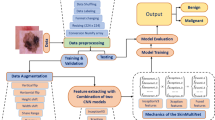
Abstract
In the past few decades, the automatic melanoma classification system has been considered a dynamic and challenging research area in the field of medical analysis. An automatic system has a significant role in lowering the death rate by identifying the disease early and providing an accurate diagnosis. This paper presents a hybrid approach for classifying melanoma from dermoscopy images. The purpose of the proposed methods is to extract more valuable and strong features for precise skin lesion classification into their related classes, like benign or melanoma. At first, the U-Net algorithm is employed to segment the skin lesion region, which is based on a convolutional neural network. Then the Inter Neighbour Mean Order Interleaved Pattern has employed for extracting robust texture features. The proposed feature descriptor encompasses Inter Neighbor Mean Order Pattern and Interleaved Neighbour Binary Pattern. After the feature extraction, a skin lesion image is classified by Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, K-Nearest Neighbor and VGG-16 classifiers. The suggested method is evaluated on the ISBI-2016, ISBI-2017 and ISBI-2019 datasets. On all three datasets, the attained classification accuracy using VGG-16 network is 94.87%, 86.88% and 93.65% respectively, which demonstrates that the proposed technique has exceptional performance. Moreover, this proposed method outperforms the accuracy of existing approaches on the same dataset.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ, Meester RG, Barzi A, Jemal A (2017) Colorectal cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 67(3):177–193
Narayanan DL, Saladi RN, Fox JL (2010) Ultraviolet radiation and skin cancer. Int J Dermatol 49(9):978–986
Andre E, Brett K, Roberto AN, Justin K, Susan MS, Helen MB, Sebastian T (2017) Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 542(7639):115–118
Kittler H, Pehamberger H, Wolff K, Binder M (2002) Diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy. Lancet Oncol 3(3):159–165
Olugbara OO, Taiwo TB, Heukelman D (2018) Segmentation of melanoma skin lesion using perceptual colour difference saliency with morphological analysis. Math Probl Eng 2018:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1524286
Garcia-Arroyo JL, Garcia-Zairain B (2019). Segmentation of skin lesions based on fuzzy classification of pixels and histogram thresholding. 168:11–19. ar**v1703.03888v1
Sreelatha T, Subramanyam MV, Prasad MNG (2019) Early detection of skin cancer using melanoma segmentation technique. J Med Syst 43(7):190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1334-1
Khan M, Sharif M, Akram T, Damasevicius R, Maskeliunas R (2021) Skin lesion segmentation and multiclass classification using deep learning features and improved moth flame optimization. Diagnostics 11:811. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050811
Pereira P, Fonseca P, Rui P, Rui P, Assunção P, Tavora L, Thomaz L, De F, Sergio. (2020) Dermoscopic skin lesion image segmentation based on local binary pattern clustering: Comparative study. Biomed Signal Process Control 59:101924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.101924
Gomez DD, Butakoff C, Ersboll BK, Stoecker W (2008) Independent histogram pursuit for segmentation of skin lesions. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 55(1):157–161. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2007.910651
Unver HM, Ayan E (2019) Skin lesion segmentation in dermoscopic images with combination of YOLO and grabcut algorithm. Diagnostics 9(3):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9030072
Warsi F, Khanam R, Kamya S, Suárez-Araujo CP (2019) An efficient 3D color-texture feature and neural network technique for 128 melanoma detection. Inform Med Unlocked 17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2019.100176
Wei L, Ding K, Hu H (2020) Automatic skin cancer detection in dermoscopy images based on ensemble lightweight deep learning network. IEEE Access 899633–99647. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2997710
Deng Z, Fan H, **e F, Cui Y, Liu J (2017) Segmentation of dermoscopy images based on fully convolutional neural network, IEEE International Conference for Image Processing. (ICIP), 1732–1736
Chitra Devi M (2020) Skin cancer classification using dermoscopic images based on ranklet transform, co-occurrence features and random forest classifier. Med Legal Update 20(3)
