Abstract
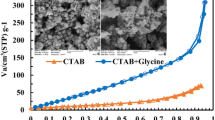
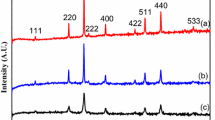
Magnetite (Fe3O4) powders were synthesized by solution combustion method using a mixture of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and citric acid fuels at various fuel to oxidant ratios (ϕ = 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2). Phase evolution investigated by x-ray diffraction method showed single-phase Fe3O4 powders were only formed at ϕ = 1 using mixture of fuels, while impurity α-Fe2O3 phase together with magnetite phase was completely disappeared at ϕ = 2 for CTAB fuel alone. The specific surface area and porous structures of the as-combusted Fe3O4 powders were characterized by N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and scanning electron microscopy techniques, respectively. The specific surface area using the mixture of fuels (37 m2/g) was higher than that of CTAB fuel alone (32 m2/g). Magnetic properties of the as-combusted powders were studied by vibration sample magnetometry method. The highest saturation magnetization of 83 emu/g was achieved by mixture of fuels at ϕ = 1, due to the high purity and large particle size.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, F.-T., Ran, J., Jaroniec, M., Qiao, S.Z.: Solution combustion synthesis of metal oxide nanomaterials for energy storage and conversion. Nanoscale 7, 17590–17610 (2015)
Varma, A., Mukasyan, A.S., Rogachev, A.S., Manukyan, K.V.: Solution combustion synthesis of nanoscale materials. Chem. Rev. 116, 14493–14586 (2016)
Nersisyan, H.H., Lee, J.H., Ding, J.-R., Kim, K.-S., Manukyan, K.V., Mukasyan, A.S.: Combustion synthesis of zero-, one-, two- and three-dimensional nanostructures: current trends and future perspectives. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 63, 79–118 (2017)
Manukyan, K.V., Chen, Y.-S., Rouvimov, S., Li, P., Li, X., Dong, S., Liu, X., Furdyna, J.K., Orlov, A., Bernstein, G.H., Porod, W., Roslyakov, S., Mukasyan, A.S.: Ultrasmall α-Fe2O3 superparamagnetic nanoparticles with high magnetization prepared by template-assisted combustion process. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 16264–16271 (2014)
Wen, W., Wu, J.-M.: Nanomaterials via solution combustion synthesis: a step nearer to controllability. RSC Adv. 4, 58090–58100 (2014)
Pourgolmohammad, B., Masoudpanah, S.M., Aboutalebi, M.R.: Effects of the fuel type and fuel content on the specific surface area and magnetic properties of solution combusted CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 43, 8262–8268 (2017)
Chen, W., Li, F., Yu, J., Liu, L.: A facile and novel route to high surface area ceria-based nanopowders by salt-assisted solution combustion synthesis. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 133, 151–156 (2006)
Radpour, M., Alamolhoda, S., Masoudpanah, S.M.: Effects of pH value on the microstructure and magnetic properties of solution combusted Fe3O4 powders. Ceram. Int. 43, 13729–13734 (2017)
Fathi, H., Masoudpanah, S.M., Alamolhoda, S., Parnianfar, H.: Effect of fuel type on the microstructure and magnetic properties of solution combusted Fe3O4 powders. Ceram. Int. 43, 7448–7453 (2017)
Alamolhoda, S., Mirkazemi, S.M., Shahjooyi, T., Benvidi, N.: Effect of cetyl trimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) amount on phase constituents and magnetic properties of nano-sized NiFe2O4 powders synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Alloys Compd. 638, 121–126 (2015)
Singh, I., Kaur, G., Bedi, R.K.: CTAB assisted growth and characterization of nanocrystalline CuO films by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 9546–9554 (2011)
Yin, W., Wang, W., Zhou, L., Sun, S., Zhang, L.: CTAB-assisted synthesis of monoclinic BiVO4 photocatalyst and its highly efficient degradation of organic dye under visible-light irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 173, 194–199 (2010)
Bedi, R.K., Singh, I.: Room-temperature ammonia sensor based on cationic surfactant-assisted nanocrystalline CuO. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2, 1361–1368 (2010)
Han, C.-G., Sheng, N., Zhu, C., Akiyama, T.: Cotton-assisted combustion synthesis of Fe3O4/C composites as excellent anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Today Energy 5, 187–195 (2017)
Wu, L., Mendoza-Garcia, A., Li, Q., Sun, S.: Organic phase syntheses of magnetic nanoparticles and their applications. Chem. Rev. 116, 10473–10512 (2016)
Lak, A., Kraken, M., Ludwig, F., Kornowski, A., Eberbeck, D., Sievers, S., Litterst, F.J., Weller, H., Schilling, M.: Size dependent structural and magnetic properties of FeO-Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Nanoscale 5, 12286–12295 (2013)
Kulkarni, S.A., Sawadh, P.S., Palei, P.K., Kokate, K.K.: Effect of synthesis route on the structural, optical and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 40, 1945–1949 (2014)
