Abstract
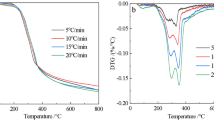
This paper described the thermal decomposition and determined the thermodynamics and kinetics for pyrolysis of soybean de-oiled cake (soya DOC). Authors analysed the physicochemical characteristics of biomass based on proximate, elemental, lignocellulosic balance, calorific value, and FTIR results. The thermogravimetric data of soya DOC were obtained at 10, 20, and 30 °C min‒1 heating rates in an inert system. Thermal analysis of soya DOC reveals that the significant mass loss occurred between 200 and 550 °C temperature ranges. The kinetic parameters (activation energy and pre-exponential factor) and thermodynamic parameters (changes in enthalpy, entropy and Gibb’s free energy) were examined by Kissinger, KAS, OFW, and CR methods. Kissinger method gives Ea 121.05 kJ mol‒1, while OFW and KAS give 162.33 and 151.88 kJ mol‒1, respectively. Results reveal that the Ea depends on decomposition. For soya DOC, the pre-exponential factor is found between 4.12 × 1012 and 6.39 × 1013 min−1, and this range depends on heating rates and conversion. In order to assess the importance of the soya DOC as a pyrolysis feedstock, the activation energy of soya DOC is also compared with the other biomass and the results are found satisfactory. Simulation of soya DOC pyrolysis using data obtained from TGA analysis showed good agreement with experimental data.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- Soya DOC:
-
Soybean de-oiled cake
- HHV:
-
Higher heating value
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- DTG:
-
Differential thermal analysis
- TGA:
-
Thermogravimetric analysis
- TG:
-
Thermogravimetric
- OFW:
-
Ozawa–Flynn–Wall
- KAS:
-
Kissinger–Akahira–Sunose
- CR:
-
Coats–Redfern
- HR:
-
Heating rate
- E a :
-
Activation energy
- VM:
-
Volatile matter
- M:
-
Moisture
- AS :
-
Ash
- FC:
-
Fixed carbon
- C:
-
Carbon
- H:
-
Hydrogen
- S:
-
Sulphur
- N:
-
Nitrogen
- O:
-
Oxygen
- T m :
-
Temperature at maximum decomposition
- g(α):
-
Conversion or decomposition Function
- k(T):
-
Rate constant
- A :
-
Pre-exponential factor
- R :
-
Ideal gas constant
- T :
-
Operating temperature
- α :
-
Decomposition/conversion
- R 2 :
-
Regression coefficient
- β :
-
Heating rate
- \(\Delta H^\circ\) :
-
Enthalpy change
- \(\Delta S^\circ\) :
-
Entropy change
- \(\Delta G^\circ\) :
-
Gibb’s free energy change
- K B :
-
Boltzmann’s constant
- H :
-
Plank’s constant
- n :
-
Reaction order
References
Oladeji JT, Itabiyi EA, Okekunle PO. A comprehensive review of biomass pyrolysis as a process of renewable energy generation. J Natural Sci Res. 2015;5(5):99–105.
Danje S. Fast pyrolysis of corn residues for energy production (doctoral dissertation). Stellenbosch: Stellenbosch University; 2011.
Jayaraman K, Kok MV, Gokalp I. Pyrolysis, combustion and gasification studies of different sized coal particles using TGA-MS. Appl Thermal Engin. 2017;125:1446–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.07.128.
Santos NA, Magriotis ZM, Saczk AA, Fássio GT, Vieira SS. Kinetic study of pyrolysis of castor beans (Ricinus communis L.) press cake: an alternative use for solid waste arising from the biodiesel production. Energy Fuels. 2015;29(4):2351–7.
Varma AK, Mondal P. Physicochemical characterisation and kinetic study of pine needle for pyrolysis process. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124(1):487–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-5126-7.
Zhang J, Zhong Z, Zhang B, Xue Z, Guo F, Wang J. Prediction of kinetic parameters of biomass pyrolysis based on the optimal mixture design method. Clean Techn Environ Policy. 2016;18(5):1621–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-016-1137-8.
