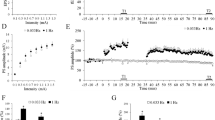
The phenomenon of long-term potentiation (LTP) is used for studies of the effects of various factors on the long-term plasticity of synapses in health and disease. One of the most important problems for these experiments is selection of a suitable stimulation protocol for comparing individual and group characteristics. Experiments on living hippocampal slices from Wistar rats aged 1–1.5 months addressed the individual features of the induction and maintenance of LTP (tetanization at 100 Hz for 1 sec) depending on the initial magnitude of the overall response of CA1 neurons to the stimulation of Schaffer collaterals used for tetanization and testing. The statistical relationship between the intensity of the synaptic input at the moment of tetanization and the magnitude of the post-tetanic increase after induction of LTP was assessed. Early potentiation was found to depend on the parameters of the test stimulation but not the amplitude of the response to the stimulation used for tetanization; the two factors acted independently. On testing with variable intensities, weak (near-threshold) responses were potentiated significantly more strongly than near-maximal responses. The saturation effect was found to limit mainly early LTP and only indirectly influenced the remaining potentiation. When differences in the level of early potentiation were excluded, late LTP depended on the intensity of tetanization but not the parameters of the test stimulation. The optimum tetanization of Schaffer collaterals for maintenance of LTP was the level inducing overall postsynaptic neuron responses of 1–2 mV, both weak and excessively strong activation on induction having negative impact on the efficiency with which LTP was maintained. This pattern may be due to a low level of depolarization, including in conditions of quite intense activation, due to the involvement of inhibitory interneurons in the response. These data provide evidence that all the study factors need to be considered for adequate comparison of groups of animals exposed to various environmental factors, including stress factors, particularly when the input characteristics of the connections of interest change.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, W. C., “Metaplasticity: tuning synapses and networks for plasticity,” Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 9, No. 5, 387 (2008).
Ahmed, T., Frey, J. U., and Korz, V., “Long-term effects of brief acute stress on cellular signaling and hippocampal LTP,” J. Neurosci., 26, 3951–3958 (2006).
Albensi, B. C., Oliver, D. R., Toupin, J., and Odero, G., “Electrical stimulation protocols for hippocampal synaptic plasticity and neuronal hyper-excitability: are they effective or relevant?” Exp. Neurol., 204, 1–13 (2007).
Alfarez, D. N., Wiegert, O., Joels, M., and Krugers, H. J., “Corticosterone and stress reduce synaptic potentiation in mouse hippocampal slices with mild stimulation,” Neuroscience, 115, No. 4, 1119–1126 (2002).
Artola, A., von Frijtag, J. C., Fermont, P. C., et al., “Long-lasting modulation of the induction of LTD and LTP in rat hippocampal CA1 by behavioural stress and environmental enrichment,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 23, No. 1, 261–272 (2006).
Barnes, C. A., Jung, M. W., Mcnaughton, B. L., et al., “LTP saturation and spatial learning disruption: effects of task variables and saturation levels,” J. Neurosci., 14, 5793–5806 (1994).
Bloch, V. and Laroche, S., “Enhancement of long-term potentiation in the rat dentate gyrus by post-trial stimulation of the reticular formation,” J. Physiol. (Lond.), 360, 215–231 (1985).
Bourne, J. N. and Harris, K. M., “Coordination of size and number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses results in a balanced structural plasticity along mature hippocampal CA1 dendrites during LTP,” Hippocampus, 21, 354–373 (2011).
Bramham, C. R., “Local protein synthesis, actin dynamics, and LTP consolidation,” Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 18, No. 5, 524–531 (2008).
Connor, S. A., Wang, Y. T., and Nguyen, P. V., “Activation of {beta}-adrenergic receptors facilitates heterosynaptic translation-dependent longterm potentiation,” J. Physiol., 589, No. 17, 4321–4340 (2011).
Duffy, S. N., Craddock, K. J., Abel, T., and Nguyen, P. V., “Environmental enrichment modifies the PKA-dependence of hippocampal LTP and improves hippocampus-dependent memory,” Learn. Mem., 8, 26–34 (2001).
