Abstract
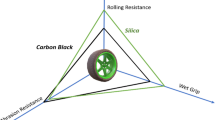
The partial or total replacement of carbon black by silica fillers is initiated through various techniques for environment-friendly, smart, and fuel-efficient NR composites for high-end dynamic applications like tyre tread. The smart properties such as low rolling resistance, better wet skid resistance, and abrasion resistance as well as noise reduction, create tyre tread compounds with superior performance. The endeavour to maximise the incorporation of eco-friendly ingredients like silica filler in rubber compound associates to produce a green tyre product indeed. The present review encompasses those approaches with a substantial contribution in the area along with critical insights in the respective efforts. Initially, the various types of commercially available silica fillers are discussed in brief, followed by the various approaches for surface modification in detail. Finally, the miscellaneous initiatives along with their achievements and drawbacks are included under five strategic verticals for better understanding along with vital remarks.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data and code availability
Available on special request.
References
Babaso PN, Sharanagouda H (2017) Rice husk and its applications: review. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 6:1144–1156. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.610.138
Intharapat P, Kongnoo A, Kateungngan K (2013) The potential of chicken eggshell waste as a bio-filler filled Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) composite and its properties. J Polym Environ 21:245–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-012-0475-9
Ren X, Geng Y, Soboyejo ABO, Cornish K (2019) Reinforced mechanical properties of functionalized silica and eggshell filled guayule natural rubber composites. Rubber Chem Technol 14–20. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.19.81485
Katueangngan K, Tulyapitak T, Saetung A et al (2016) Renewable interfacial modifier for silica filled natural rubber compound. Procedia Chem 19:447–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2016.03.037
Ngeow YW, Chapman AV, Heng JYY et al (2019) Characterization of silica modified with silanes by using thermogravimetric analysis combined with infrared detection. Rubber Chem Technol 92:237–262. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.18.82626
Tolnai G, Csempesz F, Kabai-Faix M et al (2007) Preparation and characterization of surface-modified silica-nanoparticles. Langmuir 17:2683–2687. https://doi.org/10.1021/la0007372
Castellano M, Conzatti L, Turturro A et al (2007) Influence of the silane modifiers on the surface thermodynamic characteristics and dispersion of the silica into elastomer compounds. J Phys Chem B 111:4495–4502. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0702144
Kang T, Jang I, Oh SG (2016) Surface modification of silica nanoparticles using phenyl trimethoxy silane and their dispersion stability in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 501:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.04.060
Sattayanurak S, Noordermeer JWM, Sahakaro K et al (2019) Silica-reinforced natural rubber: synergistic effects by addition of small amounts of secondary fillers to silica-reinforced natural rubber tire tread compounds. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2019:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5891051
Qiao B, Wang TJ, Gao H, ** Y (2015) High density silanization of nano-silica particles using γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES). Appl Surf Sci 351:646–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.05.174
Vieira T, Ferreira RP, Kuchiishi AK et al (2015) Evaluation of friction mechanisms and wear rates on rubber tire materials by low-cost laboratory tests. Wear 328–329:556–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2015.04.001
AbdulRafiu A, Sovacool BK, Daniels C (2022) The dynamics of global public research funding on climate change, energy, transport, and industrial decarbonisation. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 162:112420. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2022.112420
Lazaro A, Van De Griend MC, Brouwers HJH, Geus JW (2013) The influence of process conditions and Ostwald ripening on the specific surface area of olivine nano-silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 181:254–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.08.006
