Abstract
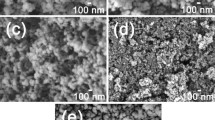
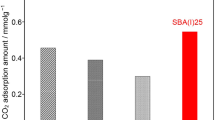
Amine hybrid titania/silsesquioxane composite aerogel (AHTSA) was prepared by an one-pot sol–gel process without any catalyst. The sol-gel reaction mechanism of AHTSA was proposed. The use of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) plays as an “internal catalyst” and promotes the formation of gel during sol–gel process. The morphology, microstructure, pore structure and CO2 capture performances of AHTSA were investigated. AHTSA exhibits microstructure of the typical silica aerogels with colloidal structure. Moreover, AHTSA has a large number of macropores which favor the CO2 adsorption. Thermogravimetric analysis reveals that AHTSA has a high CO2/N2 selectivity in CO2/N2 mixture gas. CO2 adsorption capacity with dry and humid 1 vol% CO2 is as high as 4.19 and 5.04 mmol/g, respectively. Correspondingly, amine efficiency under dry and humid conditions is 0.37 and 0.44, respectively. AHTSA has very short adsorption halftime below 4 min, and its CO2 adsorption capacity do not show obvious attenuation after 30 adsorption-regeneration cycles, indicating AHTSA is a dynamic and regenerable sorbent.
Graphical abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ren H, Zhu J, Bi Y, Xu Y, Zhang L (2016) One-step fabrication of transparent hydrophobic silica aerogels via in situ surface modification in drying process. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 80(3):635–641
Zu G, Shen J, Wang W, Zou L, Lian Y, Zhang Z (2015) Silica-titania composite aerogel photocatalysts by chemical liquid deposition of titania onto nanoporous silica scaffolds. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(9):5400–5409
Zu G, Shen J, Wang W, Lian Y, Zou L, Zhang Y, Liu B, Zhang F (2015) Heat-resistant, strong titania aerogels achieved by supercritical deposition. J Supercrit Fluids 106:145–151
Kong Y, Zhong Y, Shen X, Cui S, Yang M, Teng K, Zhang J (2012) Facile synthesis of resorcinol–formaldehyde/silica composite aerogels and their transformation to monolithic carbon/silica and carbon/silicon carbide composite aerogels. J Non-Cryst Solids 358(23):3150–3155
Firoozmandan M, Moghaddas J, Yasrebi N (2016) Performance of water glass-based silica aerogel for adsorption of phenol from aqueous solution. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 79(1):67–75
Liu H, Chu P, Li H, Zhang H, Li J (2016) Novel three-dimensional halloysite nanotubes/silica composite aerogels with enhanced mechanical strength and low thermal conductivity prepared at ambient pressure. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 80(3):651–659
Vareda JP, Matias T, Fonseca AC, Durães L (2016) Flexible acrylate-grafted silica aerogels for insulation purposes: comparison of reinforcement strategies. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 80(2):306–317
Yousefi Amiri T, Moghaddas J, Rahmani Khajeh S (2016) Silica aerogel-supported copper catalyst prepared via ambient pressure drying process. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 77(3):627–635
Cui S, Cheng W, Shen X, Fan M, Russell AT, Wu Z, Yi X (2011) Mesoporous amine-modified SiO2 aerogel: a potential CO2 sorbent. Energy Environ Sci 4(6):2070–2074
Wörmeyer K, Smirnova I (2013) Adsorption of CO2, moisture and ethanol at low partial pressure using aminofunctionalised silica aerogels. Chem Eng J 225:350–357
Begag R, Krutka H, Dong W, Mihalcik D, Rhine W, Gould G, Baldic J, Nahass P (2013) Superhydrophobic amine functionalized aerogels as sorbents for CO2 capture. Greenhouse Gases Sci Technol 3(1):30–39
Linneen NN, Pfeffer R, Lin Y (2013) Amine distribution and carbon dioxide sorption performance of amine coated silica aerogel sorbents: effect of synthesis methods. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(41):14671–14679
Linneen N, Pfeffer R, Lin Y (2013) CO2 capture using particulate silica aerogel immobilized with tetraethylenepentamine. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 176:123–131
Wang Z, Dai Z, Wu J, Zhao N, Xu J (2013) Vacuum‐dried robust bridged silsesquioxane aerogels. Adv Mater 25(32):4494–4497
Kong Y, Jiang G, Fan M, Shen X, Cui S (2014) Use of one-pot wet gel or precursor preparation and supercritical drying procedure for development of a high-performance CO2 sorbent. RSC Adv 4(82):43448–43453
Kong Y, Jiang G, Fan M, Shen X, Cui S, Russell AG (2014) A new aerogel based CO2 adsorbent developed using a simple sol-gel method along with supercritical drying. Chem Commun 50(81):12158–12161
Kong Y, Shen X, Fan M, Yang M, Cui S (2016) Dynamic capture of low-concentration CO2 on amine hybrid silsesquioxane aerogel. Chem Eng J 283:1059–1068
Kong Y, Shen X, Cui S, Fan M (2015) Facile synthesis of an amine hybrid aerogel with high adsorption efficiency and regenerability for air capture via a solvothermal-assisted sol–gel process and supercritical drying. Green Chem 17:3436–3445
Kong Y, Shen X, Cui S, Fan M (2015) Development of monolithic adsorbent via polymeric sol–gel process for low-concentration CO2 capture. Appl Energy 147:308–317
Kong Y, Shen X, Cui S (2016) Amine hybrid zirconia/silica composite aerogel for low-concentration CO2 capture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 236:269–276
