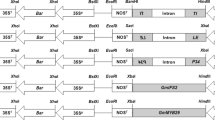
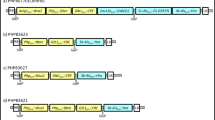
Abstract
Transgenic plants containing low copy transgene insertion free of vector backbone are highly desired for many biotechnological applications. We have investigated two different strategies for increasing the percentage of low copy events in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation experiments in maize. One of the strategies is to use a binary vector with two separate T-DNAs, one T-DNA containing an intact E.coli manA gene encoding phosphomannose isomerase (PMI) as selectable marker gene cassette and another T-DNA containing an RNAi cassette of PMI sequences. By using this strategy, low copy transgenic events containing the transgenes were increased from 43 to 60 % in maize. An alternate strategy is using selectable marker gene cassettes containing regulatory or coding sequences derived from essential plant genes such as 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) or MADS box transcription factor. In this paper we demonstrate that higher percentage of low copy transgenic events can be obtained in Agrobacterium-mediated maize transformation experiments using both strategies. We propose that the above two strategies can be used independently or in combination to increase transgenic events that contain low copy transgene insertion in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation experiments.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Buylla ER, Liljegren SJ, Soraya Pelaz S, Gold SE, Burgeff C, Ditta GS, Vergara-Silva F, Yanofsky MF (2000) MADS-box gene evolution beyond flowers: expression in pollen, endosperm, guard cells, roots and trichomes. Plant J 24:457–466
Barton KA, Binns AN, Matzke AJM, Chilton MD (1983) Regeneration of intact tobacco plants containing full length copies of genetically engineered T-DNA, and transmission of T-DNA to R1 progeny. Cell 32:1033–1043. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(83)90288-X
Becker A, Winter KU, Meyer B, Saedler H, Theissen G (2000) MADS-Box gene diversity in seed plants 300 million years ago. Mol Biol Evol 17:1425–1434
Bustin SA (2000) Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J Mol Endocrinol 25:169–193
Caplan A, Herrera-Estrella L, Inze D, Van Haute E, Van Montagu M, Schell J, Zambryski P (1983) Introduction of genetic material into plant cells. Science 222:815–821. doi:10.1126/science.222.4625.815
Chilton MD, Que Q (2003) Targeted integration of T-DNA into the tobacco genome at double-stranded breaks: new insights on the mechanism of T-DNA integration. Plant Physiol 133:956–965. doi:10.1104/pp.103.026104
Christensen AH, Quail PH (1996) Ubiquitin promoter-based vectors for high-level expression of selectable and/or screenable marker genes in monocotyledonous plants. Transgenic Res 5:213–218
DeFramond AJ, Meghji MR, New SL, Prairie AU (2013) Corn event 5307. US Patent Number 8,466,346
Depicker A, Stachel S, Dhaese P, Zambryski P, Goodman HM (1982) Nopaline synthase: transcript map** and DNA sequence. J Mol Appl Genet 1:561–573
Fraley RT, Rogers SG, Horsch RB, Sanders P, Flick J, Adams S, Bittner M, Brand L, Fink C, Fry J, Galluppi G, Goldberg S, Hoffmann N, Woo S (1983) Expression of bacterial genes in plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:4803–4807
Gelvin SB (2009) Agrobacterium in the genomics age. Plant Physiol 150:1665–1676. doi:10.1104/pp.109.139873
Hanson B, Engler D, Moy Y, Newman B, Ralston E, Gutterson N (1999) A simple method to enrich an Agrobacterium-transformed population for plants containing only T-DNA sequences. Plant J 19:727–734
Ingham DJ, Beer S, Money S, Hansen G (2001) Quantitative real-time PCR assay for determining transgene copy number in transformed plants. Biotechniques 31(132–134):136–140
Ishida Y (1996) High efficiency transformation of maize (Zea mays L.) mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Nat Biotechnol 14:745–750
Jeon JS et al (2000) leafy hull sterile1 is a homeotic mutation in a rice MADS box gene affecting rice flower development. Plant Cell 12:871–884
Jones JG, Gilbert D, Grady K, Jorgensen R (1987) T-DNA structure and gene expression in petunia plants transformed by Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 derivatives. Mol Gen Genet MGG 207:478–485. doi:10.1007/bf00331618
Kim J, Gallo M, Altpeter F (2012) Analysis of transgene integration and expression following biolistic transfer of different quantities of minimal expression cassette into sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrids). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 108:297–302. doi:10.1007/s11240-011-0043-3
Komari T (1990) Transformation of cultured cells of Chenopodium quinoa by binary vectors that carry a fragment of DNA from the virulence region of pTiBo542. Plant Cell Rep 9:303–306. doi:10.1007/BF00232856
Kononov ME, Bassuner B, Gelvin SB (1997) Integration of T-DNA binary vector ‘backbone’ sequences into the tobacco genome: evidence for multiple complex patterns of integration. Plant J 11:945–957
Lebrun M, Sailland A, Freyssinet G, Degryse E (2003) Mutated 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase, gene coding for said protein and transformed plants containing said gene. US Patent Number 6,566,587
Li X, Elumalai S (2014) Methods for generating transgenic plants. US Patent Publication Number 20140366223
