Abstract
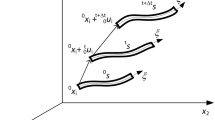
In this paper, the isogeometric cable elements based on B-spline curves are developed for the static analysis of cable structures under conservative static loads. For this, the incremental equation of cable is presented from a continuum theory by employing the total Lagrangian formulation for the geometrically non-linear analysis. The B-spline basis functions are utilized to represent the geometry of cables as well as the numerical approximation of a solution space. The h-, p- and k-refinement strategies are implemented to enrich the basis functions. Therefore, they increase the accuracy of solution fields. The penalty method is also used for the purpose of determining the initial configuration of slack cable as an alternative from-finding approach. The robustness and accuracy of the proposed elements as well as the penalty method developed by study are verified by comparing the predictions with the results given by other authors using different analytical and numerical approaches.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Irvine HM (1992) Cable structures. Dover Publications, New York
O’Brien W, Francis A (1964) Cable movements under two-dimensional loads. J Struct Div ASCE 90:89–123
Jayaraman HB, Knudson WC (1981) A curved element for the analysis of cable structures. Comput Struct 14:325–333
Chunjiang W, Renpeng W, Shilin D, Ruojun Q (2003) A new catenary cable element. Int J Space Struct 18:269–275
Andreu A, Gil L, Roca P (2006) A new deformable catenary element for the analysis of cable net structures. Comput Struct 84:1882–1890
Yang Y, Tsay JY (2007) Geometric nonlinear analysis of cable structures with a two-node cable element by generalized displacement control method. Int J Struct Stab Dyn 7:571–588
Such M, Jimenez-Octavio JR, Carnicero A, Lopez-Garcia O (2009) An approach based on the catenary equation to deal with static analysis of three dimensional cable structures. Eng Struct 31:2162–2170
Thai HT, Kim SE (2011) Nonlinear static and dynamic analysis of cable structures. Finite Elem Anal Des 47:237–246
Impollonia N, Ricciardi G, Saitta F (2011) Statics of elastic cables under 3D point forces. Int J Solids Struct 48:1268–1276
Salehi Ahmad Abad M, Shooshtari A, Esmaeili V, Naghavi Riabi A (2013) Nonlinear analysis of cable structures under general loadings. Finite Elem Anal Des 73:11–19
Gambhir ML, Batchelor Bd (1979) Finite element study of the free vibration of 3-D cable networks. Int J Solids Struct 15:127–136
Ozdemir H (1979) A finite element approach for cable problems. Int J Solids Struct 15:427–437
Coyette JP, Guisset P (1988) Cable network analysis by a nonlinear programming technique. Eng Struct 10:41–46
Ali HM, Abdel-Ghaffar AM (1995) Modeling the nonlinear seismic behavior of cable-stayed bridges with passive control bearings. Comput Struct 54:461–492
Hughes TJR, Cottrell JA, Bazilevs Y (2005) Isogeometric analysis: CAD, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry and mesh refinement. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 194:4135–4195
Aristodemo M (1985) A high-continuity finite element model for two-dimensional elastic problems. Comput Struct 21:987–993
Cuomo M, Contrafatto L, Greco L (2014) A variational model based on isogeometric interpolation for the analysis of cracked bodies. Int J Eng Sci 80:173–188
Bilotta A, Formica G, Turco E (2010) Performance of a high-continuity finite element in three-dimensional elasticity. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng 26:1155–1175
Cazzani A, Malag M, Turco E (2014b) Isogeometric analysis of plane-curved beams. Math Mech Solids 1081286514531265
Cazzani A, Malag M, Turco E, Stochino F (2015) Constitutive models for strongly curved beams in the frame of isogeometric analysis. Math Mech Solids 1081286515577043
Cazzani A, Malag M, Turco E (2014a) Isogeometric analysis: a powerful numerical tool for the elastic analysis of historical masonry arches. Continuum Mech Thermodyn 28:139–156
Greco L, Cuomo M (2013) B-spline interpolation of Kirchhoff–Love space rods. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 256:251–269
Greco L, Cuomo M (2014) An implicit \(G^1\) multi patch B-spline interpolation for KirchhoffLove space rod. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 269:173–197
Raknes SB, Deng X, Bazilevs Y, Benson DJ, Mathisen KM, Kvamsdal T (2013) Isogeometric rotation-free bending-stabilized cables: statics, dynamics, bending strips and coupling with shells. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 263:127–143
Borst RD, Crisfield MA, Remmers JJC, Verhoosel CV (2012) Nonlinear finite element analysis of solids and structures. Wiley, New Jersey
Piegl L, Tiller W (1995) The NURBS book. Monographs in Visual Communications, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Cottrell JA, Hughes TJR, Bazilevs Y (2009) Isogeometric analysis: toward integration of CAD and FEA, 1st edn. Wiley, New Jersey
Liu GR, Quek SS (2013) Finite element method: a practical course. Butterworth-Heinemann, Amsterdam
Desai YM, Popplewell N, Shah AH, Buragohain DN (1988) Geometric nonlinear static analysis of cable supported structures. Comput Struct 29:1001–1009
Greco L, Impollonia N, Cuomo M (2014) A procedure for the static analysis of cable structures following elastic catenary theory. Int J Solids Struct 51:1521–1533
Lewis WJ (1989) The efficiency of numerical methods for the analysis of prestressed nets and pin-jointed frame structures. Comput Struct 33:791–800
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology through NRF-2015R1A2A1A01007535.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thai, S., Kim, NI. & Lee, J. Isogeometric cable elements based on B-spline curves. Meccanica 52, 1219–1237 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-016-0454-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-016-0454-7