Lazaro A, Brouwers HJH, Quercia G, Geus JW (2012) The properties of amorphous nano-silica synthesized by the dissolution of olivine. Chem Eng J 211–212:112–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.09.042
Utama PS, Yamsaensung R, Sangwichien C (2018) Silica gel derived from palm oil mill fly ash. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 40:121–126. https://doi.org/10.14456/sjst-psu.2018.27
Real C, Alcalá MD, Criado JM (1996) Preparation of silica from rice husks. J Am Ceram Soc 79:2012–2016. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1996.tb08931.x
Bragg W, Gibbs RE (1925) The structure of α and β quartz. The Royal Society
Lazaro A, Sato K, Brouwers HJH, Geus JW (2018) Pore structure development of silica particles below the isoelectric point. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 267:257–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.03.031
Yuan J, Zhou S, Gu G, Wu L (2005) Effect of the particle size of nanosilica on the performance of epoxy/silica composite coatings. J Mater Sci 40:3927–3932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-0714-8
Fellow B, May R (1933) The thermal expansion of quartz by x-ray measurements. Proc R Soc London Ser A, Contain Pap a Math Phys Character 142:237–247. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1933.0165
Fricke J, Hümmer E, Morper H et al (1989) Thermal properties of silica aerogels. pp C4–87-C4–97
Primak W (1964) Radiation-induced stress relaxation in quartz and vitreous silica. J Appl Phys 35:1342–1347. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1713616
Cinaralp F, Zullo L (2012) Reinforcing filler in the rubber industry: assessment as potential nanomaterials with a focus on tyres. Eur Tyre Rubber 2–11
Barthel H, Rsch L, Weis J (2008) Fumed silica - production, properties, and applications. organosilicon chemistry set. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim, Germany, pp 761–778
Gun’ko VM, Mironyuk IF, Zarko VI, et al (2005) Morphology and surface properties of fumed silicas. J Colloid Interface Sci 289:427–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.05.051
Fan Y, Li X, Jang SH et al (2018) Reinforcement of solution styrene-butadiene rubber by incorporating hybrids of rice bran carbon and surface modified fumed silica. J Vinyl Addit Technol 24:E194–E200. https://doi.org/10.1002/VNL.21635
Michel W (2007) Pyrogenic silica as a filler for elastomeric materials. Int Polym Sci Technol 34:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/0307174x0703400701
Ten Brinke J (2002) Silica reinforced tyre rubbers. Elastomer Technology and Engineering. ISBN: 9036517583
Musić S, Filipović-Vinceković N, Sekovanić L (2011) Precipitation of amorphous SiO2 particles and their properties. Brazilian J Chem Eng 28:89–94. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-66322011000100011
Wang M-J, Tu H, Murphy LJ, Mahmud K (2011) Carbon—silica dual phase filler, a new generation reinforcing agent for rubber: Part VIII. Surface Characterization by IGC. Rubber Chem Technol 73:666–677. https://doi.org/10.5254/1.3547612
Mora-Barrantes I, Rodríguez A, Ibarra L et al (2011) Overcoming the disadvantages of fumed silica as filler in elastomer composites. J Mater Chem 21:7381–7392. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1jm10410a
Hewitt N (2007) Compounding precipitated silica in elastomers. Elsevier Inc
Ko JY, Prakashan K, Kim JK (2012) New silane coupling agents for silica tire tread compounds. J Elastomers Plast 44:549–562. https://doi.org/10.1177/0095244312439489
Bera A, Ganguly D, Ghorai SK et al (2022) Treatment of natural rubber with bio-based components: A green endeavor to diminish the silica agglomeration for tyre tread application. Chem Eng J Adv 11:100349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2022.100349
Bera A, Ganguly D, Hore R et al (2023) A feasible method of silica dispersion by introducing a pre-vulcanized gel in the natural rubber matrix. J Polym Res 30:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10965-023-03501-3/FIGURES/12
Bera A, Goswami M, Ganguly D et al (2023) The variation of structure and property of sorbitol-treated NR vulcanizates with increasing the silica loading. J Mater Sci 58:996–1011. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10853-022-08092-W/FIGURES/12
