Abstract
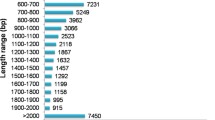
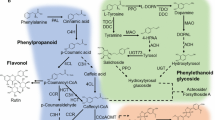
Lactuca indica Linn. (Indian lettuce) is an undomesticated, traditional medicinal plant belonging to the Compositae family. Here, we performed transcriptome assembly and functional annotation of this medicinal plant, along with secondary metabolite analysis. Sesquiterpene lactones, the most abundant secondary metabolites in Lactuca species, are mainly responsible for the medicinal properties of Lactuca. We therefore measured the levels of lactucin, a primary sesquiterpene lactone, in 61 accessions of L. indica, which varied from 1.9 μg/g to 98.7 μg/g. De novo transcriptome assembly yielded 73,300 unigenes from 127 million reads based on 12.9 Gb of data. In total, 28,970 and 34,519 unigenes were annotated using the Swiss-Prot and TAIR10 databases, respectively. The most highly enriched Gene Ontology term for these unigenes was metabolic processes. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis identified 97 significant pathways; the top two pathways were metabolic pathways and biosynthesis of secondary metabolites. Among the 9743 unigenes mapped to 97 significant KEGG pathways, 52 complete unigenes encoding 23 key enzymes in the terpenoid backbone pathway were identified. We identified 1685 transcription factor genes belonging to 53 families and 8830 simple sequence repeat (SSR) loci based on the transcripts. The high-quality transcriptomic and metabolic data on this indigenous herb obtained in this study represent a valuable genetic resource for breeding an L. indica cultivar with excellent pharmaceutical benefits.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EC:
-
Enzyme Commission
- FPKM:
-
Fragments per kilobase Million
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- KAAS:
-
KEGG Automatic Annotation Server
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- KO:
-
KEGG Orthology
- TPM:
-
Transcripts per kilobase million
References
Agarwal P, Reddy MP, Chikara J (2011) WRKY: its structure, evolutionary relationship, DNA-binding selectivity, role in stress tolerance and development of plants. Mol Biol Rep 38:3883–3896. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0504-5
Agrawal AA, Konno K (2009) Latex: a model for understanding mechanisms, ecology, and evolution of plant defense against herbivory. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 40:311–331. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.110308.120307
Bischoff TA, Kelley CJ, Karchesy Y et al (2004) Antimalarial activity of lactucin and lactucopicrin: sesquiterpene lactones isolated from Cichorium intybus L. J Ethnopharmacol 95:455–457. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2004.06.031
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30(15):2114–2120
Cho G, Lee Y, Choi S et al (2016) Variation of sesquiterpene lactones content in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) germplasm. J Korean Soc Int Agric 28:220–226. doi:10.12719/KSIA.2016.28.2.220
Duan L-X, Chen T-L, Li M et al (2012) Use of the metabolomics approach to characterize Chinese medicinal material Huangqi. Mol Plant 5:376–386. doi:10.1093/mp/ssr093
Ellis JR, Burke JM (2007) EST-SSRs as a resource for population genetic analyses. Heredity 99:125–132. doi:10.1038/sj.hdy.6801001
Ferioli F, Manco MA, D’Antuono LF (2015) Variation of sesquiterpene lactones and phenolics in chicory and endive germplasm. J Food Compos Anal 39:77–86. doi:10.1016/j.jfca.2014.11.014
Franssen MCR, Alessandrini L, Terraneo G (2005) Biocatalytic production of flavors and fragrances. Pure Appl Chem 77:273–279. doi:10.1351/pac200577010273
Fu L, Niu B, Zhu Z et al (2012) CD-HIT: accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 28:3150–3152. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bts565
Ghantous A, Gali-Muhtasib H, Vuorela H et al (2010) What made sesquiterpene lactones reach cancer clinical trials? Drug Discov Today 15:668–678. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2010.06.002
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M et al (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29:644–652. doi:10.1038/nbt.1883
Graziani G, Ferracane R, Sambo P et al (2015) Profiling chicory sesquiterpene lactones by high resolution mass spectrometry. Food Res Int 67:193–198. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2014.11.021
Guzman F, Kulcheski FR, Turchetto-Zolet AC, Margis R (2014) De novo assembly of Eugenia uniflora L. transcriptome and identification of genes from the terpenoid biosynthesis pathway. Plant Sci Int J Exp Plant Biol 229:238–246. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.10.003
He J, Giusti MM (2010) Anthocyanins: natural colorants with health-promoting properties. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 1:163–187. doi:10.1146/annurev.food.080708.100754
Hodel RGJ, Gitzendanner MA, Germain-Aubrey CC et al (2016) A new resource for the development of SSR markers: millions of loci from a thousand plant transcriptomes. Appl Plant Sci 4(6):1600024. doi:10.3732/apps.1600024
