Abstract
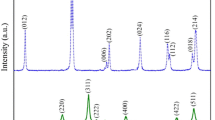
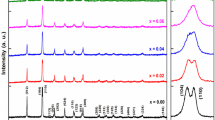
(BiFeO3)1−x(Fe3O4)x nanocomposites were prepared by dispersion of Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NP) into sol–gel synthesised BiFeO3 (BFO) matrix followed by calcination at 500 °C. Samples with x = 0.0, 0.2, 0.33 and 0.5 were investigated using X-ray diffractions (XRD), UV–vis spectroscopy, photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL), transmissions electron microscopes (TEM), electron spin resonance (ESR), vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) and photoelectrochemical (PEC) measurements. Formation of nanocomposites was confirmed by XRD and TEM. The XRD patterns showed presence of both BFO and Fe3O4 phases without any secondary phases. The crystallite size of BFO (39.1–51.1 nm) is much bigger than that of Fe3O4 (10.1–12 nm). Microstrain of BFO decreased for sample x = 0.2 and 0.33 and then increased for x = 0.5. Optical band gap of samples decreased from 2.5 eV for x = 0.0–1.96 eV for sample x = 0.5. The PL emission which centred at 428.1 eV for x = 0.0 increased gradually for samples x = 0.2 and 0.33 and then decreased for x = 0.5. Exchange bias (HEB) was observed for hysteresis loops of all samples, and the highest value of HEB was 38.4 Oe for x = 0.5. The g-values of the nanocomposites, ranged between 2.23 and 2.20, were higher than that of the BFO and Fe3O4 components. The PEC measurement showed the photocurrent density increased with x. Finally, modulations of the physical properties of BFO/Fe3O4 system were analysed and discussed in detail.

(a) Low magnification TEM image of (BiFeO3)x(Fe3O4)x composites showing dispersion of Fe3O4 small particles (some was indicated by white arrow) into BiFeO3 matrix. (b) PL spectra of sample x = 0.5, (c) Top view of PEC setup (where 1 : PC, 2 : Autolab system and 3: halogen lamp) (d) side view of PEC setup (4: PEC cell and 5 : manual chopper) and (e) Photocurrent against voltage under chopped illumination of x = 0.5.
Highlights
-
(BiFeO3)1−x(Fe3O4)x composites were successfully synthesised.
-
Lattice parameter c of BFO decreased with increasing Fe3O4 content, x.
-
(BiFeO3)1−x(Fe3O4)x composites shows fascinating physical properties, such as exchange bias.
-
The (BiFeO3)1−x(Fe3O4)x composites exhibited reduced optical band gap.
-
PEC measurement showed the photocurrent density increased with x.
-
The study showed a presence of interaction between the BiFeO3 and Fe3O4 resulting in modulated physical properties.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu J, Fan Z, **ao D, Zhu J, Wang J (2016) Multiferroic bismuth ferrite-based materials for multifunctional applications: ceramic bulks, thin films and nanostructures. Prog Mater Sci 84:335–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2016.09.001
Catalan G, Scott JF (2009) Physics and applications of bismuth ferrite. Adv Mater 21:2463–2485. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200802849
Martin LW, Crane SP, Chu YH, Holcomb MB, Gajek M, Huijben M, Yang CH, Balke N, Ramesh R (2008) Multiferroics and magnetoelectrics: thin films and nanostructures. J Phys Condens Matter 20. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/20/43/434220
Železný V, Chvostová D, Pajasová L, Vrejoiu I, Alexe M (2010) Optical properties of epitaxial BiFeO3 thin films. Appl Phys A 100:1217–1220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-010-5881-z
Xu J-P, Zhang R-J, Chen Z-H, Wang Z-Y, Zhang F, Yu X, Jiang A-Q, Zheng Y-X, Wang S-Y, Chen L-Y (2014) Optical properties of epitaxial BiFeO3 thin film grown on SrRuO3-buffered SrTiO3 substrate. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:188. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-9-188
Ren Y, Nan F, You L, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Wang J, Su X, Shen M, Fang L (2017) Enhanced photoelectrochemical performance in reduced graphene oxide/BiFeO3 heterostructures. Small 13:1603457–1603. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201603457
Dong H, Wu Z, Wang S, Duan W, Li J (2013) Improving the optical absorption of BiFeO3 for photovoltaic applications via uniaxial compression or biaxial tension. Appl Phys Lett 102. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4793397
