Abstract
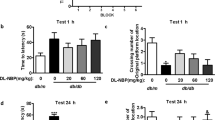
Studies have shown that diabetes is associated with the occurrence of neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive decline. However, there is currently no effective treatment for diabetes-induced cognitive dysfunction. The superior efficacy of liraglutide (LIRA) for cognitive impairment and numerous neurodegenerative diseases has been widely demonstrated. This study determined the effects of LIRA on diabetic cognitive impairment and on the levels of oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, iron metabolism and ferroptosis in the hippocampus. Mice were injected daily with liraglutide (200 μg/kg/d) for 5 weeks. LIRA could repair damaged neurons and synapses, and it increased the protein expression levels of PSD 95, SYN, and BDNF. Furthermore, LIRA significantly decreased oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation levels by downregulating the production of ROS and MDA and upregulating SOD and GSH-Px in the serum and hippocampus, and the upregulation of SOD2 expression was also proven. The decreased levels of TfR1 and the upregulation of FPN1 and FTH proteins observed in the LIRA-treated db/db group were shown to reduce iron overload in the hippocampus, whereas the increased expression of Mtft and decreased expression of Mfrn in the mitochondria indicated that mitochondrial iron overload was ameliorated. Finally, LIRA was shown to prevent ferroptosis in the hippocampus by elevating the expression of GPX4 and SLC7A11 and suppressing the excessive amount of ACSL4; simultaneously, the damage to the mitochondria observed by TEM was also repaired. For the first time, we proved in the T2DM model that ferroptosis occurs in the hippocampus, which may play a role in diabetic cognitive impairment. LIRA can reduce oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation and iron overload in diabetic cognitive disorders and further inhibit ferroptosis, thereby weakening the damage to hippocampal neurons and synaptic plasticity and ultimately restoring cognitive function.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khan MN, Khan FA, Sultana S, Dilawar M, Ijaz A, Khan MJ, Mahmood T (2007) Impact of new diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 17:327–330
Anderson RJ, Freedland KE, Clouse RE, Lustman PJ (2001) The prevalence of comorbid depression in adults with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 24:1069–1078. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.24.6.1069
Biessels GJ, Strachan MW, Visseren FL, Kappelle LJ, Whitmer RA (2014) Dementia and cognitive decline in type 2 diabetes and prediabetic stages: towards targeted interventions. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2:246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(13)70088-3
Stoeckel LE, Arvanitakis Z, Gandy S, Small D, Kahn CR, Pascual-Leone A, Pawlyk A, Sherwin R, Smith P (2016) Complex mechanisms linking neurocognitive dysfunction to insulin resistance and other metabolic dysfunction. F1000Res 5:353. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.8300.2
Gaspar JM, Baptista FI, Macedo MP, Ambrosio AF (2016) Inside the diabetic brain: role of different players involved in cognitive decline. ACS Chem Neurosci 7:131–142. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00240
Chatterjee S, Peters SA, Woodward M, Mejia Arango S, Batty GD, Beckett N, Beiser A, Borenstein AR, Crane PK, Haan M, Hassing LB, Hayden KM, Kiyohara Y, Larson EB, Li CY, Ninomiya T, Ohara T, Peters R, Russ TC, Seshadri S, Strand BH, Walker R, Xu W, Huxley RR (2016) Type 2 diabetes as a risk factor for dementia in women compared with men: a pooled analysis of 2.3 million people comprising more than 100,000 cases of dementia. Diabetes Care 39:300–307. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc15-1588
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS, Morrison B 3rd, Stockwell BR (2012) Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149:1060–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Sui X, Zhang R, Liu S, Duan T, Zhai L, Zhang M, Han X, **ang Y, Huang X, Lin H, **e T (2018) RSL3 drives ferroptosis through GPX4 inactivation and ROS production in colorectal cancer. Front Pharmacol 9:1371. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01371
Sumneang N, Siri-Angkul N, Kumfu S, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N (2020) The effects of iron overload on mitochondrial function, mitochondrial dynamics, and ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 680:108241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2019.108241
