Abstract
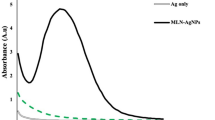
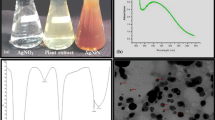
This study investigates the potential of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with Maerua crassifolia leaf extracts to enhance the production of bioactive compounds in Ruta chalepensis callus, alongside evaluating biomass growth, phytochemical content, antioxidant enzymes, and activities. AgNPs were characterized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and UV-visible spectroscopy (UV), then introduced at various concentrations (0, 7.5, 15, 30, and 60 mg/L) into Murashige and Skoog (MS) media supplemented with 10 µM 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) and 1.0 µM 6-benzyladenine (BA). Notably, the incorporation of 30 mg/L of AgNPs into the MS medium resulted in the highest callus fresh weight (FW: 4.13 g) and callus dry weight (DW: 0.298 g) compared to both the control and other AgNPs treatments. Furthermore, this concentration exhibited elevated levels of protein (24.95 mg/ml), phenolic (90.58 mg GAE/g DW), tannin (18.57 mg TAE/g DW), flavonoid (70.97 mg QE/g DW), and flavonol (27.5 mg RE/g DW). Additionally, the enhanced antioxidant enzyme activities, including catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and ascorbate peroxidase (APX) (18.81, 5.08, and 9.48 U/mg protein, respectively) were also observed at the same treatment. The 2,2-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS: 88.03%) assay and the 2,2-diphenylpicrylhydrazyl (DPPH: 85.25%) assay also showed increased activity at 30 mg/L of AgNPs, while the ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay indicated maximum activity (33.82 mg AAE/g DW) at 60 mg/L of AgNPs. Moreover, the application of AgNPs at 30 mg/L resulted in of higher concentrations of quercetin (119.15 µg/g DW), rutin (192.96 µg/g DW), and hesperidin (219.87 µg/g DW). In conclusion, the results indicate that incorporating green AgNPs has a positive influence on the phyto-biochemical profile of R. chalepensis callus cultures, leading to enhanced levels of antioxidants and phytochemicals.
Key message
Biologically synthesized AgNPs from Maerua crassifolia enhance bioactive compound synthesis in R. chalepensis callus, characterized using advanced techniques, positively impacting biomass growth, phytochemical content, antioxidant enzymes, and activities.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuzeid HM, Julien CM, Zhu L, Hashem AM (2023) Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles and their Energy Storage, Environmental, and Biomedical Applications. Crystals 13(11):1576. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13111576
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro methods in Enzymology, vol 105. Academic, pp 121–126
Aghababaei F, Hadidi M (2023) Recent advances in potential health benefits of Quercetin. Pharmaceuticals 16(7):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16071020
Ahamed M, Majeed Khan MA, Siddiqui MKJ, AlSalhi MS, Alrokayan SA (2011) Green synthesis, characterization and evaluation of biocompatibility of silver nanoparticles. Physica E 43(6):1266–1271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2011.02.014
Ajaykumar AP, Mathew A, Chandni AP, Varma SR, Jayaraj KN, Sabira O, Rasheed VA, Binitha VS, Swaminathan TR, Basheer VS, Giri S, Chatterjee S (2023) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the Leaf Extract of the Medicinal Plant, Uvaria Narum and its Antibacterial, Antiangiogenic, Anticancer and Catalytic properties. Antibiotics 12(3):564. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030564
Al-Majmaie S, Nahar L, Rahman MM, Nath S, Saha P, Talukdar AD, Sharples GP, Sarker SD (2021) Anti-MRSA constituents from Ruta chalepensis (Rutaceae) grown in Iraq, and in Silico Studies on two of most active compounds, Chalepensin and 6-Hydroxy-rutin 3’,7-Dimethyl ether. Molecules 26(4):1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26041114
Alfarraj NS, Tarroum M, Al-Qurainy F, Nadeem M, Khan S, Salih AM, Shaikhaldein HO, Al-Hashimi A, Alansi S, Perveen K (2023) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and exploring their potential of reducing the contamination of the in Vitro Culture Media and inducing the Callus Growth of Rumex Nervosus explants. Molecules 28(9):3666
Ali M, Kim B, Belfield D, Norman K, Brennan D M, Ali GS (2016) Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Artemisia absinthium aqueous extract — a comprehensive study. Mater Sci Engineering: C 58:359–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.08.045
Ali A, Mohammad S, Khan MA, Raja NI, Arif M, Kamil A, Mashwani Z-u-R (2019) Silver nanoparticles elicited in vitro callus cultures for accumulation of biomass and secondary metabolites in Caralluma tuberculata. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47(1):715–724. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1577884