Haw, C.Y., Mohamed, F., Chia, C.H., Radiman, S., Zakaria, S., Huang, N.M., Lim, H.N.: Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents. Ceram. Int. 36, 1417–1422 (2010)
Mirabello, G., Lenders, J.J.M., Sommerdijk, N.A.J.M.: Bioinspired synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45, 5085–5106 (2016)
Manikandan, A., Vijaya, J.J., Mary, J.A., Kennedy, L.J., Dinesh, A.: Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles prepared by a facile microwave combustion method. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20, 2077–2085 (2014)
Parnianfar, H., Masoudpanah, S.M., Alamolhoda, S., Fathi, H.: Mixture of fuels for solution combustion synthesis of porous Fe3O4 powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 432, 24–29 (2017)
Zhang, X., Han, D., Hua, Z., Yang, S.: Porous Fe3O4 and gamma-Fe2O3 foams synthesized in air by sol-gel autocombustion. J. Alloys Compd. 684, 120–124 (2016)
Pourgolmohammad, B., Masoudpanah, S.M., Aboutalebi, M.R.: Effect of starting solution acidity on the characteristics of CoFe2O4 powders prepared by solution combustion synthesis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 424, 352–358 (2017)
Radpour, M., Masoudpanah, S.M., Alamolhoda, S.: Microwave-assisted solution combustion synthesis of Fe3O4 powders. Ceram. Int. 43, 14756–14762 (2017)
Rahaman, M.N.: Ceramic Processing and Sintering, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2003)
Socrates, G.: Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies, 1st edn. Wiley, New York (2001)
Nakamoto, K., Nakamoto, K.: Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds. Wiley, New York (1977)
Javadi, S., Masoudpanah, S.M., Zakeri, A.: Conventional versus microwave combustion synthesis of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 79, 176–183 (2016)
Goworek, J., Kierys, A., Gac, W., Borówka, A., Kusak, R.: Thermal degradation of CTAB in as-synthesized MCM-41. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 96, 375–382 (2009)
Barbooti, M.M., Al-Sammerrai, D.A.: Thermal decomposition of citric acid. Thermochim. Acta 98, 119–126 (1986)
Erri, P., Pranda, P., Varma, A.: Oxidizer-fuel interactions in aqueous combustion synthesis. 1. Iron(III) nitrate—model fuels. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 43, 3092–3096 (2004)
Manukyan, K.V., Cross, A., Roslyakov, S., Rouvimov, S., Rogachev, A.S., Wolf, E.E., Mukasyan, A.S.: Solution combustion synthesis of nano-crystalline metallic materials: mechanistic studies. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 24417–24427 (2013)
Namduri, H., Nasrazadani, S.: Quantitative analysis of iron oxides using Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometry. Corros. Sci. 50, 2493–2497 (2008)
Naderi, P., Masoudpanah, S.M., Alamolhoda, S.: Magnetic properties of Li0.5Fe2.5O4 nanoparticles synthesized by solution combustion method. Appl. Phys. A 123, 702 (2017)
Zhao, S., Wu, H.Y., Song, L., Tegus, O., Asuha, S.: Preparation of γ-Fe2O3 nanopowders by direct thermal decomposition of Fe-urea complex: reaction mechanism and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci. 44, 926–930 (2009)
Lazarova, T., Georgieva, M., Tzankov, D., Voykova, D., Aleksandrov, L., Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z., Kovacheva, D.: Influence of the type of fuel used for the solution combustion synthesis on the structure, morphology and magnetic properties of nanosized NiFe2O4. J. Alloys Compd. 700, 272–283 (2017)
Sing, K.S.W., Everett, D.H., Haul, R.A.W., Moscou, L., Pierotti, R.A., Rouquerol, J., Siemieniewska, T.: Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems. Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA (2008)
Deshpande, K., Mukasyan, A., Varma, A.: Direct synthesis of iron oxide nanopowders by the combustion approach: reaction mechanism and properties. Chem. Mater. 16, 4896–4904 (2004)
Riaz, S., Ashraf, R., Akbar, A., Naseem, S.: Microwave assisted iron oxide nanoparticles; Structural and Magnetic Properties. IEEE Trans. Magn. 50, 1–4 (2014)
Wang, X., Qin, M., Cao, Z., Jia, B., Gu, Y., Qu, X., Volinsky, A.A.: Growth mechanism and magnetism in carbothermal synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles from solution combustion precursors. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 420, 225–231 (2016)
Cullity, B.D., Graham, C.D.: Introduction to Magnetic Materials. Wiley, New Jersey (2011)
Morales, M.P., Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S., Montero, M.I., Serna, C.J., Roig, A., Casas, L., Martínez, B., Sandiumenge, F.: Surface and internal spin canting in γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 11, 3058–3064 (1999)
Spaldin, N.A.: Magnetic Materials: Fundamentals and Applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hadadian, S., Masoudpanah, S.M. & Alamolhoda, S. Solution Combustion Synthesis of Fe3O4 Powders Using Mixture of CTAB and Citric Acid Fuels. J Supercond Nov Magn 32, 353–360 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4685-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4685-9