Li X, Volrath SL, Nicholl DBG, Chilcott CE, Johnson MA, Ward ER, Law MD (2003) Development of protoporphyrinogen oxidase as an efficient selection marker for Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of maize. Plant Physiol 133:736–747. doi:10.1104/pp.103.026245
Lowe BA, Shiva Prakash N, Way M, Mann MT, Spencer TM, Boddupalli RS (2009) Enhanced single copy integration events in corn via particle bombardment using low quantities of DNA. Transgenic Res 18:831–840. doi:10.1007/s11248-009-9265-0
Mena M, Mandel MA, Lerner DR, Yanofsky MF, Schmidt RJ (1995) A characterization of the MADS-box gene family in maize. Plant J 8:845–854. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1995.8060845.x
Meyer P, Saedler H (1996) Homology-dependent gene silencing in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:23–48. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.47.1.23
Miles JS, Guest JR (1984) Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional start point of the phosphomannose isomerase gene (manA) of Escherichia coli. Gene 32:41–48
Murai N, Kemp JD, Sutton DW, Murray MG, Slightom JL, Merlo DJ, Reichert NA, Sengupta-Gopalan C, Stock CA, Barker RF, Hall TC (1983) Phaseolin gene from bean is expressed after transfer to sunflower via tumor-inducing plasmid vectors. Science 222:476–482. doi:10.1126/science.222.4623.476
Negrotto D, Jolley M, Beer S, Wenck AR, Hansen G (2000) The use of phosphomannose-isomerase as a selectable marker to recover transgenic maize plants (Zea mays L.) via Agrobacterium transformation. Plant Cell Rep 19:798–803
Ng M, Yanofsky MF (2001) Function and evolution of the plant MADS-box gene family. Nat Rev Genet 2:186–195. doi:10.1038/35056041
Nuccio ML, Lagrimini M, Meghji M (2011) MADS gene regulatory sequences for expressing gene products in plant reproductive tissue. USA Patent Number 8,679,844
Oltmanns H, Frame B, Lee LY, Johnson S, Li B, Wang K, Gelvin SB (2010) Generation of backbone-free, low transgene copy plants by launching T-DNA from the Agrobacterium chromosome. Plant Physiol 152:1158–1166. doi:10.1104/pp.109.148585
Pramanik MH, Imai R (2005) Functional identification of a trehalose 6-phosphate phosphatase gene that is involved in transient induction of trehalose biosynthesis during chilling stress in rice. Plant Mol Biol 58:751–762
Riechmann JL, Meyerowitz EM (1997) MADS domain proteins in plant development. Biol Chem 378:1079–1101
Smyth DR (1997) Gene silencing: cosuppression at a distance. Curr Biol 7:R793–R796. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(06)00407-6
Spencer M, Mumm R, Gwyn J (2000) Glyphosate resistant maize lines. USA Patent 6,040,497, 2000
Stavolone L, Kononova M, Pauli S, Ragozzino A, de Haan P, Milligan S, Lawton K, Hohn T (2003) Cestrum yellow leaf curling virus (CmYLCV) promoter: a new strong constitutive promoter for heterologous gene expression in a wide variety of crops. Plant Mol Biol 53:663–673. doi:10.1023/B:PLAN.0000019110.95420.bb
Tijssen P (1985) Practice and theory of enzyme immunoassays. Elsevier Science, USA
Wang X, Wang P, Sun S, Darwiche S, Idnurm A, Heitman J (2012) Transgene induced co-suppression during vegetative growth in Cryptococcus neoformans. PLoS Genet 8:e1002885. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002885
Wenck A, Pugieux C, Turner M, Dunn M, Stacy C, Tiozzo A, Dunder E, van Grinsven E, Khan R, Sigareva M, Wang WC, Reed J, Drayton P, Oliver D, Trafford H, Legris G, Rushton H, Tayab S, Launis K, Chang Y-F, Chen D-F, Melchers L (2003) Reef-coral proteins as visual, non-destructive reporters for plant transformation. Plant Cell Rep 22:244–251. doi:10.1007/s00299-003-0690-x
Ye X, Williams EJ, Shen J, Esser JA, Nichols AM, Petersen MW, Gilbertson LA (2008) Plant development inhibitory genes in binary vector backbone improve quality event efficiency in soybean transformation. Transgenic Res 17:827–838. doi:10.1007/s11248-008-9169-4
Ye X et al (2011) Enhanced production of single copy backbone-free transgenic plants in multiple crop species using binary vectors with a pRi replication origin in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Transgenic Res 20:773–786. doi:10.1007/s11248-010-9458-6
Zhang Z et al (2012) Characterization and expression analysis of six MADS-box genes in maize (Zea mays L.). J Plant Physiol 169:797–806
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Vance Kramer, Jeremy Gould, Michael Schweiner, Eddie Lauer, Wenling Wang, Ryan Carlin and John Clark Jr. for their help in this project. We also thank other Syngenta colleagues for their enthusiasm and support of this work. The authors also would like to thank Drs. Liang Shi and Bruce Vrana for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 1
Nucleotide sequence alignment of MADS-domain transcription factor region in OsMADS1 (constructs 20070, 21099 and 22230), OsMADS2 (construct 22096) and OsMADS16 (construct 22072) compared with maize ZmMADS9 (GenBank accession NM_001177865) and ZmMADS10 (GenBank accession EF552705) (TIFF 123 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivamani, E., Li, X., Nalapalli, S. et al. Strategies to improve low copy transgenic events in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of maize. Transgenic Res 24, 1017–1027 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-015-9902-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-015-9902-8