Dhyani V, Bhaskar T. A comprehensive review on the pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Renewable Energy. 2018;129:695–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.04.035.
Kok MV, Özgür E. Thermal analysis and kinetics of biomass samples. Fuel Proc Technol. 2013;106:739–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2012.10.010.
Alper K, Tekin K, Karagöz S. Pyrolysis of agricultural residues for bio-oil production. Clean Tech Environ Policy. 2015;17(1):211–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-014-0778-8.
White JE, Catallo WJ, Legendre BL. Biomass pyrolysis kinetics: a comparative critical review with relevant agricultural residue case studies. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2011;91(1):1–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2011.01.004.
Varma AK, Mondal P. Physicochemical characterisation and pyrolysis kinetics of wood sawdust. Energy Sources Part A. 2016;38(17):2536–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2015.1072604.
Varma AK, Mondal P. Physicochemical characterisation and pyrolysis kinetic study of sugarcane bagasse using thermogravimetric analysis. J Energy Resour Technol. 2016;138(5):052205. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4032729.
Ceylan S, Topçu Y. Pyrolysis kinetics of hazelnut husk using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol. 2014;156:182–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.040.
Guerrero MB, da Silva Paula MM, Zaragoza MM, Gutiérrez JS, Velderrain VG, Ortiz AL, Collins-Martínez V. Thermogravimetric study on the pyrolysis kinetics of apple pomace as waste biomass. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2014;39(29):16619–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.06.012.
Islam MA, Asif M, Hameed BH. Pyrolysis kinetics of raw and hydrothermally carbonised Karanj (Pongamia Pinnata) fruit hulls via thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol. 2015;179:227–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.115.
**ang Y, **ang Y, Wang L. Thermal decomposition kinetic of hybrid poplar sawdust as biomass to biofuel. J Environ Chem Engin. 2016;4(3):3303–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.07.009.
Shukla R, Nune SK, Chanda N, Katti K, Mekapothula S, Kulkarni RR, Welshons WV, Kannan R, Katti KV. Soybeans as a phytochemical reservoir for the production and stabilisation of biocompatible gold nanoparticles. Small. 2008;4(9):1425–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200800525.
Soyabean Outlook – October 2021. [Available at https://pjtsau.edu.in/files/AgriMkt/2021/October/Soyabean-October-2021.pdf/, Accessed on 27/05/2022].
The Soybean Processors Association of India (SOPA). [Available at-http://www.sopa.org/statistics/soybean-production-by-state/, Accessed on 16/02/2022].
Ucar S, Ozkan AR. Characterisation of products from the pyrolysis of rapeseed oil cake. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99(18):8771–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.04.040.
Agrawalla A, Kumar S, Singh RK. Pyrolysis of groundnut de-oiled cake and characterisation of the liquid product. Bioresour Technol. 2011;102(22):10711–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.08.113.
Volli V, Singh RK. Production of bio-oil from de-oiled cakes by thermal pyrolysis. Fuel. 2012;96:579–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.01.016.
Volli V, Singh RK. Production of bio-oil from mahua de-oiled cake by thermal pyrolysis. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2012;4(1):013101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3676074.
Muktham R, Ball AS, Bhargava SK, Bankupalli S. Study of thermal behavior of deoiled karanja seed cake biomass: thermogravimetric analysis and pyrolysis kinetics. Energy Sci Engin. 2016;4(1):86–95. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.109.
Huang X, Cao JP, Zhao XY, Wang JX, Fan X, Zhao YP, Wei XY. Pyrolysis kinetics of soybean straw using thermogravimetric analysis. Fuel. 2016;169:93–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.12.011.
Sharma R, Sheth PN. Multi reaction apparent kinetic scheme for the pyrolysis of large size biomass particles using macro-TGA. Energy. 2018;151:1007–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.03.075.
