Abstract
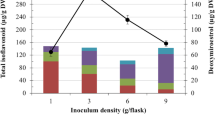
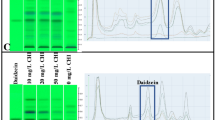
Plant tissue culture is controllable and sustainable production system of functional ingredients. Pueraria candollei is used as an herbal medicine to alleviate postmenopausal symptoms. However, conventional sources are limited by prolonged cultivation periods and inconsistent quality. Cell suspension culture of P. candollei was aimed at enhancing and controlling the production of isoflavonoids and deoxymiroestrol. This was achieved by employing 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPBCD) and cellulase as elicitors. The effect of elicitation on estrogenic and anti-inflammatory properties of P. candollei cell extracts was assessed. HPBCD elicitation increases three times the total isoflavonoid accumulation, while cellulase elicitation resulted in 2.5-fold increase in deoxymiroestrol production compared with controls, observed at day 20. Furthermore, HPBCD results in the release of isoflavonoids particularly daidzein (61.30 ± 0.26 µg/mL) into the medium. In both the elicitation groups, the upregulation of genes associated with isoflavonoid and deoxymiroestrol biosynthetic pathways was observed. Specifically, CHS gene transcription was induced within six days. On days 12 and 20, IFS and HID, which convert chalcones to isoflavonoids, were significantly upregulated. Additionally, the upregulation of CYP81E, IFR, and PT-1, which are involved in chromene production, was observed on day 3. HPBCD treatment exhibited a more potent effect on the expression of all the examined genes than cellulase. HPBCD treated extract led to increased estrogenic and anti-inflammatory activities, as evidenced by modulation of gene expression related to these pathways. In summary, HPBCD and elicitation techniques can be strategically employed to improve both quality and productivity of P. candollei cells as a source of functional ingredients.
Key Message
Cellulase increases deoxymiroestrol production in Pueraria candollei cells and 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin has affected cells to release isoflavonoids into the media. Both elicitors enhance the pharmacological activities of P. candollei cells extracts.
AbstractSection Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The supporting documentation showing the findings of this study is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Boonsnongcheep P, Korsangruang S, Soonthornchareonnon N et al (2010) Growth and isoflavonoid accumulation of Pueraria candollei var. candollei and P. candollei var. mirifica cell suspension cultures. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 101:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9668-x
Borghetti GS, Pinto AP, Lula IS et al (2011) Daidzein/cyclodextrin/hydrophilic polymer ternary systems. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 37(8):886–893. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639045.2010.548066
Brooke GN, Bevan CL (2009) The role of androgen receptor mutations in prostate cancer progression. Curr Genom 10(1):18–25. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920209787581307
Buraphaka H, Putalun W (2020) Stimulation of health-promoting triterpenoids accumulation in Centella asiatica (L.) Urban leaves triggered by postharvest application of methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid elicitors. Ind Crop Prod 146:112171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112171
Chan KK, Siu MK, Jiang YX et al (2018) Estrogen receptor modulators genistein, daidzein and ERB-041 inhibit cell migration, invasion, proliferation and sphere formation via modulation of FAK and PI3K/AKT signaling in ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell Int 18:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-018-0559-2
Chansakaow S, Ishikawa T, Seki H et al (2000) Identification of deoxymiroestrol as the actual rejuvenating principle of “Kwao Keur”, Pueraria mirifica. The known miroestrol may be an artifact. J Nat Prod 63(2):173–175. https://doi.org/10.1021/np990547v
Cherdshewasart W, Sriwatcharakul S (2007) Major isoflavonoid contents of the 1-year-cultivated phytoestrogen-rich herb Pueraria Mirifica. Biosci Biotech Bioch 71(10):2527–2533. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.70316
Cherdshewasart W, Subtang S, Dahlan W (2007) Major isoflavonoid contents of the phytoestrogen rich-herb Pueraria mirifica in comparison with Pueraria lobata. J Pharmaceut Biomed 43(2):428–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2006.07.013
Choonong R, Krittanai S, Butdapheng K et al (2023) Impact of elicitors and precursor on quassinoids and canthin-6-ones production in adventitious root culture of Eurycoma harmandiana Pierre and improvement of their anti-inflammatory activity. Ind Crop Prod 206:117652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.117652
