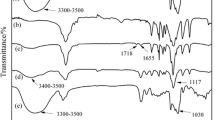
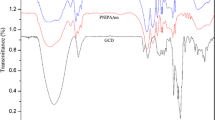
Abstract
Drug- controlled delivery can effectively avoid excessive drug use and improve the utilization rate of drugs and reduce the harm of drugs to the body. Herein, a novel poly(α-L-lysine)-based interpenetrating network (IPN) hydrogel with thermo/pH sensitivity was fabricated by synchronous free-radical polymerization and amine-anhydride click reaction in one pot. The hydrogels were characterized by FTIR, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The IPN hydrogels well integrated thermo-sensitivity and pH-sensitivity of two single-network hydrogels. The experimental results showed that the IPN hydrogel exhibited different swelling properties at different pH and temperatures. Finally, the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil (5-Fu) was chosen as a model drug to investigate the controlled release behavior of the hydrogel. The study showed that the release behavior of 5-Fu from the IPN hydrogel depended on temperature and pH changes, which followed the Korsmeyer-Peppas kinetic model. The IPN hydrogel is expected to be a candidate material for drug sustained-release carriers.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoffman AS (2012) Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Delive Rev 64:18–23
Phan VHG, Thambi T, Gil MS, Lee DS (2017) Temperature and pH-sensitive injectable hydrogels based on poly(sulfamethazine carbonate urethane) for sustained delivery of cationic proteins. Polymer 109:38–48
Chen Z, Liu J, Chen Y, Zheng X, Liu H, Li H (2021) Multiple-stimuli-responsive and cellulose conductive ionic hydrogel for smart wearable devices and thermal actuators. ACS Appl Mater Inter 13(1):1353–1366
Yu HT, Guo YT, Yao C, Perepichka DF, Meng H (2016) A smart polymer with a high sensitivity to temperature and humidity based on polyacrylamide hydrogel doped with polyiodide. J Mater Chem C 4(47):11055–11058
Shi Q, Liu H, Tang DD, Li YH, Li XJ, Xu F (2019) Bioactuators based on stimulus-responsive hydrogels and their emerging biomedical applications. NPG Asia Mater 11:64
Zhan JH, Wu YJ, Wang HH, Liu JL, Ma QZ, **ao KC, Li Z, Li J, Luo F, Tan H (2020) An injectable hydrogel with pH-sensitive and self-healing properties based on 4armPEGDA and N-carboxyethyl chitosan for local treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biol Macromol 163:1208–1222
Scarpa E, Mastronardi VM, Guido F, Algieri L, Qualtieri A, Fiammengo R, Rizzi F, De Vittorio M (2020) Wearable piezoelectric mass sensor based on pH sensitive hydrogels for sweat pH monitoring. Sci Rep 10(1):10854
Gau E, Flecken F, Ksiazkiewicz AN, Pich A (2018) Enzymatic synthesis of temperature-responsive poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) microgels with glucose oxidase. Green Chem 20(2):431–439
Grishkewich N, Akhlaghi SP, Yao ZL, Berry R, Tam KC (2016) Cellulose nanocrystal-poly(oligo(ethylene glycol) methacrylate) brushes with tunable LCSTs. Carbohydr Polym 144:215–222
Liao J, Huang HH (2019) Temperature/pH dual sensitive Hericium erinaceus residue carboxymethyl chitin/poly (N-isopropyl acrylamide) sequential IPN hydrogels. Cellulose 27(2):825–838
Liu Y, Zhang KH, Ma JH, Vancso GJ (2017) Thermoresponsive semi-IPN hydrogel microfibers from continuous fluidic processing with high elasticity and fast actuation. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9(1):901–908
Raghuwanshi VS, Garnier G (2019) Characterisation of hydrogels: Linking the nano to the microscale. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 274(2):102044
