Abstract
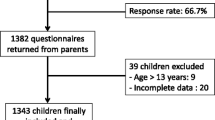
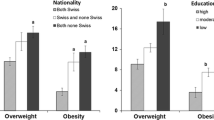
Over the last four decades, childhood overweight/obesity has dramatically increased, becoming a significant public health concern. The main aims of this study were to investigate the prevalence of overweight/obesity among first-year primary schools children in Modena and to identify the associated risk factors. Data were collected on the socio-demographic characteristics of family and weight, height, dietary habits and sedentary behaviours of the children, and on the parents’ perception of their child’s weight status, through an anonymous questionnaire administered to parents. The questionnaires were delivered by 660 out of 890 (74.2%) families, and after excluding those without anthropometric data, 588 children were included in the study. The prevalence of overweight/obesity among the children was 25.2%, significantly lower in children born to parents with a high education, and higher among children born to foreign parents and overweight/obese mothers. The multivariable analysis showed that the children most likely to become overweight/obese were those who skipped breakfast (OR 2.3, 95%CI 1.3–4.2) and/or mid-morning snacks (OR 3.2, 95%CI 1.5–6.5). Breakfast consumption was positively associated with higher parental education levels, whereas skip** mid-morning snacks is more frequent among children born to foreign parents and overweight/obese mothers. Moreover, 84.7% of the parents of overweight/obese children underestimated their child’s weight status. One in four 6–7 year-old children is already overweight or obese. Childhood overweight/obesity is significantly associated with unhealthy lifestyles and family lifestyle. It is therefore essential to implement public health intervention programs aimed at both parents and children, in order to promote healthy lifestyles in early childhood.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abarca-Gómez, L., Abdeen, Z. A., Hamid, Z. A., Abu-Rmeileh, N. M., Acosta-Cazares, B., Acuin, C., et al. (2017). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128 9 million children, adolescents, and adults. The Lancet,390(10113), 2627–2642.
WHO. (2018). Taking action on childhood obesity. Retrieved July 2, 2019, from https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/274792/WHO-NMH-PND-ECHO-18.1-eng.pdf?ua=1.
Lauria, L., Spinelli, A., Cairella, G., et al. (2015). Dietary habits among children aged 8-9 years in Italy. Annali dell’Istituto Superiore Di Sanita,51(4), 371–381. https://doi.org/10.4415/ANN_15_04_20.
Nardone, P. S. A., Buoncristiano, M., Lauria, L., Pierannunzio, D., & Galeone, D. (2018). Il Sistema di sorveglianza OKkio alla SALUTE: risultati 2016. Retrieved July 2, 2019, from https://www.epicentro.iss.it/okkioallasalute/pdf/ONLINE_OKKIO_ALLA_SALUTE.pdf.
Lloyd, L. J., Langley-Evans, S. C., & McMullen, S. (2012). Childhood obesity and risk of the adult metabolic syndrome: A systematic review. International Journal of Obesity (2005),36(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.186.
Short, K. R., Blackett, P. R., Gardner, A. W., & Copeland, K. C. (2009). Vascular health in children and adolescents: Effects of obesity and diabetes. Vascular Health and Risk Management,5, 973–990. https://doi.org/10.2147/vhrm.s7116.
Caird, J., Kavanagh, J., O’Mara-Eves, A., et al. (2014). Does being overweight impede academic attainment? A systematic review. Health Education Journal,73(5), 497–521. https://doi.org/10.1177/0017896913489289.
Quek, Y.-H., Tam, W. W. S., Zhang, M. W. B., & Ho, R. C. M. (2017). Exploring the association between childhood and adolescent obesity and depression: A meta-analysis. Obesity Reviews: An Official Journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity,18(7), 742–754. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12535.
Small, L., & Aplasca, A. (2016). Child obesity and mental health: A complex interaction. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics,25(2), 269–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chc.2015.11.008.
Farpour-Lambert, N. J., Baker, J. L., Hassapidou, M., et al. (2015). Childhood obesity is a chronic disease demanding specific health care—A position statement from the childhood obesity task force (COTF) of the European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). Obesity Facts,8(5), 342–349. https://doi.org/10.1159/000441483.
Reilly, J. J., Armstrong, J., Dorosty, A. R., et al. (2005). Early life risk factors for obesity in childhood: Cohort study. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.),330(7504), 1357. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38470.670903.E0.
Rietmeijer-Mentink, M., Paulis, W. D., van Middelkoop, M., Bindels, P. J. E., & van der Wouden, J. C. (2013). Difference between parental perception and actual weight status of children: A systematic review. Maternal & Child Nutrition,9(1), 3–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1740-8709.2012.00462.x.
Tompkins, C. L., Seablom, M., & Brock, D. W. (2015). Parental perception of child’s body weight: A systematic review. Journal of Child and Family Studies,24(5), 1384–1391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-9945-0.
Foster, B. A., & Hale, D. (2015). Perceptions of weight and health practices in hispanic children: A mixed-methods study. International Journal of Pediatrics. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/761515.
Lundahl, A., Kidwell, K. M., & Nelson, T. D. (2014). Parental underestimates of child weight: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics,133(3), e689–e703. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2013-2690.
Tripodi, A., Severi, S., Midili, S., & Corradini, B. (2011). “Community projects” in Modena (Italy): Promote regular physical activity and healthy nutrition habits since childhood. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity,6(Suppl 2), 54–56.
Cole, T. J., Bellizzi, M. C., Flegal, K. M., & Dietz, W. H. (2000). Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: International survey. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.),320(7244), 1240–1243. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.320.7244.1240.
