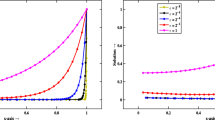
Abstract
In this paper, we present a fully discrete finite difference scheme with efficient convolution of artificial boundary conditions for solving the Cauchy problem associated with the one-dimensional linearized Benjamin-Bona-Mahony equation. The scheme utilizes the Padé expansion of the square root function in the complex plane to implement the fast convolution, resulting in significant reduction of computational costs involved in the time convolution process. Moreover, the introduction of a constant dam** term in the governing equations allows for convergence analysis under specific conditions. The theoretical analysis is complemented by numerical examples that illustrate the performance of the proposed numerical method.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of supporting data
Not Applicable.
References
Achouri, T., Khiari, N., Omrani, K.: On the convergence of difference schemes for the Benjamin Bona Mahony BBM equation. Appl. Math. Comput. 182, 999–1005 (2006)
Alazman, A., Albert, J., Bona, J., Chen, M., Wu, J.: Comparisons between the BBM equation and a Boussinesq system. Adv. Differ. Equ. 11, 121–166 (2006)
Besse, C., Gireau, B., Noble, P.: Artificial boundary conditions for the linearized Benjamin-Bona-Mahony equation. Num. Math. 139, 281–314 (2018)
Kazakova, M., Noble, P.: Discrete transparent boundary conditions for the linearized Green-Naghdi system of equations. SIAM. J. Num. Anal. 58(1), 657–683 (2020)
Zheng, C., Du, Q., Ma, X., Zhang, J.: Stability and error analysis for a second-order fast approximation of the local and nonlocal diffusion equations on the real Line. SIAM. J. Num. Anal. 58, 1893–1917 (2020)
Fevens, T., Jiang, H.: Absorbing boundary conditions for the Schrödinger equation. SIAM. J. Sci. Comput. 21, 255–282 (1999)
Antoine, X., Besse, C., Klein, P.: Absorbing boundary conditions for the one-dimensional Schrödinger equation with an exterior repulsive potential. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 312–335 (2009)
Antoine, X., Besse, C.: Unconditionally stable discretization schemes of non-reflecting boundary conditions for the one-dimensional Schrödinger equation. J. Comput. Phys. 188, 157–175 (2003)
Wu, X., Sun, Z.: Convergence of difference scheme for heat equation in unbounded domains using artificial boundary conditions. Appl. Nume. Math. 50, 261–277 (2004)
Baskakov, V., Popov, A.: Implementation of transparent boundaries for numerical solution of the Schrödinger equation. Wave Motion. 14, 123–128 (1991)
Han, H., Huang, Z.: Exact and approximating boundary conditions for the parabolic problems on unbounded domains. Comput. Mathe. Appl. 44, 655–666 (2002)
Han, H., Huang, Z.: Exact artificial boundary conditions for the Schrödinger equation in \(R^2\). Commun. Math. Sci. 2, 79–94 (2004)
Arnold, A., Ehrhardt, M., Schulte, M., Sofronov, I.: Discrete transparent boundary conditions for the Schrödinger equation on circular domains. Commun. Math. Sci. 10(3), 889–916 (2012)
Li, H., Wu, X., Zhang, J.: Local artificial boundary conditions for Schrödinger and heat equations by using high-order azimuth derivatives on circular artificial boundary. Comput. Phys. Commun. 185, 1606–1615 (2014)
Antoine, X., Besse, C., Mouysset, V.: Numerical schemes for the simulation of the two-dimensional Schrödinger equation using non-reflecting boundary conditions. Math Comput. 73, 1779–1799 (2004)
Antoine, X., Besse, C., Klein, P.: Absorbing boundary conditions for the two-dimensional Schrödinger equation with an exterior potential. Part II: Discretization and Numerical Results. Num. Math. 125, 191–223 (2013)
Antoine, X., Besse, C., Klein, P.: Absorbing boundary conditions for general nonlinear Schrödinger Equations. SIAM. J. Sci. Comput. 33, 1008–1033 (2011)
Pang, G., Yang, Y., Antoine, X., Tang, S.: Stability and convergence analysis of artificial boundary conditions for the Schrödinger equation on a rectangular domain, Preprint
Antoine, X., Arnold, A., Besse, C., Ehrhardt, M., Schaedle, A.: A review of transparent and artificial boundary conditions techniques for linear and nonlinear Schrödinger equations. Commun. Comput. Phys. 4, 729–796 (2008)
Pang, G., Tang, S.: Approximate linear relations for Bessel functions. Commun. Math. Sci. 15, 1967–1986 (2017)
Pang, G., Bian, L., Tang, S.: ALmost EXact boundary condition for one-dimensional Schrödinger equation. Phys. Rev. E. 86, 066709 (2012)
Ji, S., Yang, Y., Pang, G., Antoine, X.: Accurate artificial boundary conditions for the semi-discretized linear Schrödinger and heat equations on rectangular domains. Comput. Phys. Commun. 222, 84–93 (2018)
Arnold, A., Ehrhardt, M., Sofronov, I.: Discrete transparent boundary conditions for the Schrödinger equation: fast calculation, approximation, and stability. Commun. Math. Sci. 1, 501–556 (2003)
Jiang, S., Greengard, L.: Fast evaluation of nonreflecting boundary conditions for the Schrödinger equation in one dimension. Comput. Math. Appl. 47, 955–966 (2004)
Zheng, C.: Approximation, stability and fast evaluation of exact artificial boundary condition for one-dimensional heat equation. J. Comput. Math. 25, 730–745 (2007)
Alpert, B., Greengard, L., Hagstrom, T.: Rapid evaluation of nonreflecting boundary kernels for time-domain wave propagation. SIAM. J. Num. Anal. 37, 1138–1164 (2000)
Lu, Y.: A Padé approximation method for square roots of symmetric positive definite matrices. SIAM. J. Num. Anal. 19, 833–845 (1998)
Lubich, C., Schädle, A.: Fast convolution for nonreflecting boundary conditions. SIAM. J. Sci. Compt. 24, 161–182 (2002)
Feng, Y., Wang, X.: Matching boundary conditions for Euler-Bernoulli beam. Shock. Vib. 6685852 (2021)
Tang, S., Karpov, E.: Artificial boundary conditions for Euler-Bernoulli beam equation. Acta. Mech. Sinica-PRC. 30, 687–692 (2014)
Li, B., Zhang, J., Zheng, C.: An efficient second-order finite difference method for the one-dimensional Schrödinger equation with absorbing boundary conditions. SIAM. J. Num. Anal. 56, 766–791 (2018)
Zhao, X.: Optimal convergence of a second order low-regularity integrator for the KdV equation. IMA J. Num. Anal. to appear
Wang, X., Tang, S.: Matching boundary conditions for diatomic chains. Comput. Mech. 46(6), 813–826 (2010)
Acknowledgements
Not Applicable.
Funding
Dr Zheng is supported by the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. KJQN202301130) and Dr Liu is supported by NSFC under grant Nos. 12102282.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zheng and Liu did the computation, Pang did the numerical analysis. Pang and Ehrhardt wrote the main manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Z., Pang, G., Ehrhardt, M. et al. A fast second-order absorbing boundary condition for the linearized Benjamin-Bona-Mahony equation. Numer Algor (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-024-01864-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-024-01864-2
Keywords
- Benjamin-Bona-Mahony equation
- Artificial boundary condition
- Fast convolution quadrature
- Padé approximation
- Convergence analysis