Abstract
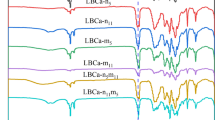
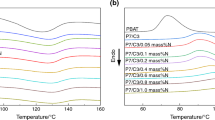
In order to evaluate the effect of the combination of micro-sized calcium carbonate (MCC) and nano-sized calcium carbonate (NCC) on the performance of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/poly(lactic acid)/calcium carbonate (PBAT/PLA/CaCO3) composites by using a comparative approach, the composites were prepared by melt mixing. The melting and crystallization of the composites were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry. The non-isothermal crystallization kinetics was investigated by using Jeziorny and Mo methods. The mechanical properties of the composites were test and the fracture surfaces were observed by scanning electron microscopy. Nano and micron calcium carbonates (nano-CaCO3 and micro-CaCO3) together improved the heat resistance of the composites more effectively than them alone. Mo method indicated that the crystallization rate of the composites containing both nano-CaCO3 and micro-CaCO3 was between the nano-CaCO3 composites and the micro-CaCO3 composites. The composite containing both 5 parts nano-CaCO3 and 10 parts micro-CaCO3 had the highest tensile, yield and impact strengths among the composites, but the composite containing both 11 parts nano-CaCO3 and 5 parts micro-CaCO3 had the lowest. SEM displayed that the morphology of the dispersed PLA in the composites with both nano-CaCO3 and micro-CaCO3 was different from that in the composites with nano-CaCO3 and micro-CaCO3 alone. Controlling the ratio of nano-CaCO3 and micro-CaCO3 achieved the synergistic enhancement in PBAT/PLA/CaCO3 composites.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gill YQ, Mehdi S, Mehmood U (2022) Mater Lett 306:130881
Sun DX, Gu T, Qi XD et al (2021) Chem Eng J 424:130558
Shen S (2022) Mater Res Express 9:025308
Saeidlou S, Huneault MA, Li H et al (2012) Prog Polym Sci 37(12):1657–1677
Mulla MZ, Rahman M, Marcos B et al (2021) Molecules 26(7):1967
Jia S, Zhao L, Wang X et al (2022) Int J Biol Macromol 201(15):662–675
Razavi M, Wang SQ (2019) Macromolecules 52(14):5429–5441
Deng Y, Yu C, Wongwiwattana P et al (2018) J Polym Environ 26:3802–3816
Li K, Peng J, Turng L-S et al (2011) Adv Polym Technol 30(2):150–157
Li G, **a Y, Mu G et al (2022) J Macromol Sci B 61(3):413–424
Jalali A, Huneault MA, Elkoun S (2016) J Mater Sci 51(16):7768–7779
Shi N, Dou Q (2015) J Therm Anal Calorim 119(1):635–642
Clizia A, Massimiliano B (2022) Chinese J Polym Sci 40(10):1269–1286
Gui H, Zhao M, Zhang S et al (2022) Foods 11(15):2252–2252
Danaya P, Phanwipa W, Khwanchat P et al (2021) Polymers 13(23):4192–4192
Yoksan R, Dang KM, Boontanimitr A et al (2021) Int J Biol Macromol 190:141–150
Xu C, Zhang X, ** X et al (2019) J Polym Environ 27(6):1273–1284
Jacek A, Michał N (2021) Materials 14(6):1523
Gutiérrez AA, Arrieta MP, López-González M et al (2020) Materials 13(21):4910
Alakrach AM, Al-Rashdi AA, Al-Omar MK et al (2021) Materials Science Forum 1021:280–289
Sanusi OM, Benelfellah A, Papadopoulos L et al (2021) J Mater Sci 56:16887–16901
Deetuam C, Samthong C, Choksriwichit S et al (2020) Iran Polym J 19(2):103–116
Rocha DB, de Carvalho JS, de Oliveira SA et al (2018) J Appl Polym Sci 135(35):46660
Lee JM, Hong JS, Ahn KH (2019) Polym Composite 40(10):4023–4032
Han LJ, Han CY, Bian JJ et al (2012) Polym Eng Sci 52(7):1474–1484
Nekhamanurak B, Patanathabutr P, Hongsriphan N (2014) Energy Procedia 56:118–128
Martin O, Avérous L (2001) Polymer 42:6209–19
Zhang J, Tashiro K, Tsuji H et al (2008) Macromolecules 41(4):1352–1357
Kawai T, Rahman N, Matsuba G (2007) Macromolecules 40(26):9463–9469
Kalish JP, Aou K, Yang X et al (2011) Polymer 52(3):814–821
Chen X, Kalish J, Hsu SL (2011) J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 49(20):1446–1454
Chen L, Dou Q (2020) J Therm Anal Calorim 139(2):1069–1090
Funding
This study was supported by the Scientific Project of Luohe Medical College (Grant No. 2020-LYZZHXM010 and 2019-LYZZHYB024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
**e, J. Effect of mixing strategy on thermal and mechanical properties of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/poly(lactic acid) incorporated with CaCO3 fillers. J Polym Res 30, 229 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-023-03618-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-023-03618-5