Forbes, G. B. (1987). Human body composition: Growth, aging, nutrition, and activity. New York: Springer.
WHO. (2018). Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative HIGHLIGHTS 2015-17. Retrieved July 2, 2019, from http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0006/372426/WH14_COSI_factsheets_v2.pdf?ua=1.
Keane, E., Layte, R., Harrington, J., Kearney, P. M., & Perry, I. J. (2012). Measured parental weight status and familial socio-economic status correlates with childhood overweight and obesity at age 9. PLoS ONE,7(8), e43503. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0043503.
Martinovic, M., Belojevic, G., Evans, G. W., et al. (2015). Prevalence of and contributing factors for overweight and obesity among Montenegrin schoolchildren. European Journal of Public Health,25(5), 833–839. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurpub/ckv071.
Kleiser, C., Schaffrath Rosario, A., Mensink, G. B. M., Prinz-Langenohl, R., & Kurth, B.-M. (2009). Potential determinants of obesity among children and adolescents in Germany: Results from the cross-sectional KiGGS Study. BMC Public Health,9, 46. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-9-46.
Dubois, L., Girard, M., Girard, A., Tremblay, R., Boivin, M., & Perusse, D. (2007). Genetic and environmental influences on body size in early childhood: A twin birth-cohort study. Twin Research and Human Genetics,10(3), 479–485. https://doi.org/10.1375/twin.10.3.479.
Casali, M. E., Borsari, L., Marchesi, I., Borella, P., & Bargellini, A. (2015). Lifestyle and food habits changes after migration: A focus on immigrant women in Modena (Italy). Annali Di Igiene: Medicina Preventiva E Di Comunita.,27(5), 748–759. https://doi.org/10.7416/ai.2015.2067.
Gualdi-Russo, E., Zaccagni, L., Manzon, V. S., Masotti, S., Rinaldo, N., & Khyatti, M. (2014). Obesity and physical activity in children of immigrants. European Journal of Public Health.,24(Suppl 1), 40–46. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurpub/cku111.
Towns, N., & D’Auria, J. (2009). Parental perceptions of their child’s overweight: An integrative review of the literature. Journal of Pediatric Nursing.,24(2), 115–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedn.2008.02.032.
Grassi, T., De Donno, A., Bagordo, F., et al. (2016). Socio-economic and environmental factors associated with overweight and obesity in children aged 6-8 years living in five Italian cities (the MAPEC_LIFE Cohort). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.,13(10), 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13101002.
Huerta, M., Bibi, H., Haviv, J., Scharf, S., & Gdalevich, M. (2006). Parental smoking and education as determinants of overweight in Israeli children. Preventing Chronic Disease,3(2), A48.
Maffeis, C. (2000). Aetiology of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents. European Journal of Pediatrics.,159(Suppl 1), S35–S44.
Swinburn, B. A., Caterson, I., Seidell, J. C., & James, W. P. T. (2004). Diet, nutrition and the prevention of excess weight gain and obesity. Public Health Nutrition.,7(1A), 123–146.
Okada, C., Tabuchi, T., & Iso, H. (2018). Association between skip** breakfast in parents and children and childhood overweight/obesity among children: A nationwide 10.5-year prospective study in Japan. International Journal of Obesity (2005),42(10), 1724–1732. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-018-0066-5.
Goulão, B., Santos, O., & Carmo, I. D. (2015). The impact of migration on body weight: A review. Cadernos De Saude Publica.,31(2), 229–245.
Wardle, J., Guthrie, C., Sanderson, S., Birch, L., & Plomin, R. (2001). Food and activity preferences in children of lean and obese parents. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders: Journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity.,25(7), 971–977. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801661.
Hannon, P. A., Bowen, D. J., Moinpour, C. M., & McLerran, D. F. (2003). Correlations in perceived food use between the family food preparer and their spouses and children. Appetite,40(1), 77–83.
Popovic-Lipovac, A., & Strasser, B. (2015). A review on changes in food habits among immigrant women and implications for health. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health.,17(2), 582–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10903-013-9877-6.
Maher, C., Olds, T. S., Eisenmann, J. C., & Dollman, J. (2012). Screen time is more strongly associated than physical activity with overweight and obesity in 9- to 16-year-old Australians. Acta Paediatrica (Oslo, Norway: 1992),101(11), 1170–1174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2012.02804.x.
Taylor, R. W., Grant, A. M., Goulding, A., & Williams, S. M. (2005). Early adiposity rebound: Review of papers linking this to subsequent obesity in children and adults. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care.,8(6), 607–612.
Ebbeling, C. B., Pawlak, D. B., & Ludwig, D. S. (2002). Childhood obesity: Public-health crisis, common sense cure. Lancet (London, England).,360(9331), 473–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09678-2.
Reilly, J. J., Methven, E., McDowell, Z. C., et al. (2003). Health consequences of obesity. Archives of Disease in Childhood.,88(9), 748–752. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.88.9.748.
Acknowledgements
This study was carried out with the support of the Urban Multicentre Environment and Health (M.U.S.A.) of the Modena municipality: Elena Mori, Bruna Rodia, Alberto Turci and Sonia Giuliani and the teachers employed in the primary schools involved in the project.
Funding
No funding source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paduano, S., Borsari, L., Salvia, C. et al. Risk Factors for Overweight and Obesity in Children Attending the First Year of Primary Schools in Modena, Italy. J Community Health 45, 301–309 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-019-00741-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-019-00741-7