Lei P, Bai T, Sun Y (2019) Mechanisms of ferroptosis and relations with regulated cell death: a review. Front Physiol 10:139. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00139
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascon S, Hatzios SK, Kagan VE, Noel K, Jiang X, Linkermann A, Murphy ME, Overholtzer M, Oyagi A, Pagnussat GC, Park J, Ran Q, Rosenfeld CS, Salnikow K, Tang D, Torti FM, Torti SV, Toyokuni S, Woerpel KA, Zhang DD (2017) Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell 171:273–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.021
Abdul Y, Li W, Ward R, Abdelsaid M, Hafez S, Dong G, Jamil S, Wolf V, Johnson MH, Fagan SC, Ergul A (2021) Deferoxamine treatment prevents post-stroke vasoregression and neurovascular unit remodeling leading to improved functional outcomes in type 2 male diabetic rats: role of endothelial ferroptosis. Transl Stroke Res 12:615–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-020-00844-7
Koekkoek PS, Kappelle LJ, van den Berg E, Rutten GE, Biessels GJ (2015) Cognitive function in patients with diabetes mellitus: guidance for daily care. Lancet Neurol 14:329–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70249-2
Gold SM, Dziobek I, Sweat V, Tirsi A, Rogers K, Bruehl H, Tsui W, Richardson S, Javier E, Convit A (2007) Hippocampal damage and memory impairments as possible early brain complications of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 50:711–719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-007-0602-7
Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR (2012) Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach. Position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 55:1577–1596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-012-2534-0
Buse JB, Rosenstock J, Sesti G, Schmidt WE, Montanya E, Brett JH, Zychma M, Blonde L, Group L-S (2009) Liraglutide once a day versus exenatide twice a day for type 2 diabetes: a 26-week randomised, parallel-group, multinational, open-label trial (LEAD-6). Lancet 374:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60659-0
Holscher C (2012) Potential role of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in neuroprotection. CNS Drugs 26:871–882. https://doi.org/10.2165/11635890-000000000-00000
Hansen HH, Fabricius K, Barkholt P, Niehoff ML, Morley JE, Jelsing J, Pyke C, Knudsen LB, Farr SA, Vrang N (2015) The GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide improves memory function and increases hippocampal CA1 neuronal numbers in a senescence-accelerated mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 46:877–888. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-143090
Yuan P, Ma D, Gao X, Wang J, Li R, Liu Z, Wang T, Wang S, Liu J, Liu X (2020) Liraglutide ameliorates erectile dysfunction via regulating oxidative stress, the RhoA/ROCK pathway and autophagy in diabetes mellitus. Front Pharmacol 11:1257. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.01257
Hayden MR (2019) Type 2 diabetes mellitus increases the risk of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease: ultrastructural remodeling of the neurovascular unit and diabetic gliopathy. Brain Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9100262
An JR, Zhao YS, Luo LF, Guan P, Tan M, Ji ES (2020) Huperzine A, reduces brain iron overload and alleviates cognitive deficit in mice exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia. Life Sci 250:117573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117573
Yang Q, Zhou L, Liu C, Liu D, Zhang Y, Li C, Shang Y, Wei X, Li C, Wang J (2018) Brain iron deposition in type 2 diabetes mellitus with and without mild cognitive impairment-an in vivo susceptibility map** study. Brain Imaging Behav 12:1479–1487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9815-7
Maiorino M, Conrad M, Ursini F (2018) GPx4, lipid peroxidation, and cell death: discoveries, rediscoveries, and open issues. Antioxid Redox Signal 29:61–74. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2017.7115
Femminella GD, Frangou E, Love SB, Busza G, Holmes C, Ritchie C, Lawrence R, McFarlane B, Tadros G, Ridha BH, Bannister C, Walker Z, Archer H, Coulthard E, Underwood BR, Prasanna A, Koranteng P, Karim S, Junaid K, McGuinness B, Nilforooshan R, Macharouthu A, Donaldson A, Thacker S, Russell G, Malik N, Mate V, Knight L, Kshemendran S, Harrison J, Holscher C, Brooks DJ, Passmore AP, Ballard C, Edison P (2019) Evaluating the effects of the novel GLP-1 analogue liraglutide in Alzheimer’s disease: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial (ELAD study). Trials 20:191. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-019-3259-x