Bera A, Ganguly D, Rath JP et al (2023) The effect of bio-based ingredients in isoprene rubber: A biomimetic approach to improve the dispersion of silica. Mater Chem Phys 295:127151. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATCHEMPHYS.2022.127151
Qian Z, Peng Z (2019) Reinforcing styrene-butadiene rubber composites by constructing multiple interaction between rubber and silica. Polym Compos 40:1740–1747. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.24928
Lockhorn D, Klüppel M (2020) Structure–property relationships of silica/silane formulations in natural rubber, isoprene rubber and styrene–butadiene rubber composites. J Appl Polym Sci 137:48435. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.48435
Jiang T, Kuila T, Kim NH et al (2013) Enhanced mechanical properties of silanized silica nanoparticle attached graphene oxide/epoxy composites. Compos Sci Technol 79:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.02.018
Hayichelaeh C, Reuvekamp LAEM, Dierkes WK et al (2020) Silica-reinforced natural rubber tire tread compounds containing bio-based process oils. II: Influence of epoxide and amino functional groups. Rubber Chem Technol 93:195–207. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.19.81461
Tripp CP, Hair ML (1993) Chemical attachment of chlorosilanes to silica: A two-step amine-promoted reaction. J Phys Chem 97:5693–5698. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100123a038
Zheng J, Han D, Ye X et al (2018) Chemical and physical interaction between silane coupling agent with long arms and silica and its effect on silica/natural rubber composites. Polymer (Guildf) 135:200–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2017.12.010
Das S, Chattopadhyay S, Dhanania S, Bhowmick AK (2019) Reactive grafting of 3-octanoylthio-1-propyltriethoxysilane in styrene butadiene rubber: Characterization and its effect on silica reinforced tire composites. Polymer (Guildf) 179:121693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2019.121693
Das S, Chattopadhyay S, Dhanania S, Bhowmick AK (2020) Improved dispersion and physico-mechanical properties of rubber/silica composites through new silane grafting. Polym Eng Sci 60:3115–3134. https://doi.org/10.1002/PEN.25541
Das S, Pal K, Chattopadhyay S, Bhowmick AK (2022) 3-Octanoylthio-1-propyltriethoxysilane functionalized silica/rubber composites for application in tire: Structure, performance and synergism. Polym Compos 43:7575–7599. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.26863
Kaewsakul W, Sahakaro K, Dierkes WK, Noordermeer JWM (2013) Optimization of rubber formulation for silica-reinforced natural rubber compounds. Rubber Chem Technol 86:313–329. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.13.87970
Movahed SO, Arsarifar A, Song M (2009) Comparing the dynamic behaviour of several rubbers filled with silanized silica nanofiller. Polym Int 58:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.2518
Siramanont J, Tangpasuthadol V, Intasiri A, Na-ranong N (2009) Sol-Gel Process of Alkyltriethoxysilane in Latex for Alkylated Silica Formation in Natural Rubber 49:1099–1106. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen
Theppradit T, Prasassarakich P, Poompradub S (2014) Surface modification of silica particles and its effects on cure and mechanical properties of the natural rubber composites. Mater Chem Phys 148:940–948. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATCHEMPHYS.2014.09.003
Yin C, Zhang Q, Liu J et al (2018) Preparation, properties of In-situ silica modified styrene-butadiene rubber and its silica-filled composites. Polym Compos 39:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.23897
Naka Y, Komori Y, Yoshitake H (2010) One-pot synthesis of organo-functionalized monodisperse silica particles in W/O microemulsion and the effect of functional groups on addition into polystyrene. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 361:162–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2010.03.034
Sae-Oui P, Sirisinha C, Thepsuwan U, Hatthapanit K (2004) Comparison of reinforcing efficiency between Si-69 and Si-264 in a conventional vulcanization system. Polym Test 23:871–879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2004.05.008
Zhang C, Tang Z, Guo B, Zhang L (2019) Concurrently improved dispersion and interfacial interaction in rubber/nanosilica composites via efficient hydrosilane functionalization. Compos Sci Technol 169:217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.11.016