Cao D, Wang Z, Nasori, Wen L, Mi Y, Lei Y (2014) Switchable charge-transfer in the photoelectrochemical energy-conversion process of ferroelectric BiFeO3 photoelectrodes. Angew Chemie 126:11207–11211. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201406044
Fan Z, Ji W, Li T, **ao J, Yang P, Ong KP, Zeng K, Yao K, Wang J (2015) Enhanced photovoltaic effects and switchable conduction behavior in BiFe0.6Sc0.4O3 thin films. Acta Mater 88:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2015.01.021
Li Z, Shen Y, Yang, C, Lei Y, Guan Y, Lin PYH, Liu D, Nan C (2013) Significant enhancement in the visible light photocatalytic properties of BiFeO3-graphene nanohybrids. J Mater Chem A 823–829. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ta00141a
Wu H, Xue P, Lu Y, Zhu X (2018) Microstructural, optical and magnetic characterizations of BiFeO3 multiferroic nanoparticles synthesized via a sol-gel process. J Alloy Compd 731:471–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.10.087
Zhang C, Li Y, Chu M, Rong N, **ao P, Zhang Y (2016) Hydrogen-treated BiFeO3 nanoparticles with enhanced photoelectrochemical performance. RSC Adv 6:24760–24767. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA23699A
Xu H-M, Wang H, Shi J, Lin Y, Nan C (2016) Photoelectrochemical performance observed in Mn-doped BiFeO3 heterostructured thin films. Nanomaterials 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110215
Adhlakha N, Yadav KL (2014) Structural, dielectric, magnetic, and optical properties of Ni0.75Zn0.25Fe2O4–BiFeO3 composites. J. Mater Sci 49:4423–4438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8139-x
Ummer RP, Sreekanth P, Raneesh B, Philip R, Rouxel D, Thomas S, Kalarikkal N (2015) Electric, magnetic and optical limiting (short pulse and ultrafast) studies in phase pure (1−x)BiFeO3−xNaNbO3 multiferroic nanocomposite synthesized by the pechini method. RSC Adv 5:67157–67164. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA10422J
Shariq M, Kaur D, Chandel VS (2017) Structural, magnetic and optical properties of mulitiferroic (BiFeO3)1−x(BaTiO3)x solid solutions. Chin J Phys 55:2192–2198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2017.04.021
Choi E-M, Weal E, Bi Z, Wang H, Kursumovic A, Fix T, Blamire MG, MacManus-Driscoll JL (2013) Strong room temperature exchange bias in self-assembled BiFeO3–Fe3O4 nanocomposite heteroepitaxial films. Appl Phys Lett 102:12905. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4773567
Kaur I, Verma NK (2015) Magnetic and electric properties of BFO-NFO nanocomposites. Mater Sci Semicond Process 33:32–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.01.032
Leostean C, Pana O, Stefan M, Popa A, Toloman D, Senila M, Gutoiu S, Macavei S (2018) New properties of Fe3O4@SnO2 core shell nanoparticles following interface charge/spin transfer. Appl Surf Sci 427:192–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.267
Stefan M, Pana O, Leostean C, Bele C, Silipas D, Senila M, Gautron E (2014) Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4–TiO2 core–shell nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 116:114312. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4896070
Yang H, ** C, Mi WB, Bai HL, Chen GF (2012) Electronic and magnetic structure of Fe3O4/BiFeO3 multiferroic superlattices: first principles calculations. J Appl Phys 112:63925. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4755805
Qu TL, Zhao YG, Yu P, Zhao HC, Zhang S, Yang LF (2012) Exchange bias effects in epitaxial Fe3O4/BiFeO3 heterostructures. Appl Phys Lett 100:242410. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4729408
Tripathy SN, Pradhan DK, Mishra KK, Sen S, Palai R, Paulch M, Scott JF, Katiyar RS, Pradhan DK (2015) Phase transition and enhanced magneto-dielectric response in BiFeO3–DyMnO3 multiferroics. J Appl Phys 117:144103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4916927
Chakrabarti K, Sarkar B, Ashok VD, Das K, Chaudhuri SS, Mitra A, De SK (2014) Exchange bias effect in BiFeO3–NiO nanocomposite. J Appl Phys 115:13906. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4861140
Liu H, Guo Y, Guo B, Zhang D (2013) Synthesis and visible-light photocatalysis capability of BiFeO3–(Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3 nanopowders by a sol–gel method. Solid State Sci 19:69–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2013.02.008