He W, Wang H, Zhao C, Tian X, Li L, Wang H (2020) Role of liraglutide in brain repair promotion through Sirt1-mediated mitochondrial improvement in stroke. J Cell Physiol 235:2986–3001. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29204
Tu XK, Chen Q, Chen S, Huang B, Ren BG, Shi SS (2021) GLP-1R agonist liraglutide attenuates inflammatory reaction and neuronal apoptosis and reduces early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Inflammation 44:397–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01344-4
Briand F, Brousseau E, Maupoint J, Dubroca C, Costard C, Breyner N, Burcelin R, Sulpice T (2020) Liraglutide shows superior cardiometabolic benefits than lorcaserin in a novel free choice diet-induced obese rat model. Eur J Pharmacol 882:173316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173316
Feng WH, Bi Y, Li P, Yin TT, Gao CX, Shen SM, Gao LJ, Yang DH, Zhu DL (2019) Effects of liraglutide, metformin and gliclazide on body composition in patients with both type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized trial. J Diabetes Investig 10:399–407. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.12888
Wang H, Chen F, Du YF, Long Y, Reed MN, Hu M, Suppiramaniam V, Hong H, Tang SS (2018) Targeted inhibition of RAGE reduces amyloid-beta influx across the blood-brain barrier and improves cognitive deficits in db/db mice. Neuropharmacology 131:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.12.026
Ye T, Meng X, Wang R, Zhang C, He S, Sun G, Sun X (2018) Gastrodin alleviates cognitive dysfunction and depressive-like behaviors by inhibiting ER Stress and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in db/db mice. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123977
Bliss TV, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1038/361031a0
Muller D, Nikonenko I, Jourdain P, Alberi S (2002) LTP, memory and structural plasticity. Curr Mol Med 2:605–611. https://doi.org/10.2174/1566524023362041
McMahon HT, Bolshakov VY, Janz R, Hammer RE, Siegelbaum SA, Sudhof TC (1996) Synaptophysin, a major synaptic vesicle protein, is not essential for neurotransmitter release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:4760–4764. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.10.4760
Zhao Y, Li Q, ** A, Cui M, Liu X (2015) E3 ubiquitin ligase Siah-1 downregulates synaptophysin expression under high glucose and hypoxia. Am J Transl Res 7:15–27
El-Husseini AE, Schnell E, Chetkovich DM, Nicoll RA, Bredt DS (2000) PSD-95 involvement in maturation of excitatory synapses. Science 290:1364–1368
Wang X, Zhao L (2016) Calycosin ameliorates diabetes-induced cognitive impairments in rats by reducing oxidative stress via the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 473:428–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.03.024
Tran PV, Fretham SJ, Carlson ES, Georgieff MK (2009) Long-term reduction of hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor activity after fetal-neonatal iron deficiency in adult rats. Pediatr Res 65:493–498. https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e31819d90a1
Robinet C, Pellerin L (2011) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances the hippocampal expression of key postsynaptic proteins in vivo including the monocarboxylate transporter MCT2. Neuroscience 192:155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.06.059
Hakansson K, Ledreux A, Daffner K, Terjestam Y, Bergman P, Carlsson R, Kivipelto M, Winblad B, Granholm AC, Mohammed AK (2017) BDNF responses in healthy older persons to 35 minutes of physical exercise, cognitive training, and mindfulness: associations with working memory function. J Alzheimers Dis 55:645–657. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-160593
**e Y, Chu A, Feng Y, Chen L, Shao Y, Luo Q, Deng X, Wu M, Shi X, Chen Y (2018) MicroRNA-146a: a comprehensive indicator of inflammation and oxidative stress status induced in the brain of chronic T2DM rats. Front Pharmacol 9:478. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00478
Wu W, Wang X, **ang Q, Meng X, Peng Y, Du N, Liu Z, Sun Q, Wang C, Liu X (2014) Astaxanthin alleviates brain aging in rats by attenuating oxidative stress and increasing BDNF levels. Food Funct 5:158–166. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3fo60400d
Zhong SZ, Ge QH, Qu R, Li Q, Ma SP (2009) Paeonol attenuates neurotoxicity and ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by d-galactose in ICR mice. J Neurol Sci 277:58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2008.10.008