Qu L, Yu G, **e X et al (2013) Effect of silane coupling agent on filler and rubber interaction of silica reinforced solution styrene butadiene rubber. Polym Compos 34:1575–1582. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.22554
Lin CJ, York WM, Cody RJ (2016) Silanization characterization and compound properties of silica-filled rubber containing a blocked mercapto silane. Rubber Chem Technol 90:126–145. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.16.83771
Xu T, Jia Z, Li J et al (2018) Study on the dispersion of carbon black/silica in SBR/BR composites and its properties by adding epoxidized natural rubber as a compatilizer. Polym Compos 39:377–385. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.23946
Manoharan P, Naskar K (2019) Eco-friendly composites derived from naturally occurring molecules in promoting dispersion of nanosized silica particulates. Polym Compos 40:871–883. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.24749
Ou Y-C, Yu Z-Z, AV and JBD, (1994) Effects of alkylation of silica filler on rubber reinforcement. Rubber Chem Technol 67:834–844
Zhong B, Jia Z, Luo Y, Jia D (2015) A method to improve the mechanical performance of styrene- butadiene rubber via vulcanization accelerator modi fi ed silica. Compos Sci Technol 117:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2015.05.012
Pines A, Gibby MG, Waugh JS (1973) Proton-enhanced NMR of dilute spins in solids. J Chem Phys. doi 10(1063/1):1680061
Hita I, Arabiourrutia M, Olazar M et al (2016) Opportunities and barriers for producing high quality fuels from the pyrolysis of scrap tires. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 56:745–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2015.11.081
Antoniou N, Stavropoulos G, Zabaniotou A (2014) Activation of end of life tyres pyrolytic char for enhancing viability of pyrolysis – Critical review, analysis and recommendations for a hybrid dual system. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 39:1053–1073. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2014.07.143
Chattopadhyay PK, Basuli U, Chattopadhyay S (2010) Studies on novel dual filler based epoxidized natural rubber nanocomposite. Polym Compos 31:835–846. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.20866
Zhang C, Tang Z, Guo B, Zhang L (2018) Signi fi cantly improved rubber-silica interface via subtly controlling surface chemistry of silica. Compos Sci Technol 156:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.12.020
Pangamol P, Malee W, Yujaroen R, Siriwong PSC (2018) Utilization of bagasse ash as a filler in natural rubber and styrene – butadiene rubber composites. Arab J Sci Eng 43:221–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2859-6
Zhuravlev LT (2000) The surface chemistry of amorphous silica. Zhuravlev model. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 173:1–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(00)00556-2
Kaewsakul W, Sahakaro K, Dierkes WK (2015) Factors influencing the flocculation process in silica-reinforced natural rubber compounds. J Elastomers Plast 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/0095244315580456
Mihara S, Datta RN, Noordermeer JWM (2011) Flocculation in silica reinforced rubber compounds. Rubber Chem Technol 82:524–540. https://doi.org/10.5254/1.3548262
Kaewsakul W, Sahakaro K, Dierkes WK, Noordermeer JWM (2015) Mechanistic aspects of silane coupling agents with different functionalities on reinforcement of silica-filled natural rubber compounds. Polym Eng Sci 836–842. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen
Snr GO, Smith RR (2002) Silica reinforced rubber composition which contains non-silane coupling agent and articles of manufacture, including a tire, having at least one component comprised of such rubber composition. 1:US645882
Tian Q, Zhang C, Tang Y et al (2021) Preparation of hexamethyl disilazane-surface functionalized nano-silica by controlling surface chemistry and its “agglomeration-collapse” behavior in solution polymerized styrene butadiene rubber/butadiene rubber composites. Compos Sci Technol 201:108482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108482
Lin J, Zhong B, Luo Y et al (2019) Enhancing interfacial and mechanical strength of styrene-butadiene rubber composites via in situ fabricated halloysite nanotubes/silica nano hybrid. Polym Compos 40:677–684. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.24707