Baqiah H, Ibrahim NB, Halim SA, Talib ZA, Flaifel MH, Abdi MH (2017) Conducting mechanisms and magnetic behaviours of Fe-doped In2O3 nanocrystalline films. Results Phys. 7:1115–1121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.03.004
Bai X, Wei J, Tian B, Liu Y, Reiss T, Guiblin N, Gemeiner P, Dkhil B, Infante C, Size I (2016) Effect on optical and photocatalytic properties in BiFeO3 nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 120:3595–3601. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b09945
Pisarev RV, Moskvin AS, Kalashnikova AM, Rasing T (2009) Charge transfer transitions in multiferroic BiFeO3 and related ferrite insulators. Phys Rev B - Condens Matter Mater Phys 79. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.79.235128
Prashanthi K, Thakur G, Thundat T (2012) Surface enhanced strong visible photoluminescence from one-dimensional multiferroic BiFeO3 nanostructures. Surf Sci 606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2012.06.003
Mishra DK, Qi X (2010) Energy levels and photoluminescence properties of nickel-doped bismuth ferrite. J Alloy Compd 504:27–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.05.107
Singh A, Khan ZR, Vilarinho PM, Gupta V, Katiyar RS (2014) Influence of thickness on optical and structural properties of BiFeO3 thin films: PLD grown. Mater Res Bull 49:531–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.08.050
Zhang C, Wang SY, Liu WF, Xu XL, Li X, Zhang H, Gao J, Li DJ (2017) Room temperature exchange bias in multiferroic BiFeO3 nano- and microcrystals with antiferromagnetic core and two-dimensional diluted antiferromagnetic shell. J Nanoparticle Res 19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3880-0
Huang F, Wang Z, Lu X, Zhang J, Min K, Lin W, Ti R, Xu T, He J, Yue C, Zhu J (2013) Peculiar magnetism of BiFeO3 nanoparticles with size approaching the period of the spiral spin structure. Sci Rep 3:2907, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02907, http://www.nature.com/articles/srep02907#supplementary-information
Mazumdar SC, Khan MNI, Islam MF, Hossain AKMA (2016) Tuning of magnetoelectric coupling in (1−y)Bi0.8Dy0.2FeO3–yNi0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 multiferroic composites. J Magn Magn Mater 401:443–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.10.051
Liu XF, Li P, ** C, Bai HL (2011) Enhancement of the magnetization in the Fe3O4/BiFeO3 epitaxial heterostructures fabricated by magnetron sputtering. Appl Phys Lett 99:182511. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3659483
Sharma A, Kotnala RK, Negi NS (2014) Observation of multiferroic properties and magnetoelectric effect in (x)CoFe2O4−(1−x)Pb0.7Ca0.3TiO3 composites. J Alloy Compd 582:628–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.08.087
Salami M, Mirzaee O, Honarbakhsh-Raouf A, Lavasani SANH, Moghadam AK (2017) Structural, morphological and magnetic parameters investigation of multiferroic (1−x)Bi2Fe4O9–xCoFe2O4 nanocomposite ceramics. Ceram Int 43:14701–14709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.07.199
Baqiah H, Talib ZA, Shaari AH, Tamchek N, Ibrahim NB (2018) Synthesis, optical and magnetic behavior of (BiFeO3)1−x(α-Fe2O3)x nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng B 231:5–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2018.03.002
Holi AM, Zainal Z, Talib ZA, Lim HN, Yap CC, Chang SK, Ayal AK (2016) Hydrothermal deposition of CdS on vertically aligned ZnO nanorods for photoelectrochemical solar cell application. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27:7353–7360
Acknowledgements
The Universiti Putra Malaysia supported this research under grant Putra No GP-IPB/2014/9449900 and the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (MOHE) under grant FRGS grant/01-01-16-1834FR/5524941.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baqiah, H., Talib, Z.A., Shaari, A.H. et al. Structural, optical, magnetic and photoelectrochemical properties of (BiFeO3)1−x(Fe3O4)x nanocomposites. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 91, 624–633 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05053-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05053-9