Faas, G. C., Raghavachari, S., Lisman, J. E., and Mody, I., “Calmodulin as a direct detector of Ca2+ signals,” Nat. Neurosci., 14, No. 3, 301–304 (2011).
Frey, S. and Frey, J. U., “’Synaptic tagging’ and ‘cross-tagging’ and related associative reinforcement processes of functional plasticity as the cellular basis for memory formation,” Prog. Brain Res., 169, 117–143 (2008).
Frey, S., Bergado, J. A., and Frey, J. U., “Modulation of late phases of longterm potentiation in rat dentate gyrus by stimulation of the medial septum,” Neuroscience, 118, 1055–1062 (2003).
Fritschy, J. and Panzanelli, P., “GABAA receptors and plasticity of inhibitory neurotransmission in the central nervous system,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 39, 1845–1865 (2014).
Gelinas, J. N., Tenorio, G., Lemon, N., et al., “Beta-adrenergic receptor activation during distinct patterns of stimulation critically modulates the PKA-dependence of LTP in the mouse hippocampus,” Learn. Mem., 15, No. 5, 281–289 (2008).
Genrikhs, E. E., Stelmashook, E. V., Popova, O. V., et al., “Mitochondriatargeted antioxidant SkQT1 decreases trauma-induced neurological deficit in rat and prevents amyloid-P-induced impairment of longterm potentiation in rat hippocampal slices,” J. Drug Target, 23, No. 4, 347–352 (2015).
Granado, N., Ortiz, O., Sudrez, L. M., et al., “D1 but not D5 dopamine receptors are critical for LTP, spatial learning, and LTP-Induced arc and zif268 expression in the hippocampus,” Cereb. Cortex, 18, No. 1, 1–12 (2008).
Gulyaeva, N. V., “Interplay between brain BDNF and glutamatergic systems: A brief state of the evidence and association with the pathogenesis of depression,” Biochemistry (Mosc.), 82, No. 3, 301–307 (2017a).
Gulyaeva, N. V., “Molecular mechanisms of neuroplasticity: An expanding universe,” Biochemistry (Mosc.), 82, No. 3, 237–242 (2017b).
Gulyaeva, N. V., “Studies on stress-induced modulation of long term potentiation in rodent hippocampus: what can we learn about pathogenesis of depression?” Transl. Brain Rhythm, 1, No. 2, 35–40 (2016).
Hayama, T., Noguchi, J., Watanabe, S., et al., “GABA promotes the competitive selection of dendritic spines by controlling local Ca2+ signaling,” Nat. Neurosci., 16, 1409–1416 (2013).
Huang, Y. Y., Colino, A., Selig, D. K., and Malenka, R. C., “The influence of prior synaptic activity on the induction of long-term potentiation,” Science, 255, 730–733 (1992).
Jeffery, K. J., “Paradoxical enhancement of long-term potentiation in poor-learning rats at low test stimulus intensities,” Exp. Brain Res., 104, No. 1, 55–69 (1995).
Joels, M. and Krugers, H. J., “LTP after stress: up or down?” Neural Plast., 9320210.1155 (2007).
Kapay, N. A., Popova, O. V., Isaev, N. K., et al., “Mitochondria-targeted plastoquinone antioxidant SkQ1 prevents amyloid-P-induced impairment of long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal slices,” J. Alzh. Dis., 36, No. 2, 377–383 (2013).
Kemp, A. and Manahan-Vaughan, D., “Hippocampal long-term depression and long-term potentiation encode different aspects of novelty acquisition,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 8192–8197 (2004).
Kleschevnikov, A. M., Belichenko, P. V., Villar, A. J., et al., “Hippocampal long-term potentiation suppressed by increased inhibition in the Ts65Dn mouse, a genetic model of Down syndrome,” J. Neurosci., 24, 8153–8160 (2004).
Kleshchevnikov, A. M. and Voronin, L. L., “Repeated induction of longterm potentiation on saturation of long-term potentiation in living hippocampal slices,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk., 340, No. 5, 694–696 (1995).