Rezvanian M, Ahmad N, Amin MCIM, Ng SF (2017) Optimization, characterization, and in vitro assessment of alginate-pectin ionic cross-linked hydrogel film for wound dressing applications. Int J Biol Macromol 97:131–140
Nezhad-Mokhtari P, Ghorbani M, Roshangar L, Rad JS (2019) A review on the construction of hydrogel scaffolds by various chemically techniques for tissue engineering. Eur Polym J 117:64–76
Kloxin CJ, Bowman CN (2013) Covalent adaptable networks: smart, reconfigurable and responsive network systems. Chem Soc Rev 42(17):7161–7173
Arkenberg MR, Nguyen HD, Lin CC (2020) Recent advances in bio-orthogonal and dynamic crosslinking of biomimetic hydrogels. J Mater Chem B 8(35):7835–7855
Li JH, Wu CT, Chu PK, Gelinsky M (2020) 3D printing of hydrogels: Rational design strategies and emerging biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 140:100543
Zhao JW, Narita T, Creton C (2020) Dual crosslink hydrogels with metal-ligand coordination bonds: Tunable dynamics and mechanics under large deformation. Adv Polym Sci 285:1–20
Bao ZT, **an CH, Yuan QJ, Liu GT, Wu J (2019) Natural polymer-based hydrogels with enhanced mechanical performances: Preparation, structure, and property. Adv Healthc Mater 8(17):e1900670
Noh W, Kim J, Lee SJ, Ryu BG, Kang CM (2018) Harvesting and contamination control of microalgae Chlorella ellipsoidea using the bio-polymeric flocculant alpha-poly-l-lysine. Bioresour Technol 249:206–211
Zheng M, Pan M, Zhang W, Lin H, Wu S, Lu C, Tang S, Liu D, Cai J (2021) Poly(alpha-l-lysine)-based nanomaterials for versatile biomedical applications: Current advances and perspectives. Bioact Mater 6:1878–1909
Kokufuta MK, Sato S, Kokufuta E (2011) Swelling-shrinking behavior of chemically cross-linked polypeptide gels from poly(alpha-L-lysine), poly(alpha-DL-lysine), poly(varepsilon-L-lysine) and thermally prepared poly(lysine): effects of pH, temperature and additives in the solution. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 87:299–309
Guo JH, Wei CZ, Wang XT, Hou YT, Guo WH (2021) An in situ mechanical adjustable double crosslinking hyaluronic acid/poly-lysine hydrogel matrix: Fabrication, characterization and cell morphology. Int J Biol Macromol 180:234–241
Divakaran AV, Azad LB, Surwase SS, Torris ATA, Badiger MV (2016) Water-stable plasma-polymerized N, N-dimethylacrylamide coatings to control cellular adhesion. Chem Mater 28(7):2120–2130
Dhand AP, Galarraga JH, Burdick JA (2020) Enhancing biopolymer hydrogel functionality through interpenetrating networks. Trends Biotechnol 39(5):519–538
Yuk H, Lu BY, Zhao XH (2019) Hydrogel bioelectronics. Chem Soc Rev 48(6):1642–1667
Saruchi KV, Mittal H, Alhassan SM (2019) Biodegradable hydrogels of tragacanth gum polysaccharide to improve water retention capacity of soil and environment-friendly controlled release of agrochemicals. Int J Biol Macromol 132:1252–1261
Wang J, Liu C, Shuai Y, Cui X, Nie L (2014) Controlled release of anticancer drug using graphene oxide as a drug-binding effector in konjac glucomannan/sodium alginate hydrogels. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 113:223–229
Zhu L, Ma J, Jia N, Zhao Y, Shen H (2009) Chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles as carriers of 5-fluorouracil: preparation, characterization and cytotoxicity studies. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 68:1–6
Afroz S, Afrose F, Alam AKMM, Khan RA, Alam MA (2018) Synthesis and characterization of polyethylene oxide (PEO)—N,N-dimethylacrylamide (DMA) hydrogel by gamma radiation. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 2(1):133–141