Hong G-J, Xue X-Y, Mao Y-B et al (2012) Arabidopsis MYC2 interacts with DELLA proteins in regulating sesquiterpene synthase gene expression. Plant Cell 24:2635–2648. doi:10.1105/tpc.112.098749
Hou C-C, Lin S-J, Cheng J-T, Hsu F-L (2003) Antidiabetic dimeric guianolides and a lignan glycoside from Lactuca indica. J Nat Prod 66:625–629. doi:10.1021/np0205349
Kalia RK, Rai MK, Kalia S et al (2011) Microsatellite markers: an overview of the recent progress in plants. Euphytica 177:309–334. doi:10.1007/s10681-010-0286-9
Kroymann J (2011) Natural diversity and adaptation in plant secondary metabolism. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:246–251. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2011.03.021
Lange BM, Ghassemian M (2003) Genome organization in Arabidopsis thaliana: a survey for genes involved in isoprenoid and chlorophyll metabolism. Plant Mol Biol 51:925–948. doi:10.1023/A:1023005504702
Lee E (1995) Serum cholesterol lowering effects and triterpenoids of the herbs of Lactuca indica. Korean J Pharmacogn 26:40–40
Li B, Dewey DC (2011) RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinf 12(1):323
Olsen AN, Ernst HA, Leggio LL, Skriver K (2005) NAC transcription factors: structurally distinct, functionally diverse. Trends Plant Sci 10:79–87. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2004.12.010
Price KR, Dupont MS, Shepherd R et al (1990) Relationship between the chemical and sensory properties of exotic salad crops—coloured lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and chicory (Cichorium intybus). J Sci Food Agric 53:185–192. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740530206
Ramakrishna A, Ravishankar GA (2011) Influence of abiotic stress signals on secondary metabolites in plants. Plant Signal Behav 6:1720–1731. doi:10.4161/psb.6.11.17613
Rodriguez E, Towers GHN, Mitchell JC (1976) Biological activities of sesquiterpene lactones. Phytochemistry 15:1573–1580. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)97430-2
Schulz MH, Zerbino DR, Vingron M, Birney E, (2012) Oases: robust de novo RNA-seq assembly across the dynamic range of expression levels. Bioinformatics 28(8):1086–1092
Seo MW, Yang DS, Kays SJ et al (2009) Sesquiterpene lactones and bitterness in Korean leaf lettuce cultivars. Hortscience 44:246–249
Skibbe M, Qu N, Galis I, Baldwin IT (2008) Induced plant defenses in the natural environment: Nicotiana attenuata WRKY3 and WRKY6 coordinate responses to herbivory. Plant Cell 20:1984–2000. doi:10.1105/tpc.108.058594
Testone G, Mele G, Di Giacomo E et al (2016) Insights into the sesquiterpenoid pathway by metabolic profiling and de novo transcriptome assembly of stem-chicory (Cichorium intybus cultigroup “Catalogna”). Front Plant Sci. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.01676
Thiel T, Michalek W, Varshney RK et al (2003) Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Theor Appl Genet 106:411–422. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-1031-0
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL, Pachter L, (2012) Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 7(3):562–578
Van Beek TA, Maas P, King BM et al (1990) Bitter sesquiterpene lactones from chicory roots. J Agric Food Chem 38:1035–1038. doi:10.1021/jf00094a026
Vranová E, Coman D, Gruissem W (2012) Structure and dynamics of the isoprenoid pathway network. Mol Plant 5:318–333. doi:10.1093/mp/sss015
Wang S-Y, Chang H-N, Lin K-T et al (2003) Antioxidant properties and phytochemical characteristics of extracts from Lactuca indica. J Agric Food Chem 51:1506–1512. doi:10.1021/jf0259415
Xu Y-H, Wang J-W, Wang S et al (2004) Characterization of GaWRKY1, a cotton transcription factor that regulates the sesquiterpene synthase gene (+)-δ-cadinene synthase-A. Plant Physiol 135:507–515. doi:10.1104/pp.104.038612
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Next Generation BioGreen 21 Program (Code No. PJ011026), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 20 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
(DOCX 13 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
(DOCX 12 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
(DOCX 14 kb)
Supplementary Table 5
(DOCX 19 kb)
Supplementary Table 6
(XLSX 18449 kb)
Supplementary Table 7
(DOCX 12 kb)
Supplementary Table 8
(DOCX 12 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 1
(DOCX 913 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
(DOCX 1201 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
(DOCX 131 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
(DOCX 8825 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ha, J., Lee, T., Kim, M.Y. et al. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis of Lactuca indica, a traditional medicinal wild plant. Mol Breeding 37, 112 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-017-0711-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-017-0711-z