Abstract
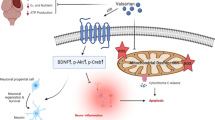
Aliskiren (ALK), a pharmacological renin inhibitor, is an effective antihypertensive drug and has potent anti-apoptotic activity, but it is currently unknown whether ALK is able to attenuate brain damage caused by acute cerebral ischemia independent of its blood pressure-lowering effects. This study aimed to investigate the role of ALK and its potential mechanism in cerebral ischemia. C57/BL6 mice were subjected to transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) and treated for 5 days with Vehicle or ALK (10 or 25 mg/kg per day via intragastric administration), whereas Sham-operated animals served as controls. Treatment with ALK significantly improved neurological deficits, infarct volume, brain water content and Nissl bodies after stroke (P < 0.05), which did not affect systemic blood pressure. Furthermore, the protection of ALK was also related to decreased levels of apoptosis in mice by enhanced activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway, increased level of Bcl-2 and reduced Bax expression (P < 0.05). In addition, ALK’s effects were reversed by PI3K inhibitors LY294002 (P < 0.05). Our data indicated that ALK protected the brain from reperfusion injuries without affecting blood pressure, and this effect may be through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blomgren K, Zhu C, Hallin U, Hagberg H (2003) Mitochondria and ischemic reperfusion damage in the adult and in the develo** brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 304:551–559
Iadecola C, Anrather J (2011) Stroke research at a crossroad: asking the brain for directions. Nat Neurosci 14:1363–1368
Brunet A, Datta SR, Greenberg ME (2001) Transcription-dependent and-independent control of neuronal survival by the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:297–305
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cellintrinsic death machinery. Cell 91:231–241
Brazil DP, Park J, Hemmings BA (2002) PKB binding proteins Getting in on the Akt. Cell 111:293–303
Sedlak TW, Oltvai ZN, Yang E, Wang K, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ (1995) Multiple Bcl-2 family members demonstrate selective dimerizations with Bax. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7834–7838
Sanoski CA (2009) Aliskiren: an oral direct renin inhibitor for the treatment of hypertension. Pharmacotherapy 29:193–212
Schmerbach K, Pfab T, Zhao Y, Culman J, Mueller S, Villringer A, Muller DN, Hocher B, Unger T, Thoene-Reineke C (2010) Effects of aliskiren on stroke in rats expressing human renin and angiotensinogen genes. PLoS One 29:e15052
Rashikh A, Ahmad SJ, Pillai KK, Kohli K, Najmi AK (2012) Aliskiren attenuates myocardial apoptosis and oxidative stress in chronic murine model of cardiomyopathy. Biomed Pharmacother 66:138–143
Westermann D, Riad A, Lettau O, Roks A, Savvatis K, Becher PM, Escher F, Jan Danser AH, Schultheiss HP, Tschöpe C (2008) Renin inhibition improves cardiac function and remodeling after myocardial infarction independent of blood pressure. Hypertension 52:1068–1075
Culman J, Blume A, Gohlke P, Unger T (2002) The reninangiotensin system in the brain: possible therapeutic implications for AT(1)-receptor blockers. J Hum Hypertens 16(Suppl 3):S64–S70
Brdon J, Kaiser S, Hagemann F, Zhao Y, Culman J, Gohlke P (2007) Comparison between early and delayed systemic treatment with candesartan of rats after ischaemic stroke. J Hypertens 25:187–196
Ito T, Yamakawa H, Bregonzio C, Terrón JA, Falcón-Neri A, Saavedra JM (2002) Protection against ischemia and improvement of cerebral blood flow in genetically hypertensive rats by chronic pretreatment with an angiotensin II AT1 antagonist. Stroke 33:2297–2303