Tahir MH, Mahmood MA, Çakman G, Ceylan S. Pyrolysis of oil extracted safflower seeds: Product evaluation, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Bioresour Technol. 2020;314:123699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123699.
Wang S, Dai G, Yang H, Luo Z. Lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis mechanism: a state-of-the-art review. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2017;62:33–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2017.05.004.
Jayaraman K, Kok MV, Gokalp I. Thermogravimetric and mass spectrometric (TG-MS) analysis and kinetics of coal-biomass blends. Renew Energy. 2017;101:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.08.072.
Jayaraman K, Kök MV, Gökalp I. Combustion mechanism and model free kinetics of different origin coal samples: thermal analysis approach. Energy. 2020;204:117905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.117905.
Blaine RL, Kissinger HE. Homer Kissinger and the Kissinger equation. Thermochim Acta. 2012;540:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2012.04.008.
Lim AC, Chin BL, Jawad ZA, Hii KL. Kinetic analysis of rice husk pyrolysis using Kissinger-Akahira-Sunose (KAS) method. Procedia Engin. 2016;148:1247–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.486.
Thakur LS, Varma AK, Mondal P. Analysis of thermal behavior and pyrolytic characteristics of vetiver grass after phytoremediation through thermogravimetric analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131(3):3053–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6788-0.
Singh G, Varma AK, Almas S, Jana A, Mondal P, Seay J. Pyrolysis kinetic study of waste milk packets using thermogravimetric analysis and product characterisation. J Material Cycles Waste Manag. 2019;21(6):1350–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00891-9.
Saikia N, Bardalai M. Thermal analysis and kinetic parameters determination of biomass using differential thermal gravimetric analysis in N2 atmosphere. Mater Today Proc. 2018;5(1):2146–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.09.212.
Dhaundiyal A, Gangwar J. Kinetics of the thermal decomposition of pine needles. Acta Univ Sapientiae Agric Environ. 2015;7(1):5–22. https://doi.org/10.1515/ausae-2015-0001.
Özsin G, Pütün AE. Kinetics and evolved gas analysis for pyrolysis of food processing wastes using TGA/MS/FT-IR. Waste Manag. 2017;64:315–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.03.020.
Sills DL, Gossett JM. Using FTIR to predict saccharification from enzymatic hydrolysis of alkali pretreated biomasses. Biotechnol Bioenegy. 2012;109(2):353–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23314.
Silverstein RM, Bassler GC. Spectrometric identification of organic compounds. J Chem Edu. 1962;39(11):546. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed039p546.
Zhao Y, Ding M, Dou Y, Fan X, Wang Y, Wei X. Comparative study on the pyrolysis behaviors of corn stalk and pine sawdust using TG-MS. Trans Tian** Univ. 2014;20(2):91–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-014-2233-7.
Slopiecka K, Bartocci P, Fantozzi F. Thermogravimetric analysis and kinetic study of poplar wood pyrolysis. Appl Energy. 2012;97:491–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.12.056.
Sbirrazzuoli N. Advanced isoconversional kinetic analysis for the elucidation of complex reaction mechanisms: a new method for the identification of rate-limiting steps. Molecules. 2019;24(9):1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091683.
Torres-García E, Ramírez-Verduzco LF, Aburto J. Pyrolytic degradation of peanut shell: activation energy dependence on the conversion. Waste Manag. 2020;106:203–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.03.021.
Mabuda AI, Mamphweli NS, Meyer EL. Model free kinetic analysis of biomass/sorbent blends for gasification purposes. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2016;53:1656–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.07.038.
Khawam A, Flanagan DR. Solid-state kinetic models: basics and mathematical fundamentals. J Phys Chem B. 2006;110(35):17315–28. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp062746a.
Zhong D, Zhong Z, Wu L, Ding K, Luo Y, Christie P. Pyrolysis of Sedum plumbizincicola, a zinc and cadmium hyperaccumulator: pyrolysis kinetics, heavy metal behaviour and bio-oil production. Clean Techn Environ Policy. 2016;18(7):2315–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-016-1150-y.