Almaraz-Abarca N, da Graça Campos M, Avila-Reyes JA, Naranjo-Jimenez N, Corral JH, Gonzalez-Valdez LS (2007) Antioxidant activity of polyphenolic extract of monofloral honeybee-collected pollen from mesquite (Prosopis juliflora, Leguminosae). J Food Compos Anal 20(2):119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2006.08.001
Anum F, Raja NI, Hussain M, Iqbal M, Chaudhari SK, Ehsan M, Javaid U, Zafar NuA (2019) Effect of green synthesised silver nanoparticles on morphogenic and biochemical variations in callus cultures of kinnow mandarin (Citrus reticulata L). IET Nanobiotechnol 13(5):541–545. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2018.5276
Barajas-Ramírez JA, Cabrera-Ramírez AH, Aguilar-Raymundo VG (2023) Antioxidant activity, total phenolic, tannin, and Flavonoid content of five plants used in Traditional Medicine in Penjamo, Guanajuato. Chem Biodivers 20(1):e202200834. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.202200834
Baumert A, Gröger D, Kuzovkina IN, Reisch J (1992) Secondary metabolites produced by callus cultures of various Ruta species. Planr Cell Tissue Organ Cult 28(2):159–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00055511
Bilal M, Rasheed T, Iqbal HMN, Li C, Hu H, Zhang X (2017) Development of silver nanoparticles loaded chitosan-alginate constructs with biomedical potentialities. Int J Biol Macromol 105:393–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.07.047
Chandran KC, Indira G (2016) Quantitative estimation of total phenolic, flavonoids, tannin and chlorophyll content of leaves of Strobilanthes Kunthiana (Neelakurinji). J Med Plants Stud 4(4):282–286
Chirumamilla P, Vankudoth S, Dharavath SB, Dasari R, Taduri S (2022) In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles and Leaf Methanolic Extract of Solanum khasianum Clarke. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section B: Biological Sciences 92(2):301–307 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-021-01337-9
Choi O, Hu Z (2008) Size dependent and reactive oxygen species related Nanosilver toxicity to nitrifying Bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 42(12):4583–4588. https://doi.org/10.1021/es703238h
Chung I-M, Rajakumar G, Thiruvengadam M (2018) Effect of silver nanoparticles on phenolic compounds production and biological activities in hairy root cultures of Cucumis anguria. Acta Biologica Hungarica Acta Biologica Hungarica 69(1):97–109. https://doi.org/10.1556/018.68.2018.1.8
Dada AO, Ojediran J, Dada F, Olalekan A, Awakan O (2017) Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Calotropis procera extract. J Appl Chem Sci Int 8(4):137–143
Dera MW, Teseme WB (2020) Review on the application of Food Nanotechnology in Food Processing. Am J Eng Technol Manage 5(2):41–47. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajetm.20200502.12
Ediyilyam S, George B, Shankar SS, Dennis TT, Wacławek S, Černík M, Padil VVT (2021) Chitosan/Gelatin/Silver Nanoparticles Composites Films for Biodegradable Food Packaging Applications. Polymers 13(11):1680. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111680
Enogieru AB, Haylett W, Hiss DC, Bardien S, Ekpo OE (2018) Rutin as a potent antioxidant: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2018:6241017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6241017
Fischer H, Römer A, Ulbrich B, Arens H (1988) A new biscoumarin glucoside ester from Ruta chalepensis cell cultures. Planta Med 54(5):398–400. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-962480
Gecer EN (2023) Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Origanum onites leaves: cytotoxic, apoptotic, and necrotic effects on Capan-1, L929, and Caco-2 cell lines. Green Process Synthesis 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2022-8126
Hashem AH, Saied E, Amin BH, Alotibi FO, Al-Askar AA, Arishi AA, Elkady FM, Elbahnasawy MA (2022) Antifungal activity of Biosynthesized Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) against Aspergilli Causing aspergillosis: Ultrastructure Study. J Funct Biomaterials 13(4):242
Hayat K, Ali S, Ullah S, Fu Y, Hussain M (2021) Green synthesized silver and copper nanoparticles induced changes in biomass parameters, secondary metabolites production, and antioxidant activity in callus cultures of Artemisia absinthium L. Green Process Synthesis 10(1):61–72. https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2021-0010
Heinrich M, Ankli A, Frei B, Weimann C, Sticher O (1998) Medicinal plants in Mexico: healers’ consensus and cultural importance. Soc Sci Med 47(11):1859–1871. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-9536(98)00181-6