Zhu C, Zhang X, Qiao H, Wang L, Zhang X, **ng Y, Wang C, Dong L, Ji Y, Cao X (2012) The Intrinsic PEDF is regulated by PPARc in permanent focal cerebral ischemia of rat. Neurochem Res 37:2099–2107
Wang L, Zhang X, Liu L, Cui L, Yang R, Li M, Du W (2010) Tanshinone II A down-regulates HMGB1 RAGE TLR4 NF-kappaB expression ameliorates BBB permeability and endothelial cell function and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Brain Res 1321:143–151
Lipton P (1999) Ischemic cell death in brain neurons. Physiol Rev 79:1431–1568
Ikeda K, Negishi H, Yamori Y (2003) Antioxidant nutrients and hypoxia/ischemia brain injury in rodents. Toxicology 189:55–61
Simonyi A, Wang Q, Miller RL, Yusof M, Shelat PB, Sun AY, Sun GY (2005) Polyphenols in cerebral ischemia: novel targets for neuroprotection. Mol Neurobiol 31:135–148
Chan PH (2001) Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:2–14
Yang C, Zhang C, Fan H, Liu Y (2009) Curcumin upregulates transcription factor Nrf2 HO-1 expression and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Brain Res 1282:133–141
Qiao H, Zhang X, Zhu C, Dong L, Wang L, Zhang X, **ng Y, Wang C, Ji Y, Cao X (2012) Luteolin downregulates TLR4 TLR5 NF-kB and p-p38MAPK expression upregulates the p-ERK expression and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Brain Res 11:71–81
Zhang X, Zhang XJ, Wang C, Li Y, Dong L, Cui L, Wang L, Liu Z, Qiao H, Zhu C, **ng Y, Cao X, Ji Y, Zhao K (2012) Neuroprotection of early and short-time applying berberine in the acute phase of cerebral ischemia: up-regulated pAkt pGSK and pCREB down-regulated NF-kB expression ameliorated BBB permeability. Brain Res 1459:61–70
Brown MJ (2008) Aliskiren. Circulation 118:773–784
Jensen C, Herold P, Brunner HR (2008) Aliskiren: the first renin inhibitor for clinical treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:399–410
Choi DE, Jeong JY, Lim BJ, Chang YK, Na KR, Shin YT, Lee KW (2011) Aliskiren ameliorates renal inflammation and fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction in mice. J Urol 186:694–701
Dong YF, Kataoka K, Toyama K, Sueta D, Koibuchi N, Yamamoto E, Yata K, Tomimoto H, Ogawa H, Kim-Mitsuyama S (2011) Attenuation of brain damage and cognitive impairment by direct renin inhibition in mice with chronic cerebral. Hypertension 58:635–642
Srivastava M, Ahmad N, Gupta S, Mukhtar H (2001) Involvement of Bcl-2 and Bax in photodynamic therapy-mediated apoptosis. Antisense Bcl-2 oligonucleotide sensitizes RIF 1 cells to photodynamic therapy apoptosis. J Biol Chem 276:15481–15488
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X, Wang X (1999) Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15:269–290
Sun D, Huang J, Zhang Z, Gao H, Li J, Shen M, Cao F, Wang H (2012) Luteolin limits infarct size and improves cardiac function after myocardium ischemia/reperfusion injury in diabetic rats. PLoS One 7:e33491
Fang F, Li D, Pan H, Chen D, Qi L, Zhang R, Sun H (2011) Luteolin inhibits apoptosis and improves cardiomyocyte contractile function through the PI3K/Akt pathway in simulated ischemia/reperfusion. Pharmacology 88:149–158
Acknowledgments
Jiangyong Miao and Lina Wang are co-first authors. This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81371287) and Hebei Province (C2010000564). The authors thank technician Ruichun Liu, Hongran Wu and Zhongyao Li for their technical assistance and Dr. Yansu Guo, Dr. Weisong Duan for providing valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jiangyong Miao, Lina Wang have contributed equal to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, J., Wang, L., Zhang, X. et al. Protective Effect of Aliskiren in Experimental Ischemic Stroke: Up-Regulated p-PI3K, p-AKT, Bcl-2 Expression, Attenuated Bax Expression. Neurochem Res 41, 2300–2310 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1944-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1944-7