Wang Z, Wang H, Shen X et al (2022) In situ assembled C3N4/SiO2 nanohybrids for high comprehensive performance solution polymerized styrene-butadiene rubber/butadiene rubber. Polym Compos 43:8228–8238. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.26994
Xu L, Huang Z, Zhang X et al (2023) Reinforcing styrene-butadiene rubber by silica/carbon black by-product composite through an in-situ polymerization process. Polym Compos 44:663–672. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.27126
Zhong B, Jia Z, Hu D et al (2015) Reinforcement and reinforcing mechanism of styrene-butadiene rubber by antioxidant-modified silica. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 78:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.08.030
Mathew G, Huh MY, Rhee JM et al (2004) Improvement of properties of silica-filled styrene-butadiene rubber composites through plasma surface modification of silica. Polym Adv Technol 15:400–408. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.482
Sengloyluan K, Sahakaro K, Dierkes WK, Noordermeer JWM (2014) Silica-reinforced tire tread compounds compatibilized by using epoxidized natural rubber. Eur Polym J 51:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2013.12.010
Martin PJ, Brown P, Chapman AV, Cook S (2015) Silica-reinforced epoxidized natural rubber tire treads — performance and durability. Rubber Chem Technol 88:390–411. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.15.85940
Cataldo F (2002) Preparation of silica-based rubber compounds without the use of a silane coupling agent through the use of epoxidized natural rubber. Macromol Mater Eng 287:348–352. https://doi.org/10.1002/1439-2054(20020501)287:5%3c348::AID-MAME348%3e3.0.CO;2-1
Silika T, Pengisi D, Zaeimoedin TZ et al (2014) Improving filler dispersion and physical properties of epoxidised natural rubber / silica compound by using dual fillers and coupling agent in mixing process (Meningkatkan Penyerakan Pengisi dan Sifat Sifat Fizikal Sebatian Getah Asli). Malaysian J Anal Sci 18:604–611
Surya I, Ismail H, Azura AR (2014) The comparison of alkanolamide and silane coupling agent on the properties of silica- fi lled natural rubber ( SMR-L ) compounds. Polym Test 40:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2014.08.007
Bian H, Chang T, Wang C et al (2021) Atomization combined with high-temperature sputtering method applied in latex compounding technology for preparation of natural rubber latex/silica composites. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03517-5
Wolff S (1981) Parameters optimization of Silane-silica OTR compounds. Part 1: Variations of mixing temperature and time during the modification of silica with bis-3-triethoxysilupropyl-tetrasulphide. Rubber Chem Technol 55:967–989
Poompradub S, Thirakulrati M, Prasassarakich P (2014) In situ generated silica in natural rubber latex via the sol e gel technique and properties of the silica rubber composites. Mater Chem Phys 144:122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.12.030
Tangpasuthadol V, Intasiri A, Nuntivanich D et al (2008) Silica-reinforced natural rubber prepared by the sol – gel process of ethoxysilanes in rubber latex. Wiley Intersci 109:424–433. https://doi.org/10.1002/app
Prasertsri S, Rattanasom N (2012) Fumed and precipitated silica reinforced natural rubber composites prepared from latex system : Mechanical and dynamic properties. Polym Test 31:593–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2012.03.003
Bera A, Manna B, Ganguly D et al (2022) Pretreatment of hevea latex by sorbitol: improving the efficacy of silica dispersion by a biomimetic approach. ACS Appl Polym Mater 5:451. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSAPM.2C01588/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/AP2C01588_0010.JPEG
Yin C, Zhang Q, Gong D (2014) Preparation and properties of silica/styrene butadiene rubber masterbatches by latex co-coagulating technology. Polym Compos 35:1212–1219. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.22770
Konno Y (2018) Method for producing wet rubber masterbatch 1
Ryu C, Yang JK, Park W et al (2020) Silica-filled NR compounds prepared by dry and wet masterbatches with different mixing times. J Appl Polym Sci 137:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.49548
Sarkawi SS, Dierkes WK, Noordermeer JWM (2012) Natural rubber-silica combinations for low rolling resistance truck tire treads. Rubber World 247:26–31
Kim JK (2012) New silane coupling agents for silica tire tread compounds. J Elastomers Plast 44:549–562. https://doi.org/10.1177/0095244312439489