Hong Y, Lin S, Jiang Y, Ashraf M (2008) Variation in contents of total phenolics and flavonoids and antioxidant activities in the leaves of 11 Eriobotrya Species. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 63(4):200–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-008-0088-6
Iravani S, Korbekandi H, Mirmohammadi SV, Zolfaghari B (2014) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: chemical, physical and biological methods. Res Pharm Sci 9(6):385
Javed R, Yucesan B, Zia M, Gurel E (2018) Elicitation of secondary metabolites in callus cultures of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni grown under ZnO and CuO nanoparticles stress. Sugar Tech 20(2):194–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-017-0539-1
Jogeswar G, Pallela R, Jakka NM, Reddy PS, Venkateswara Rao J, Sreenivasulu N, Kavi Kishor PB (2006) Antioxidative response in different sorghum species under short-term salinity stress. Acta Physiol Plant 28(5):465–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706630
Juárez-Maldonado A (2023) Influence of nanomaterials on non-enzymatic antioxidant defense activities in plants. In: Al-Khayri JM, Alnaddaf LM, Jain SM (eds) Nanomaterial interactions with Plant Cellular mechanisms and macromolecules and Agricultural implications. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 273–298
Jyoti K, Baunthiyal M, Singh A (2016) Characterization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Urtica dioica Linn. Leaves and their synergistic effects with antibiotics. J Radiation Res Appl Sci 9(3):217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.10.002
Kacem M, Kacem I, Simon G, Ben Mansour A, Chaabouni S, Elfeki A, Bouaziz M (2015) Phytochemicals and biological activities of Ruta chalepensis L. growing in Tunisia. Food Bioscience 12:73–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2015.08.001
Kenari ER, Mohsenzadeh F, Amiri ZR (2014) Antioxidant activity and total phenolic compounds of Dezful sesame cake extracts obtained by classical and ultrasound-assisted extraction methods. Food Sci Nutr 2(4):426–435. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.118
Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I (2019) Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab J Chem 12(7):908–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011
Khan A, Ikram M, Hahm JR, Kim MO (2020) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Citrus Flavonoid Hesperetin: Special Focus on Neurological disorders. Antioxidants 9(7):609. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9070609
Krishnaraj C, Jagan EG, Rajasekar S, Selvakumar P, Kalaichelvan PT, Mohan N (2010) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Acalypha indica leaf extracts and its antibacterial activity against water borne pathogens. Colloids Surf B 76(1):50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.10.008
Kusvuran S, Kiran S, Ellialtioglu SS (2016) Antioxidant enzyme activities and abiotic stress tolerance relationship in vegetable crops. Abiotic and biotic stress in plants-recent advances and future perspectives. 481–503. https://doi.org/10.5772/62235
Maqbool M, Ishtiaq M, Mazhar MW, Casini R, Mahmoud EA, Elansary HO (2023) Enhancing Bioactive Metabolite production in Aerva sanguinolenta callus cultures through silver nanoparticle and salicylic acid elicitation. Sustainability 15(13):10395. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310395
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47(3):469–474. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03714.x
Martínez-Pérez EF, Hernández-Terán F, Serrano-Gallardo LB (2017) In vivo effect of Ruta chalepensis extract on hepatic cytochrome 3a1 in rats. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med 14(4):62–68. https://doi.org/10.21010/ajtcam.v14i4.8
Masum MMI, Siddiqa MM, Ali KA, Zhang Y, Abdallah Y, Ibrahim E, Qiu W, Yan C, Li B (2019) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Phyllanthus emblica Fruit Extract and its inhibitory action against the Pathogen Acidovorax oryzae strain RS-2 of Rice Bacterial Brown stripe. Front Microbiol 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00820
Meena M, Zehra A, Swapnil P, Harish, Marwal A, Yadav G, Sonigra P (2021) Endophytic nanotechnology: an Approach to study scope and potential applications. Front Chem 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2021.613343
Mensor LL, Menezes FS, Leitão GG, Reis AS, Santos TCd, Coube CS, Leitão SG (2001) Screening of Brazilian plant extracts for antioxidant activity by the use of DPPH free radical method. Phytother Res 15(2):127–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.687