Korz, V. and Frey, J. U., “Hormonal and monoamine signaling during reinforcement of hippocampal long-term potentiation and memory retrieval,” Learn. Mem., 14, No. 3, 160–166 (2007).
Kudryashova, I. V. and Gulyaeva, N. V., “Unpredictable stress: the ambiguity of stress reactivity in studies of long-term plasticity,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 66, No. 4, 414–428 (2016).
Kudryashova, I. V., “Analysis of the conditions for the onset of the consolidation process in a model of long-term synaptic potentiation,” Neirokhimiya, 30, No. 3, 207–215 (2013).
Kudryashova, I. V., “Plasticity of inhibitory synapses as a factor in longterm modification,” Neirokhimiya, 32, No. 3, 181–191 (2015).
Kulla, A. and Manahan-Vaughan, D., “Modulation by serotonin 5-HT(4) receptors of long-term potentiation and depotentiation in the dentate gyrus of freely moving rats,” Cereb. Cortex, 12, 150–162 (2002).
Larson, J., Wong, D., and Lynch, G., “Patterned stimulation at the theta frequency is optimal for the induction of hippocampal long-term potentiation,” Brain Res., 19, 347–350 (1986).
Lemon, N. and Manahan-Vaughan, D., “Dopamine D1/D5 receptors gate the acquisition of novel information through hippocampal long-term potentiation and long-term depression,” J. Neurosci., 26, 7723–7729 (2006).
Lovett-Barron, M., Turi, G. F., Kaifosh, P., et al., “Regulation of neuronal input transformations by tunable dendritic inhibition,” Nat. Neurosci., 15, No. 3, 423–430 (2012).
Lynch, G., Rex, C. S., and Gall, C. M., “LTP consolidation: substrates, explanatory power, and functional significance,” Neuropharmacology, 52, No. 1, 12–23 (2007).
Maity, S., Rah, S., Sonenberg, N., et al., “Norepinephrine triggers metaplasticity of LTP by increasing translation of specifi c mRNAs,” Learn. Mem., 22, No. 10, 499–508 (2015).
Martin, S. J., Grimwood, P. D., and Morris, R. G. M., “Synaptic plasticity and memory: an evaluation of the hypothesis,” Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 23, 649–711 (2000).
Martin, S. J., Shires, K. L., and Spooner, P. A., “The relationship between tetanus intensity and the magnitude of hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo,” Neuroscience, 231, 363–372 (2013).
Matsuyama, S., Taniguchi, T., Kadoyama, K., and Matsumoto, A., “Longterm potentiation-like facilitation through GABAA receptor blockade in the mouse dentate gyrus in vivo,” Neuroreport, 19, 1809–1813 (2008).
McNaughton, B. L., Douglas, R. M., and Goddard, G. V., “Synaptic enhancement in fascia dentata: cooperativity among coactive afferents,” Brain Res., 157, 277–293 (1978).
Moser, E. I. and Moser, M. B., “Is learning blocked by saturation of synaptic weights in the hippocampus?” Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 23, No. 5, 661–672 (1999).
Müller, C., Beck, H., Coulter, D., and Remy, S., “Inhibitory control of linear and supralinear dendritic excitation in CA1 pyramidal Neurons,” Neuron, 75, 851–864 (2012).
Onufriev, M. V., Freiman, S. V., Peregud, D. I., et al., “Neonatal proinflammatory stress induces accumulation of corticosterone and interleukin-6 in the hippocampus of juvenile rats: potential mechanism of synaptic plasticity impairments,” Biochemistry (Mosc.), 82, No. 3, 275–281 (2017).
Onufriev, M., Lazareva, N., and Gulyaeva, N., “Neonatal proinflammatory challenge in male Wistar rats: Effects on behavior, synaptic plasticity, and adrenocortical stress response,” Behav. Brain Res., 1, No. 304, 1–10 (2016).
Ormond, J. and Woodin, M. A., “Disinhibition mediates a form of hippocampal long-term potentiation in area CA1,” PLoS One, 4, No. 9, e7224 (2009).
