Abstract
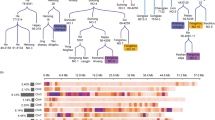
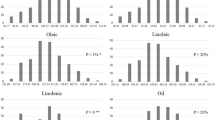
Improvement of soybean seed oil content was a major goal in soybean breeding. In this study, a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population derived from elite cultivar “Jidou 12” and landrace accession “Heidou” was used to identify major and stable QTL underlying oil content via linkage analysis across four environments. Of the six QTL associated with oil content, only qOIL_8_1 flanked by Satt177 and Satt341 was detected across four environments and explained a high percentage of phenotypic variance. The Jidou 12 allele could increase average oil content by 7.2 mg g−1 compared with the Heidou allele and had no significant drag on protein content. Eight quantitative trait nucleotides (QTNs) were associated with oil content underlying qOIL_8_1 via genome wide association study (GWAS) of four soybean panels. Among these, three located in the same haplotype block from Chr08_8291045 to Chr08_8512373. A strong domestication selection footprint in the block was detected as indicated by high Fst values, and significant difference of haplotype frequency between wild and landrace soybean in the region. This study will facilitate selection of soybean parent and breeding lines for seed oil content improvement.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessandro V, Dry IB, Marianna F, Sara Z, Margherita L (2012) Genome-wide analysis of the grapevine stilbene synthase multigenic family: genomic organization and expression profiles upon biotic and abiotic stresses. BMC Plant Biol 12(1):130
Bandillo N, Jarquin D, Song Q, Nelson R, Cregan P, Specht J, Lorenz A (2015) A population structure and genome-wide association analysis on the USDA soybean germplasm collection. Plant Genome, 8(3)
Bethke G, Thao A, **ong GY, Li BH, Soltis NE, Hatsugai N, Hillmer RA, Katagiri F, Kliebenstein DJ, Pauly M, Glazebrook J (2016) Pectin biosynthesis is critical for cell wall integrity and immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 28(2):537–556
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association map** of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23(19):2633–2635
Chang RZ, Sun JY (1991) Catalogues of Chinese soybean germplasm and resources: continuation I. China Agricultural Press, Bei**g, China
Chang RZ, Sun JY, Qiu LJ, Chen YW (1996) Catalogues of Chinese soybean germplasm and resources: continuation II. China Agricultural Press, Bei**g, China
Cregan P, Jarvik T, Bush A, Shoemaker R, Lark K, Kahler A, Kaya N, VanToai T, Lohnes D, Chung J, Specht JE (1999) An integrated genetic linkage map of the soybean genome. Crop Sci 39:1464–1490
Dong Y, Yang X, Liu J, Wang BH, Liu BL, Wang YZ (2013) Pod shattering resistance associated with domestication is mediated by a NAC gene in soybean. Nat Commun 5:3352
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14(8):2611–2620
Excoffier L, Lischer HE (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour 10(3):564–567
Grant D, Nelson RT, Cannon SB, Shoemaker RC (2010) SoyBase, the USDA-ARS soybean genetics and genomics database. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D843–D846
Han Y, **e D, Teng W, Zhang S, Chang W, Li W (2011) Dynamic QTL analysis of linolenic acid content in different developmental stages of soybean seed. Theor Appl Genet 122(8):1481–1488
Hwang EY, Song Q, Jia G, Specht JE, Hyten DL, Costa J, Cregan PB (2014) A genome-wide association study of seed protein and oil content in soybean. BMC Genomics 15(1):1
Hymowitz T, Dudley JW, Collins FI, Brown CM (1974) Estimations of protein and oil concentration in corn, soybean, and oat seed by near-infrared light reflectance. Crop Sci 14:713–715
Hyten DL, Song Q, Zhu Y, Choi IY, Nelson RL, Costa JM, Specht JE, Shoemaker RC, Cregan PB (2006) Impacts of genetic bottlenecks on soybean genome diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(45):16666–16671
Li YH, Zhao SC, Ma JX, Li D, Yan L, Li J, Qi XT, Guo XS, Zhang L, He WM (2013) Molecular footprints of domestication and improvement in soybean revealed by whole genome re-sequencing. BMC Genomics 14:579
Liang HZ, Yong-Liang YU, Wang SF, Lian Y, Wang TF, Wei YL, Gong PT, Liu XY, Fang XJ, Zhang MC (2010) QTL map** of isoflavone, oil and protein contents in soybean. J Integr Agric 9(8):1108–1116
Mansur LM, Lark KG, Kross H, Oliveira A (1993) Interval map** of quantitative trait loci for reproductive, morphological, and seed traits of soybean (Glycine max L.). Theor Appl Genet 86(8):907–913
Nyquist WE, Baker RJ (1991) Estimation of heritability and prediction of selection response in plant populations. Crit Rev Plant Sci 10(3):235–322
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155(2):945–959
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, De Bakker PI, Daly MJ (2007) PLINK:A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81(3):559–575
Qi X, Bakht S, Qin B, Leggett M, Hemmings A, Mellon F, Eagles J, Werck-Reichhart D, Schaller H, Lesot A, Melton R, Osbourn A (2006) A different function for a member of an ancient and highly conserved cytochrome p450 family: from essential sterols to plant defense. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(49):18848–18853
Reboul R, Geserick C, Pabst M, Frey B, Wittmann D, Lützmeindl U, Léonard R, Tenhaken R (2011) Down-regulation of udp-glucuronic acid biosynthesis leads to swollen plant cell walls and severe developmental defects associated with changes in pectic polysaccharides. J Biol Chem 286(2):39982–39992
SAS Institute Inc. (2011) SAS/STAT 9.3 User’s guide: survey data analysis. SAS Publishing, Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc
Song, QJ, Marek LF, Shoemaker RC, Lark KG, Concibido VC, Delannay X, Specht JE, Cregan PB, (2004) A new integrated genetic linkage mapof the soybean. Theor Appl Genet 109:122–128.