Seeja RD, Suresh A (2021) Melanoma classification employing inter neighbor statistical color and mean order pattern texture feature. Multimed Tools Appl 80:20045–20064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10685-7
Abbas Q, Celebi ME (2019) DermoDeep-A classification of melanoma-nevus skin lesions using multi-feature fusion of visual features and deep neural network. Multimed Tools Appl 78:23559–23580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7652-y
Chatterjee S, Dey D, Munshi S (2019) Integration of morphological preprocessing and fractal based feature extraction with recursive feature elimination for skin lesion types classification. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 178:201–218
Khan MA, Akram T, Sharif M, Shahzad A, Aurangzeb K, Alhussein M, Haider SI, Altamrah A (2018) An implementation of normal distribution based segmentation and entropy controlled features selection for skin lesion detection and classification. BMC Cancer 18(1):638
Arasi MA, El-Harbaty EM, El-Dahshan EA, Salem AM (2016) Intelligent methodologies for melanoma diagnosis. Int J Curr Trends Eng Technol 2(5):429–435. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICITECH.2017.8079915
Gessert N, Shaikh Nielsen M, M, Werner R, Schlaefer A, (2020) Skin lesion classification using ensembles of multi-resolution efficientnets with meta data. MethodsX 7:100864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2020.100864
Harangi B, Baran A, Hajdu A (2018) Classification of skin lesions using an ensemble of deep neural networks. Ann Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2018:2575–2578. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2018.8512800
Wang Y, Pan H, Yang B, Bian X, Cui Q (2019) Mutual learning model for skin lesion classification. In: International Conference of Pioneering Computer Scientists, Engineers and Educators, Springer, Singapore, 214-222
Jayapriya K, Jeena Jacob I (2019) Hybrid fully convolutional networks-based skin lesion segmentation and melanoma detection using deep feature. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 29(4):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/ima.22377
Mahbod A, Ecker R, Ellinger I (2017) Skin lesion classification using hybrid deep neural networks
Seeja RD, Suresh A (2019) Deep learning based skin lesion segmentation and classification of melanoma using support vector machine (SVM). Asian Pac J Cancer Prev: APJCP 20(5):1555–1561. https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.5.1555
Kwasigroch A, Mikołajczyk A, Grochowski M (2017) Deep neural networks approach to skin lesions classification — A comparative analysis. International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics (MMAR), 1069–1074. https://doi.org/10.1109/MMAR.2017.8046978
Yang G, Luo S, Greer P (2023) A novel vision transformer model for skin cancer classification. Neural Process Lett. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCISci.2019.8716400
Gessert N, Sentker T, Madesta F, Schmitz R, Kniep H, Baltruschat I, Werner R, Schlaefer A (2019) Skin lesion classification using cnns with patch-based attention and diagnosis-guided loss weighting. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 67:495–503
Yang G, Luo S, Greer P (2023) A novel vision transformer model for skin cancer classification. Neural Process Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-023-11204-5
Zhang J, **e Y, **a Y, Shen C (2019) Attention residual learning for skin lesion classification. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2019.2893944
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. Int Conf Med Image Comput Comput-Assist Intervent 9351:234–241
Haralick RM, Shanmugam K, Dinstein I (1973) Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 6:610–621
Boser BE, Guyon IM, Vapnik VN (1992) A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. In: COLT ’92: Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Workshop on Computational Learning Theory, edited by David Haussler, 144–152, New York: ACM
Gutman AD, Codella N, Tschandl P, Clebi ME et al (2016) Skin leson analysis toward melanoma detection: A Challenge at the International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2016. Hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC) 2016; ar**v:1605.01397v1
Al-mansi MA, Al-antari MA, Choi MT, Han SM, Kim TS (2018) Skin lesion segmentation in dermoscopy images via deep full resolution convolutional networks. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 162:221–231
