Abstract
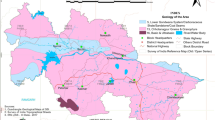
Present work deals with radon (Rn-222) activity measurement of deep tube-well water samples collected from Raghunathpur and Jhalda, two municipalities of Purulia district, West Bengal, India. Concentration of Rn-222 in water samples collected from Raghunathpur municipality vary from 11.82 ± 0.95 to 155.64 ± 2.33 Bq/l with an average of 49.78 ± 1.81 Bq/l, whereas for Jhalda municipality the concentrations vary from 12.08 ± 1.02 to 74.74 ± 2.12 Bq/l with an average of 39.06 ± 1.40 Bq/l. The total annual effective dose associated with Rn-222 activity has been estimated for three different categories viz. adults, children and infants in terms of inhalation and ingestion. Additionally, pH and the major cations (Na+, K+, Li+, Ca2+) present in the water samples are also measured to observe the possible correlation with the Rn-222 activity. The results indicate that the groundwater in these two municipalities are radiologically safe in terms of Rn-222 and thus do not provide significant health threats to the local inhabitants.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinnagbe DM, Orosun MM, Orosun RO, Osanyinlusi O, Yusuk KA, Akinyose FC, Ige SO (2018) Assessment of Radon concentration of ground water in Ijero Ekiti. MJS 11:32–41
Singla AK, Kansal S, Mehra R (2021) Quantification of radon contamination in drinking water of Rajasthan, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 327:1149–1157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07599-x
Naskar AK, Gazi M, Barman C, Chowdhury S, Mondal M, Ghosh D, Deb A (2018) Estimation of underground water radon danger in Bakreswar and Tantloi Geothermal Region, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 315:273–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5668-1
Mitra S, Chowdhury S, Mukherjee J, Sutradhar S, Mondal S, Barman C, Deb A (2021) Assessment of radon (222 Rn) activity in groundwater and soil-gas in Purulia district, West Bengal, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 330:1331–1338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07989-1
Mukherjee J, Mitra S, Sutradhar S, Chowdhury S, Mondal S, Deb A, Barman C (2023) Analysis of radon concentration in ground water and estimation of associated health risks in Purulia Municipality, West Bengal. India Arab J Geosci 16(2):125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11202-w
Chowdhury S, Barman C, Deb A, Raha S, Ghose D (2019) Study of variation of soil radon exhalation rate with meteorological parameters in Bakreswar-Tantloi geothermal region of West Bengal and Jharkhand, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 319:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-6286-2
Naskar AK, Gazi M, Barman C, Chowdhury S, Akhter J, Mondal M, Deb A (2017) Assessment of health hazards due to water radon around Bakreswar area. Int J Res Eng 7:1–9
Duggal V, Sharma S, Srivastava AK, Mehra R (2018) Measurement of radon concentration in drinking water in Bhiwani district of Haryana. J Geol Soc India 91:700–703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-0926-6
Naskar AK, Gazi M, Mondal M, Deb A (2022) Water radon risk in Susunia hill area: an assessment in terms of radiation dose. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(8):11160–11171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16362-4
World Health Organization (2004) Guidelines for drinking-water quality (Vol.1) World Health Organization.
