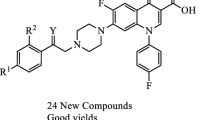
Abstract
Bacterial resistance to fluoroquinolone has been increasing at an alarming rate worldwide. In an attempt to find more potent anti-bacterial agents, an efficient, straightforward protocol was performed to obtain a large substrate scope of novel ciprofloxacin and sarafloxacin analogues conjugated with 4-(arylcarbamoyl)benzyl 7a–ab. All prepared compounds were evaluated for their anti-bacterial activities against three gram-positive strains (Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Staphylococcus aureus, and Enterococcus faecalis) as well as three gram-negative strains (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumonia, and Escherichia coli) through three standard methods including broth microdilution, agar-disc diffusion, and agar-well diffusion assays. Most of the compounds exhibited great to excellent anti-bacterial potencies against MRSA and S. aureus. Among the targeted compounds, derivative 7n exhibited great antibacterial potency, which was noticeably more potent than parent ciprofloxacin. Subsequently, a molecular docking study was performed for this compound to find out its probable binding mode with the active site of S. aureus DNA gyrase (PDB ID: 2XCT).



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the finding of this study are available within the manuscript.
References
Armstrong GL, Conn LA, Pinner RW (1999) Trends in infectious disease mortality in the United States during the 20th century. Jama 281:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.281.1.61
Chambers HF (2005) Community-associated MRSA—resistance and virulence converge. N Engl Med 352:1485–1487. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejme058023
Song R, Wang Y, Wang M, Gao R, Yang T, Yang S, Yang C-G, ** Y, Zou S, Cai J (2020) Design and synthesis of novel desfluoroquinolone-aminopyrimidine hybrids as potent anti-MRSA agents with low hERG activity. Bioorg Chem 103:104176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104176
Moran GJ, Krishnadasan A, Gorwitz RJ, Fosheim GE, McDougal LK, Carey RB, Talan DA (2006) Methicillin-resistant S. aureus infections among patients in the emergency department. N Engl J Med 355:666–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2007.07.004
Moran GJ, Amii RN, Abrahamian FM, Talan DA (2005) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in community-acquired skin infections. Emerg Infect Dis 11:928. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1106.040641
Wilson P, Andrews J, Charlesworth R, Walesby R, Singer M, Farrell D, Robbins M (2003) Linezolid resistance in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother 51:186–188. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkg104
Frazee BW, Lynn J, Charlebois ED, Lambert L, Lowery D, Perdreau-Remington F (2005) High prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in emergency department skin and soft tissue infections. Ann Emerg Med 45:311–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2004.10.011
Fridkin SK, Hageman JC, Morrison M, Sanza LT, Como-Sabetti K, Jernigan JA, Harriman K, Harrison LH, Lynfield R, Farley MM (2005) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus disease in three communities. N Engl J Med 352:1436–1444. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.aog.0000170861.29348.64
Hooper DC (1998) Clinical applications of quinolones. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA 1400:45–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-4781(98)00127-4
Owens RC Jr, Ambrose PG (2000) Clinical use of the fluoroquinolones. Med Clin N Am 84:1447–1469. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-7125(05)70297-2
Drlica K, Hiasa H, Kerns R, Malik M, Mustaev A, Zhao X (2009) Quinolones: action and resistance updated. Curr Top Med Chem 9:981–998. https://doi.org/10.2174/156802609789630947
Aldred KJ, Kerns RJ, Osheroff N (2014) Mechanism of quinolone action and resistance. Biochemistry 53:1565–1574. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi5000564
Dougherty TJ, Beaulieu D, Barrett JF (2001) New quinolones and the impact on resistance. Drug Discov Today 6:529–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1359-6446(01)01760-3
Timsit Y (2011) Local sensing of global DNA topology: from crossover geometry to type II topoisomerase processivity. Nucleic Acids Res 39:8665–8676. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr556
Zhang G-F, Zhang S, Pan B, Liu X, Feng L-S (2018) 4-Quinolone derivatives and their activities against Gram positive pathogens. Eur J Med Chem 143:710–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.11.082
Domagala JM (1994) Structure-activity and structure-side-effect relationships for the quinolone antibacterials. J Antimicrob Chemother 33:685–706. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/33.4.685