Jayapriya K, Jacob IJ (2019) Hybrid fully convolutional networks-based skin lesion segmentation and melanoma detection using deep feature. Int J Imaging Systems and Technol 1–10
Wang Y, Pan H, Yang B, Bian X, Cui Q (2019) Mutual learning model for skin lesion classification. In International Conference of Pioneering Computer Scientists, Engineers and Educators, 214–222, Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0121-0_17
Romero Lopez A, Giro-i-Nieto X, Burdick J, Marques O (2017) Skin lesion classification from dermoscopic images using deep learning techniques. 2017 13th IASTED International Conference on Biomedical Engineering (BioMed),.49–54
Majtner T, Yildirim YS, Hardeberg J (2016) Combining deep learning and hand-crafted features for skin lesion classification. In the 2016 Sixth International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications (IPTA). 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/IPTA.2016.7821017
Yu L, Chen H, Dou Q, Qin J, Heng PA (2017) Automated melanoma recognition in dermoscopy images via very deep residual networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 36(4):994
Codella N, Cai J, Abedini M, Garnavi R, Halpern A, Smith JR (2015) Deep learning, sparce coding, and SVM for melanoma recognition in dermoscopy images. Machine Learning in Medical Imaging. MLMI 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer, Cham 9352: 118-26
Ge Z, Demyanov S, Bozorgtabar B, Abedini M, Chakravorty R, Bowling A, Garnavi R (2017) Exploiting local and generic features for accurate skin lesions classification using clinical and dermoscopy imaging. IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2017), 986–990. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2017.7950681
Seeja RD, Suresh A (2021) elanoma classification employing inter neighbor statistical color and mean order pattern texture feature. Multimed Tools Appl 80:20045–20064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10685-7
Harangi B (2018) Skin lesion classification with ensembles of deep convolutional neural networks. J Biomed Inf 86:25–32
Zhang J, **e Y, **a Y, Shen C (2019) Attention residual learning for skin lesion classification. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(9):2092–2210
Li Y, Shen L (2018) Skin Lesion Analysis towards melanoma detection using deep learning network. Sensors (Basel) 18(2):556. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020556
Serte S, Demirel H (2019) Gabor wavelet-based deep learning for skin lesion classification. Comput Biol Med 113:103423
Sultana NN, Mandal B, Puhan NB (2018) Deep residual network with regularized fisher framework for detection of melanoma. IET Comput Vision 12(8):1096–1104
Hoang L, Lee S-H, Lee E-J, Kwon K-R (2022) Multiclass skin lesion classification using a novel lightweight deep learning framework for smart healthcare. Appl Sci 12:2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052677
Kassem MA, Hosny KM, Fouad MM (2020) Skin lesions classification into eight classes for ISIC 2019 using deep convolutional neural network and transfer learning. IEEE Access 8:114822–114832. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3003890
Gessert N, Nielsen M, Shaikh M, Werner R, Schlaefer A (2019) Skin lesion classification using ensembles of multi-resolution EfficientNets with metadata, 2019, ar**v:1910.03910. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1910.03910
Zhang J, **e Y, **a Y, Shen C (2019) Attention residual learning for skin lesion classification. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(9):2092–2103. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2893944
Salma W, Eltrass AS (2022) Automated deep learning approach for classification of malignant melanoma and benign skin lesions. Multimed Tools Appl 81:32643–32660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13081-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declarations
The manuscript entitled “Effective Melanoma Classification Using Inter Neighbour Mean Order Interleaved Pattern on Dermoscopy Images” has not been published elsewhere and that it has not been submitted simultaneously for publication elsewhere.
Conflict of Interest
We, R.D Seeja and Dr. A.Geetha have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Seeja, R.D., Geetha, A. Effective melanoma classification using inter neighbour mean order interleaved pattern on dermoscopy images. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 27481–27505 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16632-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-16632-y