Mahata D, Sarkar K, Mondal P et al (2020) Guayule natural rubber composites: impact of fillers on their cure characteristics, dynamic and mechanical behavior. Iran Polym J English Ed 29:393–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13726-020-00803-X
Zhong B, Zeng X, Chen W et al (2019) Nonsolvent-assisted surface modification of silica by silane and antioxidant for rubber reinforcement. Polym Test 78:105949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2019.105949
Andriani F, Surya I (2018) Silica dispersion enhancement in natural rubber composites utilising stearyl alcohol. J Phys Conf Ser 1116:042005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1116/4/042005
Idrus SS, Ismail H, Palaniandy S (2011) Study of the effect of different shapes of ultrafine silica as fillers in natural rubber compounds. Polym Test 30:251–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2010.10.002
Wang J, Chen D (2013) Mechanical properties of natural rubber nanocomposites filled with thermally treated attapulgite 2013
Rooj S, Das A, Thakur V et al (2010) Preparation and properties of natural nanocomposites based on natural rubber and naturally occurring halloysite nanotubes. Mater Des 31:2151–2156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.11.009
Goswami M, Ghosh MM, Dalmiya MS et al (2020) A finite element method based comparative fracture assessment of carbon black and silica filled elastomers: Reinforcing efficacy of carbonaceous fillers in flexible composites. Polym Test 91:106856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2020.106856
Ghorai S, Mondal D, Dhanania S, et al (2018) Reclaiming of waste guayule natural rubber vulcanizate—reclaim rubber for green tire applications: An approach for sustainable development. 51:193–210. https://doi.org/10.1177/0095244318780539
Al-Hartomy OA, Al-Ghamdi AA, Farha Al Said SA et al (2016) Influence of carbon black/silica ratio on the physical and mechanical properties of composites based on epoxidized natural rubber. J Compos Mater 50:377–386. https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998315575336
An D, Cui Y, He R et al (2023) Improved interfacial interactions of modified graphene oxide/natural rubber composites with the low heat build-up and good mechanical property for the green tire application. Polym Compos. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.27444
Wang X, Luo Z, Liang J, Zhong J (2023) Hybrid enhancement of silica and aramid pulp on improving performance and reducing dynamic heat generation of natural rubber composites. Polym Compos. https://doi.org/10.1002/PC.27511
Ansarifar MA, Nuhawan R (2000) Filled natural rubber compounds. J Rubber Res 3:169–184
Stauch C, Ballweg T, Haas KH et al (2019) Silanization of silica nanoparticles and their processing as nanostructured micro-raspberry powders—a route to control the mechanical properties of isoprene rubber composites. Polym Compos 40:E732–E743. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.24980
Rattanasom N, Prasertsri S, Ruangritnumchai T (2009) Comparison of the mechanical properties at similar hardness level of natural rubber filled with various reinforcing-fillers. Polym Test 28:8–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2008.08.004
Surya I, Ismail H, Azura AR (2013) Alkanolamide as an accelerator, filler-dispersant and a plasticizer in silica-filled natural rubber compounds. Polym Test 32:1313–1321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2013.07.015
Abhitha K, Kurian T (2017) Epoxidised natural rubber - a substitute for silane coupling agent in safe silica-filled natural rubber formulations VI:23–29
Zhang Y, Liu Q, Zhang Q, Lu Y (2010) Gas barrier properties of natural rubber/kaolin composites prepared by melt blending. Appl Clay Sci 50:255–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2010.08.006
Manna AK, Tripathy DK, De PP et al (1999) Bonding between epoxidized natural rubber and clay in presence of silane coupling agent. J Appl Polym Sci 72:1895–1903. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19990628)72:14%3c1895::AID-APP10%3e3.0.CO;2-2
Wang Y, Liao L, Zhong J et al (2016) The behavior of natural rubber-epoxidized natural rubber-silica composites based on wet masterbatch technique. J Appl Polym Sci 133:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43571