Council Directive 2013/51/EURATOM (2013) Laying down requirements for the protection of the health of the general public with regard to radioactive substances in water intended for human consumption. Official J Eur Union L 296:12–21
Nalukudiparambil J, Gopinath G, Ramakrishnan RT, Surendran AK (2021) Groundwater radon (222 Rn) assessment of a coastal city in the high background radiation area (HBRA), India. Arab J Geosci 14:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07082-7
Bertin C, Bourg AC (1994) Radon-222 and chloride as natural tracers of the infiltration of river water into an alluvial aquifer in which there is significant river/groundwater mixing. Environ Sci Technol 28(5):794–798. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00054a008
Hoehn E, Von Gunten HR (1989) Radon in groundwater: a tool to assess infiltration from surface waters to aquifers. Water Resour Res 25(8):1795–1803. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR025i008p01795
Ramola RC, Kandari MS, Rawat RBS, Ramachandran TV, Choubey VM (1998) A study of seasonal variations of radon levels in different types of houses. J Environ Radioact 39(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0265-931X(97)00049-0
Shilpa GM, Anandaram BN, Mohankumari TL (2017) Measurement of 222Rn concentration in drinking water in the environs of Thirthahalli taluk, Karnataka. India J Radiat Res Appl Sci 10(3):262–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2017.05.007
Kullab MK, Al-Bataina BA, Ismail AM, Abumurad KM (2001) Seasonal variation of radon-222 concentrations in specific locations in Jordan. Radiat Meas 34(1–6):361–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1350-4487(01)00186-X
Al-Khateeb HM, Nuseirat M, Aljarrah K, Al-Akhras MAH, Bani-Salameh H (2017) Seasonal variation of indoor radon concentration in a desert climate. Appl Radiat Isot 130:49–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2017.08.017
Rani S, Kansal S, Singla AK, Mehra R (2021) Radiological risk assessment to the public due to the presence of radon in water of Barnala district, Punjab, India. Environ Geochem Health 43(12):5011–5024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01012-y
Miklyaev PS, Petrova TB (2021) Study of abnormal seasonal variations in the radon exhalation rate in a fault zone. Geochem Int 59:435–447. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702921040042
Girija Rengan A, Joseph S, Sellamuthu S (2022) Seasonal and geological controls of radon (222Rn) in groundwater of Vamanapuram river basin, SW India. Geocarto Int 1:26. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2022.2142961
Sanyal S, Sengupta P (2012) Metamorphic evolution of the Chotanagpur granite gneiss complex of the east Indian shield: current status. Geol Soc Lond 365(1):117–145. https://doi.org/10.1144/SP365.7
Acharya T, Nag SK (2013) Study of groundwater prospects of the crystalline rocks in Purulia District, West Bengal, India using remote sensing data. Earth Resources 1(2):54–59
Acharya T, Nag SK, Basumallik S (2012) Hydraulic significance of fracture correlated lineaments in precambrian rocks in Purulia district. West Bengal J Geol Soc India 80(5):723–730
Baidya TK (1992) Apatite-magnetite deposit in the Chhotanagpur Gneissic Complex, Panrkidih area, Purulia District. West Bengal Indian Jour Geol 64(1):88–95
Gupta A, Basu A (2000) North Singhbhum Proterozoic mobile belt Eastern India-A review. Geol Surv India Spec Publ no.55, pp 195–226
Dolui G, Chatterjee S, Das CN (2016) Geophysical and geochemical alteration of rocks in granitic profiles during intense weathering in southern Purulia district, West Bengal, India. Model Earth Syst Environ 2:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-016-0188-5
https://weatherspark.com/s/111226/1/Average-Summer-Weather-in-Raghunathpur-India
Das B (2018) A Geo-spatial prelude of water prospect and their sustainable utilisation in drought prone region of West Bengal: a case study of Raghunathpur-I Block, Purulia District. Int J Res Anal Rev 5(3):297–303
Chakraborty K, Ray A, Chakraborti TM, Deb GK, Mandal A, Kimura K, Mukhopadhyay S (2022) Petrology, geochemistry and U-Pb zircon geochronology of alkali granites of Jhalda, eastern India and their possible linkage to Rodinia Supercontinent. J Earth Syst Sci 131(4):253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-022-01989-9
https://drive.google.com/file/d/17g16**6lapac87Os1d0bNHX30l-w-XZx/view?usp=share_link
AlphaGuardManual: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ZzKVpL1PWEuFlg2m7dHfWXFCtMG4fHM0/view?usp=sharing
AquaKIT Manual: https://www.bertin-instruments.com/wp-content/uploads/secured-file/AquaKIT-Brief-Instruction_E.pdf
Cothern CR (2014) Radon, radium, and uranium in drinking water. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Binesh A, Pourhabib Z (2011) Evaluation of the radiation dose from radon ingestion and inhalation in springs, wells, rivers and drinking water of Ramsar in Iran. Int J Adv Sci Technol 1:170–172
Duggal V, Sharma S, Mehra R (2020) Risk assessment of radon in drinking water in Khetri Copper Belt of Rajasthan, India. Chemosphere 239:124782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124782
Ademola JA, Oyeleke OA (2017) Radon-222 in groundwater and effective dose due to ingestion and inhalation in the city of Ibadan. Nigeria J Radiol Prot 37(1):189. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6498/37/1/189
UNSCEAR (2000) Sources and effects of atomic radiation, report to General Assembly, Annex B. United Nations, New York