Song Q, Hyten DL, Jia G, Quigley CV, Fickus EW, Nelson RL, Cregan PB (2013) Development and evaluation of SoySNP50K, a high-density genoty** array for soybean. PLoS One 8(1):e54985
Song Q, Hyten DL, Jia G, Quigley CV, Fickus EW, Nelson RL, Cregan PB (2015) Fingerprinting soybean germplasm and its utility in genomic research. G3 genes, genomes. Genetics 5(10):1999–2006
Song Q, Jerry J, Jia G, Hyten DL, Vince P, Jackson SA, Schmutz J, Cregan PB (2016) Construction of high resolution genetic linkage maps to improve the soybean genome sequence assembly glyma1.01. BMC Genomics 17(1):33
Sun LJ, Miao ZY, Cai CM, Zhang DJ, Zhao MX, Wu YY, Zhang XL, Swarm SA, Zhou LW, Zhang ZY, Nelson RL, Ma JX (2015) GmHs1-1, encoding a calcineurin-like protein, controls hard-seededness in soybean. Nat Genet 47:939–945
Tajuddin T, Watanabe S, Yamanaka N, Harada K (2003) Analysis of quantitative trait loci for protein and lipid contents in soybean seeds using recombinant inbred lines. Breed Sci 53(2):133–140
Tian ZX, Wang XB, Lee R, Li YH, Specht JE, Nelson RL, Mcclean PE, Qiu LJ, Ma JX (2010) Artificial selection for determinate growth habit in soybean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(19):8563–8568
Wang S, Basten C, Zeng Z (2007) Windows QTL cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC
Wilcox JR (2001) Sixty years of improvement in publicly developed elite soybean lines. Crop Sci 41:1711–1716
Xuan L, Zhang C, Yan T, Wu D, Hussain N, Li Z, Chen M, Pan J, Jiang L (2018) TRANSPARENT TESTA 4-mediated flavonoids negatively affect embryonic fatty acid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 41(12):2773–2790
Yan L, Deng Y, Song Q, Cregan PB, Chen P, Lei Y, Yang C, Chen Q, Di R, Liu B (2016) Identifying and validating a quantitative trait locus on chromosome 14 underlying stearic acid in a soybean landrace. J Crop Improv 30(2):152–164
Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Bi IV, Yamasaki M, Doebley JF, McMullen MD, Gaut BS, Nielsen DM, Holland JB (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association map** that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38(2):203–208
Zhang DJ, Sun LJ, Li S, Wang WD, Ding YH, Swarm SA, Li LH, Wang XT, Tang XM, Zhang ZF, Tian ZX, Brown PJ, Cai CM, Nelson RL, Ma JX (2017) Elevation of soybean seed oil content through selection for seed coat shininess. Nature Plants 4(1):30
Zhou Z, Jiang Y, Wang Z, Gou Z, Lyu J, Li W, Yu Y, Shu L, Zhao Y, Ma Y (2015) Resequencing 302 wild and cultivated accessions identifies genes related to domestication and improvement in soybean. Nat Biotechnol 33(4):408–414
Funding
This study was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31871652 and 31471522), Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System in Hebei, China (HBCT2018090203), and Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (C2015301012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, L., Di, R., Wu, C. et al. Haplotype analysis of a major and stable QTL underlying soybean (Glycine max) seed oil content reveals footprint of artificial selection. Mol Breeding 39, 57 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-019-0951-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-019-0951-1