Emami S, Shafiee A, Foroumadi A (2006) Structural features of new quinolones and relationship to antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria. Mini Rev Med Chem 6:375–386. https://doi.org/10.2174/138955706776361493
Redgrave LS, Sutton SB, Webber MA, Piddock LJ (2014) Fluoroquinolone resistance: mechanisms, impact on bacteria, and role in evolutionary success. Trends Microbiol 22:438–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2014.04.007
Peterson LR (2001) Quinolone molecular structure-activity relationships: what we have learned about improving antimicrobial activity. Clin Infect Dis 33:S180–S186. https://doi.org/10.1086/321846
Letafat B, Emami S, Mohammadhosseini N, Faramarzi MA, Samadi N, Shafiee A, Foroumadi A (2007) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of new N-[2-(thiophen-3-yl) ethyl] piperazinyl quinolones. Chem Pharm Bull 55:894–898. https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.200748152
Emami S, Foroumadi A, Faramarzi MA, Samadi N (2008) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of quinolone-based compounds containing a coumarin moiety. Arch Pharm 341:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/ardp.200700090
Kumar R, Kumar A, Jain S, Kaushik D (2011) Synthesis, antibacterial evaluation and QSAR studies of 7-[4-(5-aryl-1, 3, 4-oxadiazole-2-yl) piperazinyl] quinolone derivatives. Eur J Med Chem 46:3543–3550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.04.035
Emami S, Ghafouri E, Faramarzi MA, Samadi N, Irannejad H, Foroumadi A (2013) Mannich bases of 7-piperazinylquinolones and kojic acid derivatives: synthesis, in vitro antibacterial activity and in silico study. Eur J Med Chem 68:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.07.032
Sharma PC, Jain A, Yar MS, Pahwa R, Singh J, Goel S (2015) Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of novel analogs of fluoroquinolones annulated with 6-substituted-2-aminobenzothiazoles. Arab J Chem 8:671–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2011.04.008
Dileep K, Polepalli S, Jain N, Buddana SK, Prakasham R, Murty M (2018) Synthesis of novel tetrazole containing hybrid ciprofloxacin and pipemidic acid analogues and preliminary biological evaluation of their antibacterial and antiproliferative activity. Mol Diversity 22:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-017-9795-y
Soleimani E, Torkaman S, Sepahvand H, Ghorbani S (2019) Ciprofloxacin-functionalized magnetic silica nanoparticles: as a reusable catalyst for the synthesis of 1 H-chromeno [2, 3-d] pyrimidine-5-carboxamides and imidazo [1, 2-a] pyridines. Mol Diversity 23:739–749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-018-9907-3
Seliem IA, Panda SS, Girgis AS, Nagy YI, George RF, Fayad W, Fawzy NG, Ibrahim TS, Al-Mahmoudy AM, Sakhuja R (2020) Design, synthesis, antimicrobial, and DNA gyrase inhibitory properties of fluoroquinolone–dichloroacetic acid hybrids. Chem Biol Drug Design 95:248–259. https://doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.13638
Yang P, Luo J-B, Wang Z-Z, Zhang L-L, **e X-B, Shi Q-S, Zhang X-G (2022) Synthesis and in vitro antibacterial activity of N-acylarylhydrazone-ciprofloxacin hybrids as novel fluoroquinolone derivatives. J Mol Struct 1262:133007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.133007
Tan Y-M, Li D, Li F-F, Ansari MF, Fang B, Zhou C-H (2022) Pyrimidine-conjugated fluoroquinolones as new potential broad-spectrum antibacterial agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 73:128885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128885
Ibrahim NM, Fahim SH, Hassan M, Farag AE, Georgey HH (2022) Design and synthesis of ciprofloxacin-sulfonamide hybrids to manipulate ciprofloxacin pharmacological qualities: potency and side effects. Eur J Med Chem 228:114021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.114021
Kumar N, Khanna A, Kaur K, Kaur H, Sharma A, Bedi PMS (2022) Quinoline derivatives volunteering against antimicrobial resistance: rational approaches, design strategies, structure activity relationship and mechanistic insights. Mol Diversity. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-022-10537-y
Mohammed HH, Ali DME, Badr M, Habib AG, Mahmoud AM, Farhan SM, Gany SSHAE, Mohamad SA, Hayallah AM, Abbas SH (2022) Synthesis and molecular docking of new N 4-piperazinyl ciprofloxacin hybrids as antimicrobial DNA gyrase inhibitors. Mol Diversity. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-022-10528-z
Allaka TR, Kummari B, Polkam N, Kuntala N, Chepuri K, Anireddy JS (2022) Novel heterocyclic 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole derivatives of fluoroquinolones as a potent antibacterial agent: synthesis and computational molecular modeling. Mol Diversity 26:1581–1596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-021-10287-3
Aziz HA, El-Saghier AM, Badr M, Abuo-Rahma GE-DA, Shoman ME (2022) Thiazolidine-2, 4-dione-linked ciprofloxacin derivatives with broad-spectrum antibacterial, MRSA and topoisomerase inhibitory activities. Mol Diversity 26:1743–1759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-021-10302-7