Islek C, Ustun AS, Koc ESRA (2014) The effects of cellulase on capsaicin production in freely suspended cells and immobilized cell cultures of Capsicum annuum L. Pak J Bot 46(5):1883–1887
Jain S, Rathod M, Mishra G et al (2023) Plant tissue culture for medical therapy: unlocking the potential of medicinal plants. Curr J App Sci Technol 42(46):7–22. https://doi.org/10.9734/cjast/2023/v42i464289
Ji G, Zhang Y, Yang Q et al (2012) Genistein suppresses LPS-induced inflammatory response through inhibiting NF-κB following AMP kinase activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. PLoS ONE 7(12):e53101. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053101
** SE, Son YK, Min BS et al (2012) Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of constituents isolated from Pueraria lobata roots. Arch Pharm Res 35:823–837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-0508-x
Juengsanguanpornsuk W, Yusakul G, Kraithong W et al (2021) Simple preparation and analysis of a phytoestrogen-rich extract of Pueraria candollei var. mirifica and its in vitro estrogenic activity. J Herb Med 29:100463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hermed.2021.100463
Komaikul J, Kitisripanya T, Likhitwitayawuid, et al (2019) Improvement of stilbenoid production by 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin in white mulberry (Morus alba L.) callus cultures. Nat Prod Res 33(19):2762–2769. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1499643
Korsangruang S, Soonthornchareonnon N, Chintapakorn Y et al (2010) Effects of abiotic and biotic elicitors on growth and isoflavonoid accumulation in Pueraria candollei var. candollei and P. candollei var. mirifica cell suspension cultures. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 103:333–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9785-6
Kraithong W, Juengsanguanpornsuk W, Krittanai S et al (2021) Phytoestrogen constituents and estrogenic activity of Pueraria candollei var. mirifica callus and its extract preparation for removing cytotoxic constituents. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 43(3):703–710
Kumar V, Chauhan SS (2021) Daidzein induces intrinsic pathway of apoptosis along with ER α/β ratio alteration and ROS production. Asian Pac J Cancer Prevent 22(2):603. https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.2.603
Leach DA, Mohr A, Giotis ES et al (2021) The antiandrogen enzalutamide downregulates TMPRSS2 and reduces cellular entry of SARS-CoV-2 in human lung cells. Nat Commun 12(1):4068. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24342-y
Li S, Yuan L, Chen Y et al (2017) Studies on the inclusion complexes of daidzein with β-cyclodextrin and derivatives. Molecules 22(12):2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122183
Makkliang F, Siriwarin B, Yusakul G et al (2021) Biocompatible natural deep eutectic solvent-based extraction and cellulolytic enzyme-mediated transformation of Pueraria mirifica isoflavones: a sustainable approach for increasing health-bioactive constituents. Bioresour Bioprocess 8(76):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-021-00428-9
Pons DG, Nadal-Serrano M, Torrens-Mas M et al (2016) The phytoestrogen genistein affects breast cancer cells treatment depending on the ERα/ERβ ratio. J Cell Biochem 117(1):218–229. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.25268
Prodea A, Mioc A, Banciu C et al (2022) The role of cyclodextrins in the design and development of triterpene-based therapeutic agents. Int J Mol Sci 23(2):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020736
Rani D, Meelaph T, Kobtrakul K et al (2018) Optimizing Pueraria candollei var. mirifica cell suspension culture for prolonged maintenance and decreased variation of isoflavonoid from single cell lines. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 134:433–443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-1433-6
Rani D, Buranasudja V, Kobtrakul K et al (2021a) Elicitation of Pueraria candollei var. mirifica suspension cells promises antioxidant potential, implying antiaging activity. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 145:29–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01990-4
Rani D, Kobtrakul K, Luckanagul JA et al (2021b) Differential gene expression levels, chemical profiles, and biological activities of Pueraria candollei var mirifica callus cultures at different growth stages. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 147(1):61–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02105-3
Rani D, Kobtrakul K, De-Eknamkul W et al (2022) Magnetized water: A way to enhance isoflavonoids in cultured Pueraria candollei var. mirifica cells. Ind Crop Prod 180:114779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114779