Kong Y, Shen X, Cui S, Fan M (2014) Use of monolithic silicon carbide aerogel as a reusable support for development of regenerable CO2 adsorbent. RSC Adv 4(109):64193–64199
Marques LM, Carrott PJM, Carrott MMLR (2013) Amine-modified carbon aerogels for CO2 capture. Adsorpt Sci Technol 31(2–3):223–232
Kong Y, Jiang G, Wu Y, Cui S, Shen X (2016) Amine hybrid aerogel for high-efficiency CO2 capture: effect of amine loading and CO concentration. Chem Eng J 306:362–368
Hüsing N, Schubert U, Mezei R, Fratzl P, Riegel B, Kiefer W, Kohler D, Mader W (1999) Formation and structure of gel networks from Si(OEt)4/(MeO)3Si(CH2)3NR'2 mixtures (NR'2=NH2 or NHCH2CH2NH2). Chem Mater 11(2):451–457
Pierre AC, Pajonk GM (2002) Chemistry of aerogels and their applications. Chem Rev 102(11):4243–4265
Livage J, Henry M, Sanchez C (1988) Sol-gel chemistry of transition metal oxides. Prog Solid State Chem 18(4):259–341
Maleki H (2016) Recent advances in aerogels for environmental remediation applications: a review. Chem Eng J 300:98–118
Schmidt H, Scholze H, Kaiser A (1984) Principles of hydrolysis and condensation reaction of alkoxysilanes. J Non-Cryst Solids 63(1):1–11
Buckley AM, Greenblatt M (1994) The sol-gel preparation of silica gels. J Chem Educ 71(7):599
Zelenak V, Badanicova M, Halamova D, Cejka J, Zukal A, Murafa N, Goerigk G (2008) Amine-modified ordered mesoporous silica: Effect of pore size on carbon dioxide capture. Chem Eng J 144(2):336–342
He L, Fan M, Dutcher B, Cui S, Shen X, Kong Y, Russell AG, McCurdy P (2012) Dynamic separation of ultradilute CO2 with a nanoporous amine-based sorbent. Chem Eng J 189:13–23
Irani M, Fan M, Ismail H, Tuwati A, Dutcher B, Russell AG (2015) Modified nanosepiolite as an inexpensive support of tetraethylenepentamine for CO2 sorption. Nano Energy 11:235–246
Wang W, **ao J, Wei X, Ding J, Wang X, Song C (2014) Development of a new clay supported polyethylenimine composite for CO2 capture. Appl Energy 113:334–341
Liu ZL, Teng Y, Zhang K, Chen HG, Yang YP (2015) CO2 adsorption performance of different amine-based siliceous MCM-41 materials. J Energy Chem 24(3):322–330
Alhwaige AA, Ishida H, Qutubuddin S (2016) Carbon aerogels with excellent CO2 adsorption capacity synthesized from clay-reinforced biobased chitosan-polybenzoxazine nanocomposites. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4(3):1286–1295
Masika E, Mokaya R (2013) High surface area metal salt templated carbon aerogels via a simple subcritical drying route: preparation and CO2 uptake properties. RSC Adv 3(39):17677–17681
Chai SH, Liu ZM, Huang K, Tan S, Dai S (2016) Amine functionalization of microsized and nanosized mesoporous carbons for carbon dioxide capture. Ind Eng Chem Res 55(27):7355–7361
Rezaei F, Sakwa-Novak MA, Bali S, Duncanson DM, Jones CW (2015) Sha** amine-based solid CO2 adsorbents: effects of pelletization pressure on the physical and chemical properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 204:34–42
Choi S, Drese JH, Jones CW (2009) Adsorbent materials for carbon dioxide capture from large anthropogenic point sources. ChemSusChem 2(9):796–854
Planas N, Dzubak AL, Poloni R, Lin L-C, McManus A, McDonald TM, Neaton JB, Long JR, Smit B, Gagliardi L (2013) The mechanism of carbon dioxide adsorption in an alkylamine-functionalized metal–organic framework. J Am Chem Soc 135(20):7402–7405
Sakwa-Novak MA, Tan S, Jones CW (2015) Role of additives in composite PEI/oxide CO2 adsorbents: Enhancement in the amine efficiency of supported PEI by PEG in CO2 capture from simulated ambient air. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(44):24748–24759
Chen Z, Deng S, Wei H, Wang B, Huang J, Yu G (2013) Polyethylenimine-impregnated resin for high CO2 adsorption: an efficient adsorbent for CO2 capture from simulated flue gas and ambient air. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(15):6937–6945
Chaikittisilp W, Khunsupat R, Chen TT, Jones CW (2011) Poly(allylamine)–mesoporous silica composite materials for CO2 capture from simulated flue gas or ambient air. Ind Eng Chem Res 50(24):14203–14210
Yue MB, Sun LB, Cao Y, Wang Y, Wang ZJ, Zhu JH (2008) Efficient CO2 capturer derived from as-synthesized MCM-41 modified with amine. Chem Eur J 14(11):3442–3451
Drese JH, Choi S, Lively RP, Koros WJ, Fauth DJ, Gray ML, Jones CW (2009) Synthesis–structure–property relationships for hyperbranched aminosilica CO2 adsorbents. Adv Funct Mater 19(23):3821–3832
Sayari A, Belmabkhout Y (2010) Stabilization of amine-containing CO2 adsorbents: dramatic effect of water vapor. J Am Chem Soc 132(18):6312–6314
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51602151), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institution (PAPD)—China, the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province—China (BK20161003), the Natural Science Research Project in Colleges and Universities of Jiangsu Province—China (16KJB430014), and the Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Coal-based CO2 Capture and Geological Storage, Jiangsu Province (2016B02)—China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, Y., Zhang, J. & Shen, X. One-pot sol–gel synthesis of amine hybrid titania/silsesquioxane composite aerogel for CO2 capture. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 84, 422–431 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4516-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4516-7