Kaewsakul W, Sahakaro K, Dierkes WK, Noordermeer JWM (2016) Factors influencing the flocculation process in silica-reinforced natural rubber compounds. J Elastomers Plast 48:426–441. https://doi.org/10.1177/0095244315580456
Mensah B, Agyei-Tuffour B, Nyankson E et al (2018) Preparation and characterization of rubber blends for industrial tire tread fabrication. Int J Polym Sci 2018:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2473286
Thaptong P, Sae-Oui P, Sirisinha C (2016) Effects of silanization temperature and silica type on properties of silica-filled solution styrene butadiene rubber (SSBR) for passenger car tire tread compounds. J Appl Polym Sci 133:3–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43342
Fathurrohman MI. Better balance of silica-reinfoeced natural rubber tire tread compound properties by the use of montmorillonite with optimum surface modifier content. Rubber Chem Technol. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.20.80407
Sengloyluan K, Sahakaro K, Dierkes WK, Noordermeer JWM (2016) Reduced ethanol emissions by a combination of epoxidized natural rubber and silane coupling agent for silica-reinforced natural rubber-based tire treads. Rubber Chem Technol 89:419–435. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.16.84813
Qian M, Huang W, Wang J et al (2019) Surface treatment effects on the mechanical properties of silica carbon black reinforced natural rubber/butadiene rubber composites. Polymers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111763
Manoharan P, Naskar K (2016) Exploring a highly dispersible silica-elastomer composite for tire applications. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43531
Yang SY, Liu L, Jia ZX et al (2014) Study on the structure-properties relationship of natural rubber/SiO2 composites modified by a novel multi-functional rubber agent. Express Polym Lett 8:425–435. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2014.46
Chaichua B, Prasassarakich P, Poompradub S (2009) In situ silica reinforcement of natural rubber by sol-gel process via rubber solution. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 52:219–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-009-2019-x
Arayapranee W, Rempel GL (2013) Effects of polarity on the filler-rubber interaction and properties of silica filled grafted natural rubber composites. J Polym 2013:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/279529
Prasertsri S, Rattanasom N (2011) Mechanical and dam** properties of silica/natural rubber composites prepared from latex system. Polym Test 30:515–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2011.04.001
Rattanasom N, Saowapark T, Deeprasertkul C (2007) Reinforcement of natural rubber with silica/carbon black hybrid filler. Polym Test 26:369–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2006.12.003
Thaptong P, Sae-Oui P, Sirisinha C (2017) Influences of styrene butadiene rubber and silica types on performance of passenger car radial tire tread. Rubber Chem Technol 90:699–713. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.17.83724
Saramolee P, Sahakaro K, Lopattananon N et al (2016) Compatibilization of silica-filled natural rubber compounds by combined effects of functionalized low molecular weight rubber and silane. J Elastomers Plast 48:145–163. https://doi.org/10.1177/0095244314568469
Sirisinha C, Sae-oui P, Suchiva K, Thaptong P (2019) Properties of tire tread compounds based on functionalized styrene butadiene rubber and functionalized natural rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 48696:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.48696
Martinopoulos G, Papakostas KT, Papadopoulos AM (2018) A comparative review of heating systems in EU countries, based on efficiency and fuel cost. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 90:687–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2018.03.060
Gray N, O’Shea R, Smyth B et al (2022) What is the energy balance of electrofuels produced through power-to-fuel integration with biogas facilities? Renew Sustain Energy Rev 155:111886. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2021.111886
Ren X, Sancaktar E (2019) Use of fly ash as eco-friendly filler in synthetic rubber for tire applications. J Clean Prod 206:374–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.202
Filled ES, Composites R, Vaikuntam SR et al (2020) Friction, abrasion and crack growth behavior of. 1–14