Dinari M, Atabaki F, Pahnavar Z, Soltani R (2020) Adsorptive removal properties of bivalent cadmium from aqueous solution using porous poly(N-2-methyl-4-nitrophenyl maleimide-maleic anhydride-methyl methacrylate) terpolymers. J Environ Chem Eng 8(6):104560
Wu ZJ, Zhang JJ, Lin QQ, Zhu YL, Wang L, Li YJ (2021) Movable-crosslinking tough hydrogels with lithium ion as sensitive and durable compressive sensor. Polymer 214:123257
Bashir S, Omar FS, Hina M, Numan A, Iqbal J, Ramesh S, Ramesh K (2020) Synthesis and characterization of hybrid poly (N, N-dimethylacrylamide) composite hydrogel electrolytes and their performance in supercapacitor. Electrochim Acta 332:135438
Egghe T, Cools P, Van Guyse JFR, Asadian M, Khalenkow D, Nikiforov A, Declercq H, Skirtach AG, Morent R, Hoogenboom R, De Geyter N (2020) Water-stable plasma-polymerized N, N-dimethylacrylamide coatings to control cellular adhesion. ACS Appl Mater Inter 12(2):2116–2128
Sheikhy S, Safekordi AA, Ghorbani M, Adibkia K, Hamishehkar H (2021) Synthesis of novel superdisintegrants for pharmaceutical tableting based on functionalized nanocellulose hydrogels. Int J Biol Macromol 167:667–675
Dutta S, Chowdhury T, Ghosh AK (2020) Green synthesis of poly-L-lysine-coated sericin nanoparticles and their molecular size-dependent antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 188:110822
Shen JM, Chen J, Ma JB, Fan LL, Zhang XL, Yue T, Yan YP, Zhang YH (2020) Enhanced lysosome escape mediated by 1,2-dicarboxylic-cyclohexene anhydride-modified poly-l-lysine dendrimer as a gene delivery system. Asian j Pharm sci 15(6):759–776
Liu JN, Chang SL, Xu PW, Tan MH, Zhao B, Wang XD, Zhao QS (2020) Structural changes and antibacterial activity of epsilon-poly-l-lysine in response to pH and phase transition and their mechanisms. J Agric Food Chem 68(4):1101–1109
Shin Y, Choi J, Na JH, Kim SY (2021) Thermally triggered soft actuators based on a bilayer hydrogel synthesized by gamma ray irradiation. Polymer 212:123163
Eftekhari-Sis B, Rahimkhoei V, Akbari A, Araghi HY (2018) Cubic polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nano-cross-linked hybrid hydrogels: Synthesis, characterization, swelling and dye adsorption properties. React Funct Polym 128:47–57
Wei HL, Geng LF, Zhu HZ, Li JJ (2019) Facile fabrication of thermosensitive hydrogel microspheres based on a combination of metal-free click chemistry and spray drying. Chem Eng Process 136:116–122
Ribeiro CA, Martins MVS, Bressiani AH, Bressiani JC, Leyva ME, de Queiroz AAA (2017) Electrochemical preparation and characterization of PNIPAM-HAp scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mat Sci Eng C- Mater 81:156–166
Wei HL, Yang XQ, Chu HJ, Li JJ (2019) Facile and green preparation of thermal and pH sensitive hydrogel microspheres based on spray drying and the diels–alder reaction. Polym Eng Sci 59(10):1999–2007
Boral S, Gupta AN, Bohidar HB (2006) Swelling and de-swelling kinetics of gelatin hydrogels in ethanol-water marginal solvent. Int J Biol Macromol 39(4–5):240–249
Hamedi S, Shojaosadati SA, Najafi V, Alizadeh V (2020) A novel double-network antibacterial hydrogel based on aminated bacterial cellulose and schizophyllan. Carbohydr Polym 229:115383
Oh J, Jung KI, Jung HW, Khan A (2019) A modular and practical synthesis of zwitterionic hydrogels through sequential amine-epoxy “click” chemistry and n-alkylation reaction. Polymers 11(9):1491
Song WJ, **n JN, Zhang JW (2017) One-pot synthesis of soy protein (SP)-poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) superabsorbent hydrogels via facile preparation of SP macromonomer. Ind Crops Prod 100:117–125