Gajera B, Panwar NL. Pyrolysis and kinetic behaviour of black gram straw using thermogravimetric analysis. Energy Sources Part A Recov Util Environ Eff. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1662138.
Singh S, Sawarkar AN. Thermal decomposition aspects and kinetics of pyrolysis of garlic stalk. Energy Sources Part A Recov Util Environ Eff. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1716891.
Singh RK, Pandey D, Patil T, Sawarkar AN. Pyrolysis of banana leaves biomass: physico-chemical characterisation, thermal decomposition behavior, kinetic and thermodynamic analyses. Bioresour Technol. 2020;310:123464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123464.
Mishra RK, Mohanty K. Kinetic analysis and pyrolysis behaviour of waste biomass towards its bioenergy potential. Bioresour Technol. 2020;311:123480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123480.
Williams CL, Westover TL, Emerson RM, Tumuluru JS, Li C. Sources of biomass feedstock variability and the potential impact on biofuels production. Bioenergy Res. 2016;9(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-015-9694-y.
Zhu F, Feng Q, Xu Y, Liu R, Li K. Kinetics of pyrolysis of ramie fabric wastes from thermogravimetric data. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119(1):651–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4179-3.
Chandrasekaran A, Ramachandran S, Subbiah S. Determination of kinetic parameters in the pyrolysis operation and thermal behavior of Prosopis Juliflora using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol. 2017;233:413–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.119.
Ahmad MS, Mehmood MA, Al Ayed OS, Ye G, Luo H, Ibrahim M, Rashid U, Nehdi IA, Qadir G. Kinetic analyses and pyrolytic behavior of Para grass (Urochloa mutica) for its bioenergy potential. Bioresour Technol. 2017;224:708–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.10.090.
Alhumade H, da Silva JC, Ahmad MS, Çakman G, Yıldız A, Ceylan S, Elkamel A. Investigation of pyrolysis kinetics and thermal behavior of Invasive Reed Canary (Phalaris Arundinacea) for bioenergy potential. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2019;140:385–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2019.04.018.
Gupta GK, Mondal MK. Iso-conversional kinetic and thermodynamic studies of Indian sagwan sawdust pyrolysis for its bioenergy potential. Environ Prog Sustain Energy. 2019;38(4):13131. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13131.
Guida M, Lanaya S, Rbihi Z, Hannioui A. Thermal degradation behaviours of sawdust wood waste: pyrolysis kinetic and mechanism. J Mater Environ Sci. 2019;10:742–55.
Sriram A, Swaminathan G. Pyrolysis of Musa balbisiana flower petal using thermogravimetric studies. Bioresour Technol. 2018;265:236–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.05.043.
Malika A, Jacques N, Fatima B, Mohammed A. Pyrolysis investigation of food wastes by TG-MS-DSC technique. Biomass Conv Bioref. 2016;6(2):161–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-015-0171-9.
Xu Y, Chen B. Investigation of thermodynamic parameters in the pyrolysis conversion of biomass and manure to biochars using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol. 2013;146:485–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.086.
Xu Z, **ao X, Fang P, Ye L, Huang J, Wu H, Tang Z, Chen D. Comparison of combustion and pyrolysis behavior of the peanut shells in air and N2: kinetics, thermodynamics and gas emissions. Sustainability. 2020;12(2):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020464.
Aboulkas A, Nadifiyine M, Benchanaa M, Mokhlisse A. Pyrolysis kinetics of olive residue/plastic mixtures by non-isothermal thermogravimetry. Fuel Proc Technol. 2009;90(5):722–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2009.01.016.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OPB, LST, and AKV planned and designed the research. OPB performed the experiments and analysed the data. LST supervised the work, and so on. LST, AKV, VN, RS, and PM wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bamboriya, O.P., Varma, A.K., Shankar, R. et al. Thermal analysis and determination of kinetics and thermodynamics for pyrolysis of soybean de-oiled cake using thermogravimetric analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim 147, 14381–14392 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11610-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11610-2