Martin-Gallan P, Carrascosa A, Gussinye M, Dominguez C (2003) Biomarkers of diabetes-associated oxidative stress and antioxidant status in young diabetic patients with or without subclinical complications. Free Radic Biol Med 34:1563–1574. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0891-5849(03)00185-0
Zhang SY, Ji SX, Bai XM, Yuan F, Zhang LH, Li J (2019) L-3-n-butylphthalide attenuates cognitive deficits in db/db diabetic mice. Metab Brain Dis 34:309–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0356-6
Hussein AM, Eldosoky M, El-Shafey M, El-Mesery M, Abbas KM, Ali AN, Helal GM, Abulseoud OA (2019) Effects of GLP-1 receptor activation on a pentylenetetrazole-kindling rat model. Brain Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9050108
Song D, Wang D, Yang Q, Yan T, Wang Z, Yan Y, Zhao J, **e Z, Liu Y, Ke Z, Qazi TJ, Li Y, Wu Y, Shi Q, Lang Y, Zhang H, Huang T, Wang C, Quan Z, Qing H (2020) The lateralization of left hippocampal CA3 during the retrieval of spatial working memory. Nat Commun 11:2901. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16698-4
Wilson JG, Lindquist JH, Grambow SC, Crook ED, Maher JF (2003) Potential role of increased iron stores in diabetes. Am J Med Sci 325:332–339. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000441-200306000-00004
Ambachew S, Biadgo B (2017) Hepcidin in iron homeostasis: diagnostic and therapeutic implications in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Acta Haematol 138:183–193. https://doi.org/10.1159/000481391
Liu J, Hu X, Xue Y, Liu C, Liu D, Shang Y, Shi Y, Cheng L, Zhang J, Chen A, Wang J (2020) Targeting hepcidin improves cognitive impairment and reduces iron deposition in a diabetic rat model. Am J Transl Res 12:4830–4839
Moos T, Rosengren Nielsen T, Skjorringe T, Morgan EH (2007) Iron trafficking inside the brain. J Neurochem 103:1730–1740. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04976.x
Zhao Y, **n Z, Li N, Chang S, Chen Y, Geng L, Chang H, Shi H, Chang YZ (2018) Nano-liposomes of lycopene reduces ischemic brain damage in rodents by regulating iron metabolism. Free Radic Biol Med 124:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.05.082
Zou MJ, Palte AA, Deik H, Li JK, Eaton W, Wang YY, Tseng R, Deasy M, Kost-Alimova V, Dancik ES, Leshchiner VS, Viswanathan S, Signoretti TK, Choueiri JS, Boehm BK, Wagner JG, Doench CB, Clish PA, Clemons SL (2019) Schreiber, A GPX4-dependent cancer cell state underlies the clear-cell morphology and confers sensitivity to ferroptosis. Nat Commun 10:1617. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09277-9
Killion EA, Reeves AR, El Azzouny MA, Yan QW, Surujon D, Griffin JD, Bowman TA, Wang C, Matthan NR, Klett EL, Kong D, Newman JW, Han X, Lee MJ, Coleman RA, Greenberg AS (2018) A role for long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase-4 (ACSL4) in diet-induced phospholipid remodeling and obesity-associated adipocyte dysfunction. Mol Metab 9:43–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2018.01.012
Chen X, Li J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Tang D (2020) Ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Autophagy. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1810918
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. En-Sheng Ji and Prof. Ya-Shuo Zhao in Hebei University of Chinese Medicine for their technical support in western blot and immunofluorescence.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Leading Talents Support Program of Chinese Medicine- Qihuang Scholar (Grant Number [2018]12); Liaoning **ngliao Talent Plan Project (Grant Number XLYC1807145); Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Postdoctoral Research Fund (Grant Number 21601A2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J-RA, J-NS, Y-FY and YS carried out the experiments, analyzed the results, performed the experimental detection and wrote the manuscript. G-YS, Q-FW, Y-DF and NJ performed the animal models and part of the experimental detection.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of financial interest or benefit.
Ethical Approval
The animal research was approved by the Animal Experimental Ethics Committee of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Ethics Approval Number: SYXK 2019–0004).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, JR., Su, JN., Sun, GY. et al. Liraglutide Alleviates Cognitive Deficit in db/db Mice: Involvement in Oxidative Stress, Iron Overload, and Ferroptosis. Neurochem Res 47, 279–294 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03442-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03442-7