Abdel-Aziz SA, Cirnski K, Herrmann J, Abdel-Aal MA, Youssif BG, Salem OI (2023) Novel fluoroquinolone hybrids as dual DNA gyrase and urease inhibitors with potential antibacterial activity: design, synthesis, and biological evaluation. J Mol Struct 1271:134049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134049
Cardoso-Ortiz J, Leyva-Ramos S, Baines KM, Gómez-Durán CFA, Hernández-López H, Palacios-Can FJ, Valcarcel-Gamiño JA, Leyva-Peralta MA, Razo-Hernández RS (2023) Novel ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin-tetrazole hybrids as potential antibacterial and antiviral agents: targeting S. aureus topoisomerase and SARS-CoV-2-MPro. J Mol Struct 1274:134507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134507
Marc G, Araniciu C, Oniga SD, Vlase L, Pîrnău A, Nadăș GC, Novac CȘ, Matei IA, Chifiriuc MC, Măruțescu L (2019) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new piperazin-4-yl-(acetyl-thiazolidine-2, 4-dione) norfloxacin analogues as antimicrobial agents. Molecules 24:3959. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213959
Mustaev A, Malik M, Zhao X, Kurepina N, Luan G, Oppegard LM, Hiasa H, Marks KR, Kerns RJ, Berger JM (2014) Fluoroquinolone-gyrase-DNA complexes: two modes of drug binding. J Biol Chem 289:12300–12312. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.529164
Akahane K, Sekiguchi M, Une T, Osada Y (1989) Structure-epileptogenicity relationship of quinolones with special reference to their interaction with gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor sites. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 33:1704–1708. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.33.10.1704
Goswami M, Mangoli S, Jawali N (2014) Importance of chemical modification at C-7 position of quinolones for glutathione-mediated reversal of antibacterial activity. Int J Antimicrob Agents 43:387–388
Jazayeri S, Moshafi MH, Firoozpour L, Emami S, Rajabalian S, Haddad M, Pahlavanzadeh F, Esnaashari M, Shafiee A, Foroumadi A (2009) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of nitroaryl thiadiazole–gatifloxacin hybrids. Eur J Med Chem 44:1205–1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2008.09.012
Norouzbahari M, Salarinejad S, Güran M, Şanlıtürk G, Emamgholipour Z, Bijanzadeh HR, Toolabi M, Foroumadi A (2020) Design, synthesis, molecular docking study, and antibacterial evaluation of some new fluoroquinolone analogues bearing a quinazolinone moiety. DARU J Pharm Sci 28:661–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40199-020-00373-6
Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK (2016) Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: a review. J Pharm Anal 6:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2015.11.005
Okada Y, Tsuda Y, Tada M, Wanaka K, Okamoto U, Hijikata-Okunomiya A, Okamoto S (2000) Development of potent and selective plasmin and plasma kallikrein inhibitors and studies on the structure-activity relationship. Chem Pharm Bull 48:1964–1972. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.48.1964
Liu Y-F, Wang C-L, Bai Y-J, Han N, Jiao J-P, Qi X-L (2008) A facile total synthesis of imatinib base and its analogues. Org Process Res Dev 12:490–495. https://doi.org/10.1021/op700270n
Khan SA, Saleem K, Khan Z (2008) Synthesis, structure elucidation and antibacterial evaluation of new steroidal-5-en-7-thiazoloquinoxaline derivatives. Eur J Med Chem 43:2257–2261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2007.09.022
Temiz-Arpaci O, Zeyrek CT, Arisoy M, Erol M, Celik I, Kaynak-Onurdag F (2021) Synthesis, quantum mechanical calculations, antimicrobial activities and molecular docking studies of five novel 2, 5-disubstituted benzoxazole derivatives. J Mol Struct 1245:131084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.131084
Funding
This work was supported and funded by Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS); Grant Nos. 9211266096 and 9123120022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Prof. AF designed the study and conducted the experiments. Dr. FP, TS, and MN synthesized the targeted compounds. Dr. FP, Dr. MGD, and Dr. HRB wrote the manuscript and analyzed the characterization data. Dr. LF and Dr. ZE carried out the docking studies. Dr. MN, Dr. MG, and GŞ performed the biological evaluations. Dr. MBT revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study did not involve human subjects and/or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Peytam, F., Norouzbahari, M., Saadattalab, T. et al. Novel fluoroquinolones analogues bearing 4-(arylcarbamoyl)benzyl: design, synthesis, and antibacterial evaluation. Mol Divers (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-023-10676-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-023-10676-w