713–1723.
Prahas, D., Kartika, Y., Indraswati, N., & Ismadji, S. (2008). Activated carbon from jackfruit peel waste by H3PO4 chemical activation: pore structure and surface chemistry characterization. Chemical Engineering Journal, 140(1–3), 32–42.
Rafatullah, M., Sulaiman, O., Hashim, R., & Ahmad, A. (2010). Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177(1–3), 70–80.
Rattanapan, S., Srikram, J., & Kongsune, P. (2017). Adsorption of methyl orange on coffee grounds activated carbon. Energy Procedia, 138, 949–954.
Salimi, F., Tahmasobi, K., Karami, C., & Jahangiri, A. (2017). Preparation of modified nano-SiO2 by bismuth and iron as a novel remover of methylene blue from water solution. Journal of the Mexican Chemical Society. https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v61i3.351.
Song, J., Zou, W., Bian, Y., Su, F., & Han, R. (2011). Adsorption characteristics of methylene blue by peanut husk in batch and column modes. Desalination, 265(1–3), 119–125.
Stevulova, N., Cigasova, J., Estokova, A., Terpakova, E., Geffert, A., Kacik, F., et al. (2014). Properties characterization of chemically modified hemp hurds. Materials, 7(12), 8131–8150.
Tan, I. A. W., Ahmad, A. L., & Hameed, B. H. (2008). Preparation of activated carbon from coconut husk: optimization study on removal of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol using response surface methodology. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 153(1–2), 709–717.
Theydan, S. K., & Ahmed, M. J. (2012). Adsorption of methylene blue onto biomass-based activated carbon by FeCl3 activation: equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 97, 116–122.
Uddin, M. T., Islam, M. A., Mahmud, S., & Rukanuzzaman, M. (2009). Adsorptive removal of methylene blue by tea waste. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164(1), 53–60.
Unugul, T., & Nigiz, F. U. (2020). Synthesis of acid treated carbonized mandarin peel for purification of copper. Water Practice Technology, 15(2), 460–471.
Vadivelan, V., & Vasanth Kumar, K. (2005). Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 286(1), 90–100.
Yang, C. L., & McGarrahan, J. (2005). Electrochemical coagulation for textile effluent decolorization. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 127(1–3), 40–47.
Zhang, W., Li, H., Kan, X., Dong, L., Yan, H., Jiang, Z., et al. (2012). Adsorption of anionic dyes from aqueous solutions using chemically modified straw. Bioresource Technology, 117, 40–47.
Zhao, H., Huang, D., Hao, T. H., Hu, G. H., Ye, G. B., Jiang, T., & Zhang, Q. C. (2017). Synthesis and investigation of well-defined silane terminated and segmented waterborne hybrid polyurethanes. New Journal of Chemistry, 41(17), 9268–9275.
Zhou, Y., Zhang, L., & Cheng, Z. (2015). Removal of organic pollutants from aqueous solution using agricultural wastes: a review. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 212, 739–762.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Unugul, T., Nigiz, F.U. Preparation and Characterization an Active Carbon Adsorbent from Waste Mandarin Peel and Determination of Adsorption Behavior on Removal of Synthetic Dye Solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 538 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04903-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04903-5