Ju S-H (2022) Increasing the fatigue life of offshore wind turbine jacket structures using yaw stiffness and dam**. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 162:112458. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2022.112458
Sarkawi SS, Aziz AKC, Rahim RA et al (2016) Properties of epoxidized natural rubber tread compound: The hybrid reinforcing effect of silica and silane system. Polym Polym Compos 24:775–782. https://doi.org/10.1177/096739111602400914
Choi S, Nah C, Jo B (2003) Properties of natural rubber composites reinforced with silica or carbon black : influence of cure accelerator content and filler dispersion 1389:1382–1389. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.1232
Kaewsakul W, Sahakaro K (2012) Optimization of mixing conditions for silica-reinforced natural rubber tire tread compounds. Rubber Chem Technol 85:277–294. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.12.88935
Veiga VDA, Rossignol TM, da Crespo J, S, Carli LN, (2017) Tire tread compounds with reduced rolling resistance and improved wet grip. J Appl Polym Sci 134:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.45334
Vleugels N, Pille-Wolf W, Dierkes WK, Noordermeer JWM (2015) Understanding the influence of oligomeric resins on traction and rolling resistance of silica-reinforced tire treads. Rubber Chem Technol 88:65–79. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.14.86947
Kim K, Lee JY, Choi BJ et al (2014) Styrene-butadiene-glycidyl methacrylate terpolymer/silica composites: Dispersion of silica particles and dynamic mechanical properties. Compos Interfaces 21:685–702. https://doi.org/10.1080/15685543.2014.927720
Paul I, Sandstrom H, Eaw H (2002) (12) United States Patent. 1
Wang MJ, Zhang P, Mahmud K (2001) Carbon-silica dual phase filler, a new generation reinforcing agent for rubber: Part IX. Application to truck tire tread compound. Rubber Chem Technol 74:124–137. https://doi.org/10.5254/1.3547633
Wang MJ, Kutsovsky Y, Zhang P et al (2002) New generation carbon-silica dual phase filler part I. Characterization and application to passenger tire. Rubber Chem Technol 75:247–263. https://doi.org/10.5254/1.3544975
Data RUSA, Examiner P, Cain EJ et al (2001) (12) United States Patent. 1
Riehm P, Unrau HJ, Gauterin F (2018) A model based method to determine rubber friction data based on rubber sample measurements. Tribol Int 127:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.05.039
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to acknowledge the Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur and Apollo Tyres Pvt. Ltd, Chennai for their financial support and all kinds of facilities. The authors are also thankful to the Central Research Facility of IIT Kharagpur for carrying out the different characterizations of the samples. The author also likes to thank Mr. Rajesh De, Junior Technician/ Junior Laboratory Assistant, Rubber Technology Centre, IIT Kharagpur.
Funding
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, Apollo Tyres Ltd. Global R&D Asia, IIT/SRIC/RT/TRF/2018-19/288, Abhijit Bera.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Abhijit Bera: Conceptualization, Writing- Original draft preparation; Writing- Reviewing and Editing. Kajal Sarkar: Conceptualization, Writing- Original draft preparation. Debabrata Ganguly: Writing- Reviewing and Editing. Sanjoy Kumar Ghorai: Writing- Reviewing and Editing. Roumita Hore: Writing- Reviewing and Editing. Nikhil Kumar: Writing- Reviewing and Editing. S. K. P. Amarnath: Writing- Reviewing and Editing. Santanu Chattopadhyay: Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
No testing on human or animal was carried out for this work therefore ethical approval is not applicable for this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• This review highlights strategies on NR based environment friendly green compound.
• Summarized various renewable approaches of silica modification.
• Various generations of silane based coupling agents are discussed.
• Extensive coverage to overcome the dispersion problem of silica in NR compound.
• The review encompasses more than 155 salient articles spanning over 90 years.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bera, A., Sarkar, K., Ganguly, D. et al. Recent advancements in silica filled natural rubber composite: A green approach to achieve smart properties in tyre. J Polym Res 31, 122 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-024-03956-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-024-03956-y