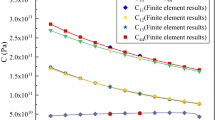
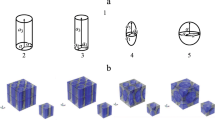
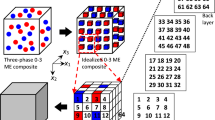
The aim of this paper is to develop a micromechanical method based on a proper representative volume element to investigate the effective coefficients and fully coupled electromagnetoelastic responses for three-dimensional smart composites. Relations between the particulate volume fraction, effective moduli, piezoelectric coefficients, and dielectric coefficients are investigated for the composites. Their effective responses, with account of electric, magnetic, and displacement fields, are analyzed. The numerical results obtained indicate that the overall strains of piezoelectric-piezomagnetic composites strongly depend on variations of the electric and magnetic fields.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Benveniste, “Magnetoelectric effect in fibrous composites with piezoelectric and piezomagnetic phases,” Phys. Rev., 51, 16424-16427 (1995).
F. B. Feng, D. B. Futch, D. H. D. Hsu, and M. V. Manuel, “Effect of phase on debonds strength in shape memory alloy reinforced composites,” Mater. Des., 57, 98-102 (2014).
S. S. Gohari and Z. Vrcelj, “New explicit solution for static shape control of smart laminated cantilever piezo-composite-hybrid plates/beams under thermo-electro-mechanical loads using piezoelectric actuators,” Compos. Struct., 145, 89-112 (2016).
Z. K. Zhang and A. K. Soh, “Micromechanics predictions of the effective moduli of magneto electro elastic composite materials,” Eur. J. Mech. A-Solids, 24, 1054-1067 (2005).
C. H. Lin and A. Muliana, “Micromechanics models for the effective nonlinear electro-mechanical responses of piezoelectric composites,” Acta Mech., 224, 1471-1492 (2013).
J. J. Ye, Y. Y. Qiu, X. F. Chen, Z. Zhai, C. L. Huang, and X. L. Zhang “Numerical investigations of microscopic characteristic influences on the mechanical properties of polymer-matrix composites,” Polym. Compos., 38, No. 7, 2734-2742 (2017).
M. C. Ray, “Micromechanics of piezoelectric composites with improved effective piezoelectric constant,” Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des., 3, 361-371 (2006).
Y. M. Shabana and M. Ristinmaa, “Micromechanical modeling of smart composites considering debonding of reinforcements,” Int. J. Solids Struct., 48, 3209-3216 (2011).
A. V. Georgiades, K. S. Challagulla, and A. L. Kalamkarov. “Modeling of the thermopiezoelastic behavior of prismatic smart composite structures made of orthotropic materials,” Compos. Part B-Eng., 37, 569-582 (2006).
G. Sharifishourabi and R. Alebrahim. “Mechanical properties of potentially-smart carbon/epoxy composites with asymmetrically embedded shape memory wires,” Mater. Design., 59, 486-493 (2014).
J. Sladek, V. Sladek, S. Krahulec, and C. Song, “Micromechanics determination of effective properties of voided magnetoelectroelastic materials,” Compos. Mater. Sci., 116, 103-112 (2016).
T. Tang and S. D. Felicelli. “Numerical characterization of effective fully coupled thermo- electro-magneto- viscoelasticplastic response of smart composites,” Int. J. NonLin. Mech., 71, 52-62 (2015).
Y. Zhong and W. Qin, “Variational asymptotic homogenization of magneto-electro-elastic materials with coated fibers,” Compos. Struct., 133, 300-311 (2015).
M. H. Malakooti and H. A. Sodano, “Multi-inclusion modeling of multiphase piezoelectric composites,” Compos. Part B-Eng., 47, 181-189 (2013).
Z. Zhang and X. Wang, “Effective multi-field properties of electro-magneto-thermoelastic composites estimated by finite element method approach,” Acta Mech. Solida. Sini., 28, 145-155 (2015).
K. S. Challagulla and A. V. Georgiades. Micromechanical analysis of magneto-electro- thermo-elastic composite materials with applications to multilayered structures,” Int. J. Eng. Sci., 49, 85-104 (2011).
J. Lv, “A hierarchical multiscale approach for predicting thermo-electro-mechanical behavior of heterogeneous piezoelectric smart materials,” Compos. Mater. Sci., 87, 88-99 (2014).
J. Aboudi, Mechanics of Composite Materials-A Unified Micromechanical Approach, Elsevier Science Publ. Ltd., London, (1991).
H. Li and B. Zhang, “A new viscoelastic model based on generalized method of cells for fiber-reinforced composites,” Int. J. Plasticity, 65, 22-32 (2015).
J. J. Ye, Y. Y. Qiu, X. F. Chen, and J. Ma, “Initial and final failure strength analysis of composites based on a micromechanical method,” Compos. Struct., 125, 328-335 (2015);.
B. A. Bednarcy and P. W. Yarrington, “Collier Research Corporation, Hampton, Virginia Coupled Thermo-Electro-Magneto-Elastic Respose of Smart Stiffened Panels,” NASA Contractor Report CR-2009-215269 (2009).
J. Aboudi, M. J. Pindera, and S. M.Arnold, “High-fidelity generalized method of cells for inelastic periodic multiphase materials,” NASA Contractor Report TM-2002-211469 (2002).
J. Aboudi, “Micromechanical analysis of fully coupled electro-magneto-thermo-elastic multiphase composites,” Smart Mater. Struct., 10, 867-877 (2001).
K. ** and J. Aboudi, “Macroscopic behavior prediction of multiferroic composites,” Int. J. Eng. Sci., 94, 226-241 (2015).
J. Aboudi, “Micromechanical prediction of the effective behavior of fully coupled electro-magneto-thermo-elasti multiphase composites,” NASA Contractor Report CR-2000-209787 (2000).
J. Aboudi Micromechanical Analyses of Smart Composite Materials, New York: Nova Science Publ.; 2007.
Q. Chen, X. F. Chen, Z. Zhai, and Z. B. Yang, “A new and general formulation of three-dimensional finite-volume micromechanics for particulate reinforced composites with viscoplastic phases,” Compos. Part B-Eng., 85, 216-232, 2016.
Y. Y. Qiu, Y. M. He, J. Ma, X. L. Zhang, and C.L. Huang, “Studying the nonlinear properties and strain-rate sensitivity of SiC short fiber-reinforced Al matrix composites,” Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater., 2015.
T. Tang and W. Yu, “Micromechanical modeling of multiphysical behaviors of smart materials using variational asymptotic method,” Smart Mater. Sturct., 18, 125026-125040 (2009).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51675397, 51505364) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JB150402).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Russian translation published in Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 54, No. 1, pp. 37-50, January-February, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, J.J., Chu, C.C., Wang, Y.K. et al. A Micromechanical Method for the Analysis of Three-Dimensional Smart Composites. Mech Compos Mater 54, 23–32 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-018-9714-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-018-9714-z