Otnaess, M. K., Brun, V. H., Moser, M. B., and Moser, E. I., “Pre-training prevents spatial learning impairment after saturation of hippocampal long-term potentiation,” J. Neurosci., 19, RC49 (1999).
Paille, V., Fino, E., Du, K., et al., “GABAergic circuits control spike-timing-dependent plasticity,” J. Neurosci., 33, No. 22, 9353–9363 (2013).
Povarov, I. S., Kondratenko, R. V., Derevyagin, V. I., et al., “Nootropic dipeptide noopept enhances inhibitory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus,” Byull. Exp. Biol. Med., 158, No. 3, 349–351 (2015).
Rannals, M. D. and Kapur, J., “Homeostatic strengthening of inhibitory synapses is mediated by the accumulation of GABAA receptors,” J. Neurosci., 31, No. 48, 17701–17712 (2011).
Richter-Levin, G. and Akirav, I., “Emotional tagging of memory formation in the search for neural mechanisms,” Brain Res. Rev., 43, No. 3, 247–256 (2003).
Saraga, F., Balena, T., Wolansky, T., et al., “Inhibitory synaptic plasticity regulates pyramidal neuron spiking in the rodent hippocampus,” Neuroscience, 155, 64–75 (2008).
Seidenbecher, T., Reymann, K. G., and Balschun, D., “A post-tetanic time window for the reinforcement of long-term potentiation by appetitive and aversive stimuli,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 1494–1499 (1997).
Shen, H., Sabaliauskas, N., Sherpa, A., et al., “A critical role for alpha-4betadelta GABAA receptors in sha** learning deficits at puberty in mice,” Science, 327, 1515–1518 (2010).
Shors, T. J. and Matzel, L. D., “Long-term potentiation: what’s learning got to do with it?” Behav. Brain Sci., 20, 597–614 (1997).
Skrebitsky, V. G. and Shtark, M. B., “Basics of nervous system plasticity,” Vestn. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk, 9, 39–44 (2012).
Skrebitsky, V. G. and Vorobyev, V. S., “A study of synaptic plasticity in hippocampal slices,” Acta Neurobiol. Exp. (Wars.), 39, No. 6, 633–642 (1979).
Skrebitsky, V. G., Kondratenko, R. V., Povarov, I. S., and Derevyagin, V. I., “Peptidergic modulation of synaptic activity in the hippocampus,” Neurosci. Behav. Physiol., 43, No. 5, 650–655 (2013).
Solntseva, E. I., Kapai, N. A., Popova, O. V., et al., “The involvement of sigma1 receptors in donepezil-induced rescue of hippocampal LTP impaired by beta-amyloid peptide,” Brain Res. Bull., 106, 56–61 (2014).
Uzakov, Sh., Frey, J. U., and Korz, V., “Reinforcement of rat hippocampal LTP by holeboard training,” Learn. Mem., 12, No. 2, 165–171 (2005).
Voronin, L., Byzov, A., Kleschevnikov, A., et al., “Neurophysiological analysis of long-term potentiation in mammalian brain,” Behav. Brain Res., 66, No. 1–2, 45–52 (1995).
Wakita, M., Kotani, N., Kogure, K., and Akaike, N., “Inhibition of excitatory synaptic transmission in hippocampal neurons by levetiracetam involves Zn2+-dependent GABAA receptor-mediated presynaptic modulation,” J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 348, 246–259 (2013).
Wang, L. and Maffei, A., “Inhibitory plasticity dictates the sign of plasticity at excitatory synapses,” J. Neurosci., 34, 1083–1093 (2014).
Willadt, S., Nenniger, M., and Vogt, K. E., “Hippocampal feedforward inhibition focuses excitatory synaptic signals into distinct dendritic compartments,” PLoS One, 8, No. 11, e80984 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 67, No. 6, pp. 705–720, November–December, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kudryashova, I.V. Relationship between Long-Term Potentiation and the Initial Properties of CA3–CA1 Synapses: Importance of the Effects of External Factors on Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity for Studies. Neurosci Behav Physi 49, 603–614 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-019-00776-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-019-00776-2