Brahim S, Narinesingh D, Guiseppi EA (2003) Synthesis and hydration properties of pH-sensitive p(HEMA)-based hydrogels containing 3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl methacrylate. Biomacromolecules 4(3):497–503
Xu K, Tan Y, Chen Q, An HY, Li WB, Dong LS, Wang PX (2010) A novel multi-responsive polyampholyte composite hydrogel with excellent mechanical strength and rapid shrinking rate. J Colloid Interface Sci 345(2):360–368
Hebeish A, Farag S, Sharaf S, Shaheen TI (2014) Thermal responsive hydrogels based on semi interpenetrating network of poly(NIPAm) and cellulose nanowhiskers. Carbohydr Polym 102:159–166
Han J, Wang K, Yang D, Nie J (2009) Photopolymerization of methacrylated chitosan/PNIPAAm hybrid dual-sensitive hydrogels as carrier for drug delivery. Int J Biol Macromol 44:229–235
El-Sherbiny IM, Smyth HD (2010) Poly(ethylene glycol)-carboxymethyl chitosan-based pH-responsive hydrogels: photo-induced synthesis, characterization, swelling, and in vitro evaluation as potential drug carriers. Carbohydr Res 345:2004–2012
Chang GR, Chen Y, Li YJ, Li SK, Huang FZ, Shen YH, **e AJ (2015) Self-healable hydrogel on tumor cell as drug delivery system for localized and effective therapy. Carbohydr Polym 122:336–342
** H, Liu X, Gui R, Wang Z (2015) Facile synthesis of gold nanorods/hydrogels core/shell nanospheres for pH and near-infrared-light induced release of 5-fluorouracil and chemo-photothermal therapy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 128:498–505
Pancholi NJ, Sonker N, Bajpai J, Bajpai AK (2020) Predictions of drug-protein Interactions and study of Magnetically Assisted Release dynamics of 5-fluorouracil from soya protein-coated Iron oxide rore-Shell Nanoparticles. ACS Appl Bio Mater 3:3170–3186
Rao KM, Nagappan S, Seo DJ, Ha CS (2014) pH sensitive halloysite-sodium hyaluronate/poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) nanocomposites for colon cancer drug delivery. Appl Clay Sci 97–98:33–42
Costa P, Lobo JMS (2001) Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur J Pharm Sci 13:123–133
Dey KP, Mishra S, Chandra N (2017) Colon targeted drug release studies of 5-ASA using a novel pH sensitive polyacrylic acid grafted barley. Polym Bull 74(8):3431–3453
Siepmann J, Peppas NA (2011) Higuchi equation: derivation, applications, use and misuse. Int J Pharm 418:6–12
Bardajee GR, Hooshyar Z, Asli MJ, Shahidi FE, Dianatnejad N (2014) Synthesis of a novel supermagnetic iron oxide nanocomposite hydrogel based on graft copolymerization of poly((2-dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) onto salep for controlled release of drug. Mat Sci Eng C- Mater 36:277–286
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by Natural Science Project of Zhengzhou Science and Technology Bureau [grant number 21ZZXTCX14]; the Innovative Funds Plan of Henan University of Technology [grant number: 2021ZKCJ08]; Henan University of Technology [grant number: HAUTZX202003]; the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number: U1904171]; the Key Science and Technology Project of Henan Province, China [grant number: 212102210630].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, C., Wei, H., Hua, B. et al. Preparation and application of poly(α-L-lysine)-based interpenetrating network hydrogel via synchronous free-radical polymerization and amine-anhydride reaction in water. J Polym Res 29, 194 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03054-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03054-x