Sae-Foo W, Krittanai S, Juengsanguanpornsuk W et al (2021) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using fragment antigen-binding (Fab) antibody for determination of deoxymiroestrol, a potent phytoestrogen from Pueraria candollei. Food Agric Immunol 32(1):336–348. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540105.2021.1946486
Sae-Foo W, Yusakul G, Kitisripanya T et al (2023b) Comparative stability and analytical performance of anti-miroestrol recombinant antibody in different cassettes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107(9):2887–2896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12492-6
Sae-Foo W, Yusakul G, Nualkaew N, Putalun W (2024) Identification of major bioactive anti-inflammatory compounds of Derris scandens stem using RAW 264.7 cells and HPLC-UV analysis. Planta Med 90(2):126–137. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-2192-2281
Sae-Foo W, Singkham S, Srisongkhram P et al (2023a) Development and characterisation of highly specific monoclonal antibody-based immunoassays for the detection and quantification of genistein-7-O-[α-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→ 6)]-β-glucopyranoside in Derris scandens (Roxb.) Benth. Phytochem Analysis https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.3305
Shaw LJ, Morris P, Hooker JE (2006) Perception and modification of plant flavonoid signals by rhizosphere microorganisms. Environ Microbiol 8(11):1867–1880. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01141.x
Srivastava M, Singh G, Sharma S et al (2019) Elicitation enhanced the yield of glycyrrhizin and antioxidant activities in hairy root cultures of Glycyrrhiza glabra L. J Plant Growth Regul 38:373–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-018-9847-2
Suntichaikamolkul N, Tantisuwanichkul K, Prombutara P et al (2019) Transcriptome analysis of Pueraria candollei var. mirifica for gene discovery in the biosyntheses of isoflavones and miroestrol. BMC Plant Biol 19:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-2205-0
Udomsin O, Yusakul G, Kitisripanya T et al (2020) The deoxymiroestrol and isoflavonoid production and their elicitation of cell suspension cultures of Pueraria candollei var. mirifica: from shake flask to bioreactor. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 190:57–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03094-y
Udomsuk L, Juengwattanatrakul T, Jarukamjorn K et al (2012) Increased miroestrol, deoxymiroestrol and isoflavonoid accumulation in callus and cell suspension cultures of Pueraria candollei var. mirifica. Acta Physiol Plant 34:1093–1100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-011-0906-6
Wijerathna-Yapa A, Hiti-Bandaralage J (2023) Tissue culture—a sustainable approach to explore plant stresses. Life 13(3):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030780
**e Z, Tian Z, Liu S et al (2022) Effects of different amounts of cellulase on the microstructure and soluble substances of cotton stalk bark. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(2):1294–1306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00400-3
Yusakul G, Putalun W, Udomsin O et al (2011) Comparative analysis of the chemical constituents of two varieties of Pueraria candollei. Fitoterapia 82(2):203–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2010.09.009
Yusakul G, Juengsanguanpornsuk W, Sritularak B et al (2021) (+)-7-O-Methylisomiroestrol, a new chromene phytoestrogen from the Pueraria candollei var. mirifica root. Nat Prod Res 35(21):4110–4114. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2020.1727473
Zhu C, **ong Z, Chen X et al (2012) Artemisinin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated proinflammatory responses by inhibiting NF-κB pathway in microglia cells. PLoS ONE 7(4):e35125. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035125
Acknowledgements
This research project is funded by National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT):
(Contract No. N41A650080) and Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Khon Kaen University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. WSF carried out the plant, HPLC, ELISA, cells culture experiments and statistical analysis. WSF wrote original draft and visualization. GY and WP reviewed and edited the manuscript. Supervision and critical revision were done by WP. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Ali R. Alan
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sae-Foo, W., Yusakul, G. & Putalun, W. Enhancement of isoflavonoid production and release in Pueraria candollei cell suspension culture using elicitors for improving pharmacological activities. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 156, 99 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-024-02725-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-024-02725-5