Moraes LC, Figueiredo RC, Ribeiro-Andrade R, Pontes-Silva AV, Arantes ML, Giani A, Figueredo CC (2021) High diversity of microalgae as a tool for the synthesis of different silver nanoparticles: a species-specific green synthesis. Colloid Interface Sci Commun 42:100420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2021.100420
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15(3):473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22(5):867–880. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a076232
Nazeruddin GM, Prasad NR, Waghmare SR, Garadkar KM, Mulla IS (2014) Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticle using Azadirachta indica leaf extract and its anti-microbial activity. J Alloys Compd 583:272–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.07.111
Oluwaniyi OO, Adegoke HI, Adesuji ET, Alabi AB, Bodede SO, Labulo AH, Oseghale CO (2016) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extract of Thevetia peruviana Juss and its antimicrobial activities. Appl Nanosci 6(6):903–912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-015-0505-8
Osman AI, Zhang Y, Farghali M, Rashwan AK, Eltaweil AS, Abd El-Monaem EM, Mohamed IMA, Badr MM, Ihara I, Rooney DW, Yap P-S (2024) Synthesis of green nanoparticles for energy, biomedical, environmental, agricultural, and food applications: a review. Environ Chem Lett 22(2):841–887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01682-3
Paramo LA, Feregrino-Pérez AA, Guevara R, Mendoza S, Esquivel K (2020) Nanoparticles in Agroindustry: applications, toxicity, challenges, and Trends. Nanomaterials 10(9):1654
Prasad T, Elumalai EK (2011) Biofabrication of Ag nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera leaf extract and their antimicrobial activity. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 1(6):439–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2221-1691(11)60096-8
Qahtan AA, Faisal M, Alatar AA, Abdel-Salam EM (2022) Callus-mediated high-frequency plant regeneration, phytochemical profiling, antioxidant activity and Genetic Stability in Ruta chalepensis L. Plants 11(12):1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11121614
Qahtan AA, Alatar AA, Faisal M (2023) In vitro regeneration, phytochemical profiling and antioxidant activity in Ruta chalepensis plants established from alginate encapsulated synthetic seeds. South Afr J Bot 161:575–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2023.08.065
Qian H, Peng X, Han X, Ren J, Sun L, Fu Z (2013) Comparison of the toxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver ions on the growth of terrestrial plant model Arabidopsis thaliana. J Environ Sci 25(9):1947–1956. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60301-5
Rahmawati M, Mahfud C, Risuleo G, Jadid N (2022) Nanotechnology in Plant Metabolite Improvement and in Animal Welfare. Appl Sci 12(2):838. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020838
Ratheesh M, Sindhu G, Helen A (2013) Anti-inflammatory effect of quinoline alkaloid skimmianine isolated from Ruta graveolens L. Inflamm Res 62(4):367–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-013-0588-1
Rathod S, Preetam S, Pandey C, Bera SP (2024) Exploring synthesis and applications of green nanoparticles and the role of nanotechnology in wastewater treatment. Biotechnol Rep 41:e00830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2024.e00830
Rauwel P, Küünal S, Ferdov S, Rauwel E (2015) A review on the Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and their morphologies studied via TEM. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2015(682749). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/682749
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala A, Yang M, Rice-Evans C (1999) Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol Med 26(9):1231–1237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00315-3
Rivero-Montejo SdJ, Vargas-Hernandez M, Torres-Pacheco I (2021) Nanoparticles as Novel Elicitors to Improve Bioactive compounds in plants. Agriculture 11(2):134
Salih AM, Al-Qurainy F, Khan S, Nadeem M, Tarroum M, Shaikhaldein HO (2022) Biogenic silver nanoparticles improve bioactive compounds in medicinal plant Juniperus procera in vitro. Front Plant Sci 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.962112
Santos Junior CM, Silva SMC, Sales EM, Velozo ES, dos Santos EKP, Canuto GAB, Azeredo FJ, Barros TF, Biegelmeyer R (2023) Coumarins from Rutaceae: Chemical diversity and biological activities. Fitoterapia 168:105489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2023.105489
Selvakesavan RK, Kruszka D, Shakya P, Mondal D, Franklin G (2023) Impact of nanomaterials on plant secondary metabolism. In: Al-Khayri JM, Alnaddaf LM, Jain SM (eds) Nanomaterial interactions with Plant Cellular mechanisms and macromolecules and Agricultural implications. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 133–170