UNSCER (2008) United Nations. Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. Report of the United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation: Fifty-sixth Session (10–18 July 2008) (No. 46). United Nations Publications
Mittal S, Rani A, Mehra R (2016) Estimation of radon concentration in soil and groundwater samples of Northern Rajasthan, India. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 9(2):125–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.10.006
World Health Organization (1993) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edition, World Health Organization
NYS:DoH. https://www.health.ny.gov/environmental/water/drinking/salt_drinkingwater.htm
Elango L, Kannan R (2007) Chapter 11 Rock-water interaction and its control on chemical composition of groundwater. Dev Environ Sci 5:229–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-8177(07)05011-5
Telahigue F, Agoubi B, Souid F, Kharroubi A (2018) Groundwater chemistry and radon-222 distribution in Jerba Island, Tunisia. J Environ Radioact 182:74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2017.11.025
Daniele L, Vallejos Á, Corbella M, Molina L, Pulido-Bosch A (2013) Hydrogeochemistry and geochemical simulations to assess water–rock interactions in complex carbonate aquifers: the case of Aguadulce (SE Spain). Appl Geochemistry 29:43–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.11.011
Kumar M, Puri A (2012) A review of permissible limits of drinking water. Indian J Occup Environ Med 16(1):40. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5278.99696
Maoui A, Kherici N, Derradji F (2010) Hydrochemistry of an Albian sandstone aquifer in a semi arid region, Ain oussera, Algeria. Environ Earth Sci 60:689–701
Press WH, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT, Flannery BP (2007) Numerical recipes 3rd edition: the art of scientific computing. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kim HY (2013) Statistical notes for clinical researchers: assessing normal distribution (2) using skewness and kurtosis. Restor Dent Endod 38(1):52–54. https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.52
Sharma C, Ojha CSP (2020) Statistical parameters of hydrometeorological variables: standard deviation, SNR, skewness and kurtosis. In: Advances in water resources engineering and management: select proceedings of TRACE 2018. Springer Singapore, pp 59–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8181-2_5
Cucu MI, Dupleac D (2021) The contribution of the radioactive gas, radon, to the effective dose received by the population of Mioveni City, Arges County. Romania Educ Res (IJMCER) 3(4):131–139
Tan W, Li Y, Tan K, **e Y, Han S, Wang P (2019) Distribution of radon and risk assessment of its radiation dose in groundwater drinking for village people nearby the W-polymetallic metallogenic district at Dongpo in southern Hunan province, China. Appl Radiat Isot 151:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2019.05.008
Qadir RW, Asaad N, Qadir KW, Ahmad ST (2021) Relationship between radon concentration and physicochemical parameters in groundwater of Erbil city. Iraq J Radiat Res Appl Sci 14(1):61–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/16878507.2020.1856588
Rahimi M, Abadi AAM, Koopaei LJ (2022) Radon concentration in groundwater, its relation with geological structure and some physicochemical parameters of Zarand in Iran. Appl Radiat Isot 185:110223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2022.110223
Romano D, Magazù S, Sabatino G, Di Bella M, Tripodo A, Nania G, Gattuso A, Italiano F (2022) Radon concentration in groundwater of north-eastern Sicily (Italy). J Instrum 17(09):P09003. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-0221/17/09/P09003
Bem H, Plota U, Staniszewska M, Bem EM, Mazurek D (2014) Radon (222Rn) in underground drinking water supplies of the Southern Greater Poland Region. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 299:1307–1312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-013-2912-1
Branco R, Cruz JV, Silva C, Coutinho R, Andrade C, Zanon V (2021) Radon (222 Rn) occurrence in groundwater bodies on São Miguel Island (Azores archipelago, Portugal). Environ Earth Sci 80:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09906-x
Kumar M, Kumar P, Agrawal A, Sahoo BK (2022) Radon concentration measurement and effective dose assessment in drinking groundwater for the adult population in the surrounding area of a thermal power plant. J Water Health 20(3):551–559. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2022.265
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Sidho-Kanho-Birsha University for providing the essential infrastructural facility and also the local people of the area under study for their cooperation. CB acknowledges the financial assistance from Department of Science & Technology-Fund for Improvement of Science &Technology Infrastructure (SR/FST/PS-1/2020/159) New Delhi, India and RUSA grant of SKBU, University Grant Commissions-Faculty Research Promotion Scheme Start-up-Grant [(No.F.30-557/2021(BSR) Dated: 21 Jan, 2022)], seed grant of faculty research, SKBU (R/847/SKBU/2022 dated 20th July, 2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could have influenced this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, J., Mitra, S., Sutradhar, S. et al. Radon (Rn-222) activity measurement in ground water and associated dose estimation in Raghunathpur and Jhalda municipalities of Purulia district, West Bengal, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 333, 1427–1441 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09041-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-023-09041-w