Shah MZ, Guan Z-H, Din AU, Ali A, Rehman AU, Jan K, Faisal S, Saud S, Adnan M, Wahid F, Alamri S, Siddiqui MH, Ali S, Nasim W, Hammad HM, Fahad S (2021) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Plantago lanceolata extract and assessing their antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Sci Rep 11(1):20754. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-00296-5
Shaikhaldein HO, Al-Qurainy F, Nadeem M, Khan S, Tarroum M, Salih AM (2020) Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Ochradenus arabicus and their physiological effect on Maerua Oblongifolia raised in vitro. Sci Rep 10(1):17569. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-74675-9
Singh Y, Kumar U, Panigrahi S, Balyan P, Mehla S, Sihag P, Sagwal V, Singh KP, White JC, Dhankher OP (2023) Nanoparticles as novel elicitors in plant tissue culture applications: current status and future outlook. Plant Physiol Biochem 203:108004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.108004
Sreelatha S, Padma PR (2009) Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of Moringa oleifera leaves in two stages of Maturity. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 64(4):303–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-009-0141-0
Sreelekshmi R, Siril EA, Muthukrishnan S (2022) Role of Biogenic Silver nanoparticles on Hyperhydricity Reversion in Dianthus chinensis L. an in Vitro Model Culture. J Plant Growth Regul 41(1):23–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10276-0
Szewczyk A, Marino A, Molinari J, Ekiert H, Miceli N (2022) Phytochemical Characterization, and Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Agitated Cultures of Three Rue Species: Ruta chalepensis, Ruta corsica, and Ruta graveolens Antioxidants. vol 11
Szewczyk A, Grabowski M, Zych D (2023) Ruta chalepensis L. In Vitro cultures as a source of Bioactive Furanocoumarins and Furoquinoline alkaloids. Life 13(2):457
Thirunavoukkarasu M, Balaji U, Behera S, Panda PK, Mishra BK (2013) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticle from leaf extract of Desmodium gangeticum (L.) DC. And its biomedical potential. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 116:424–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.07.033
Thuesombat P, Hannongbua S, Akasit S, Chadchawan S (2014) Effect of silver nanoparticles on rice (Oryza sativa L. Cv. KDML 105) seed germination and seedling growth. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 104:302–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.03.022
Velioglu YS, Mazza G, Gao L, Oomah BD (1998) Antioxidant activity and total phenolics in selected fruits, vegetables, and Grain products. J Agric Food Chem 46(10):4113–4117. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9801973
Wang Z, Ding Z, Li Z, Ding Y, Jiang F, Liu J (2021) Antioxidant and antibacterial study of 10 flavonoids revealed rutin as a potential antibiofilm agent in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from hospitalized patients. Microb Pathog 159:105121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105121
Zaeem A, Drouet S, Anjum S, Khurshid R, Younas M, Blondeau JP, Tungmunnithum D, Giglioli-Guivarc’h N, Hano C, Abbasi BH (2020) Effects of Biogenic Zinc Oxide nanoparticles on Growth and oxidative stress response in Flax seedlings vs. Vitro Cultures: Comp Anal Biomolecules 10(6):918
Funding
The authors are thankful to the Researchers Supporting Project (RSP-2024R86), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ALL authors contributed to this study. AAA, AQ and MF: Conceptualization, investigation, methodology. AQ and MF: Data collection, analysis and first draft of the manuscript. AAA, AQ and MF: Reviewed the data analysis, interpretation and finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Research work reported in the MS complies all ethical responsibilities.
Conflict of interest
the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. MF is one of the Associate Editor of the journal at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Additional information
Communicated by Jericó Jabín Bello-Bello.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alatar, A.A., Qahtan, A.A. & Faisal, M. Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles: unraveling their influence on callus proliferation, secondary metabolite production, and antioxidant activities in Ruta chalepensis L.. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 157, 55 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-024-02778-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-024-02778-6