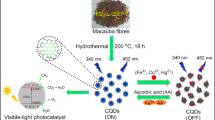
Abstract
Green and economical self-doped nitrogen-containing fluorescent carbon quantum dots (N-CQDs) were synthesized using a one-pot hydrothermal treatment method. The optical and structural properties of the N-CQDs were investigated in detail by UV-vis and fluorescence spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectroscopy, and elemental analysis illustrate the surface function and composition of N-CQDs. N-CQDs emit a broad fluorescence between365 ̴ 465 nm and fluoresce most strongly at the excitation wavelength of 415 nm. Meanwhile, Cr (VI) could significantly burst the fluorescence intensity of N-CQDs. N-CQDs showed an excellent sensitivity and selectivity to Cr (VI), which exhibited good linearity in the range of 0 ̴ 40 µmol/L with a detection limit of 0.16 µmol/L. In addition, the mechanism of Fluorescence quenching of N-CQDs by Cr (VI) was investigated. This work well provides a research idea for the preparation of green carbon quantum dots from biomass and their use for the detection of metal ions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the relevant data are included in the manuscript.
References
Yang ST, Cao L, Luo PG et al (2009) Carbon dots for optical imaging in vivo. J Am Chem Soc 131(32):11308–11309
Li H, Kang Z, Liu Y et al (2012) Carbon nanodots: synthesis, properties and applications. J Mater Chem 22(46):24230–24253
Dong Y, Pang H, Yang HB et al (2013) Carbon-based dots co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur for high quantum yield and excitation-independent emission. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(30):7800–7804
Mohammadi R, Naderi-Manesh H, Farzin L et al (2022) Fluorescence sensing and imaging with carbon-based quantum dots for early diagnosis of cancer: a review. J Pharm Biomed Anal 212:114628
Qian CG, Zhu S, Feng PJ et al (2015) Conjugated polymer nanoparticles for fluorescence imaging and sensing of neurotransmitter dopamine in living cells and the brains of zebrafish Larvae. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(33):18581–18589
You J, Ji J, Wu J et al (2020) Ratiometric fluorescent test pen filled with a mixing ink of carbon dots and CdTe quantum dots for portable assay of silver ion on paper. Microchim Acta 187(7):391
Arul V, Edison TNJI, Lee YR et al (2017) Biological and catalytic applications of green synthesized fluorescent N-doped carbon dots using Hylocereus undatus. J Photochem Photobiol B 168:142–148
Cao L, Sahu S, Anilkumar P et al (2011) Carbon nanoparticles as visible-light photocatalysts for efficient CO2 conversion and beyond. J Am Chem Soc 133(13):4754–4757
Luo W, Chen W, Quan H et al (2022) Strongly coupled carbon quantum dots/NiCo-LDHs nanosheets on carbon cloth as electrode for high performance flexible supercapacitors. Appl Surf Sci 591:153161
Kumar VB, Sher I, Rencus-Lazar S et al (2023) Functional carbon quantum dots for ocular imaging and therapeutic applications. Small 19(7):1613
Zhu S, Meng Q, Wang L et al (2013) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(14):3953–3957
Salinas-Castillo A, Ariza-Avidad M, Pritz C et al (2013) Carbon dots for copper detection with down and upconversion fluorescent properties as excitation sources. Chem Commun 49(11):1103–1105
Yang S, Zeng H, Zhao H et al (2011) Luminescent hollow carbon shells and fullerene-like carbon spheres produced by laser ablation with toluene. J Mater Chem 21(12):4432–4436
Liu H, Ye T, Mao C (2007) Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles derived from candle soot. Angew Chem Int Ed 46(34):6473–6475
Xu X, Ray R, Gu Y et al (2004) Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J Am Chem Soc 126(40):12736–12737
Jiang H, Chen F, Lagally MG et al (2010) New strategy for synthesis and functionalization of carbon nanoparticles. Langmuir 26(3):1991–1995
Surendran P, Lakshmanan A, Priya SS et al (2020) Bioinspired fluorescence carbon quantum dots extracted from natural honey: efficient material for photonic and antibacterial applications. Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects, 24: 100589.
Shabbir H, Wojtaszek K, Rutkowski B et al (2022) Milk-derived carbon quantum dots: study of biological and chemical properties provides evidence of toxicity. Molecules 27(24):8728
Han L, Zhu P, Liu H et al (2022) Molecularly imprinted bulk and solgel optosensing based on biomass carbon dots derived from watermelon peel for detection of ethyl carbamate in alcoholic beverages. Microchim Acta 189(8):286
Zhai Z, Xu J, Gong T et al (2022) Sustainable fabrication of N-doped carbon quantum dots and their applications in fluorescent inks, Fe (III) detection and fluorescent films. Inorg Chem Commun 140:109387
Preethi M, Murugan R, Viswanathan C et al (2022) Potato starch derived N-doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing tool for ascorbic acid. J Photochem Photobiol A 431:114009
Chaudhary N, Gupta PK, Eremin S et al (2020) One-step green approach to synthesize highly fluorescent carbon quantum dots from banana juice for selective detection of copper ions. J Environ Chem Eng 8(3):103720
Wang C, Shi H, Yang M et al (2020) Facile synthesis of novel carbon quantum dots from biomass waste for highly sensitive detection of iron ions. Mater Res Bull 124:110730
He L, Du H (2023) Detection of tartrazine with fluorescence sensor from crayfish shell carbon quantum dots. J Food Compos Anal 118:105200
Youn UJ, Lee JY, Kil Y-S et al (2016) Identification of new pyrrole alkaloids from the fruits of Lycium Chinense. Arch Pharm Res 39(3):321–327
Ju J, Chen W (2014) Synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for sensitive, label-free detection of Fe (III) in aqueous media. Biosens Bioelectron 58:219–225
Wu P, Li Y, Yan X-P, CdTe (2009) Quantum dots (QDs) based kinetic discrimination of Fe2+ and Fe3+, and CdTe QDs-fenton hybrid system for sensitive photoluminescent detection of Fe2+. Anal Chem 81(15):6252–6257
Huang LS, Lin KC (2001) Detection of iron species using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry under cold plasma temperature conditions. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy 56(1):123–128
Bobrowski A, Nowak K, Zarębski J (2005) Application of a bismuth film electrode to the voltammetric determination of trace iron using a Fe (III)–TEA–BrO3 – catalytic system. Anal Bioanal Chem 382(7):1691–1697
Jia Y, Wu S, Duan Z et al (2022) A facile fluorescence platform for chromium and ascorbic acid detection based on “on-off-on” strategy. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 278:121343
Ding S, Gao Y, Ni B et al (2021) Green synthesis of biomass-derived carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probe for Fe3+ detection. Inorg Chem Commun 130:108636
Gu L, Zhang J, Yang G et al (2022) Green preparation of carbon quantum dots with wolfberry as on-off-on nanosensors for the detection of Fe3+ and l-ascorbic acid. Food Chem 376:131898
Jiang K, Sun S, Zhang L et al (2015) Bright-yellow-emissive N-doped carbon dots: preparation, cellular imaging, and bifunctional sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(41):23231–23238
Fan YZ, Zhang Y, Li N et al (2017) A facile synthesis of water-soluble carbon dots as a label-free fluorescent probe for rapid, selective and sensitive detection of picric acid. Sens Actuators B 240:949–955
Yang L, Jiang W, Qiu L et al (2015) One pot synthesis of highly luminescent polyethylene glycol anchored carbon dots functionalized with a nuclear localization signal peptide for cell nucleus imaging. Nanoscale 7(14):6104–6113
Wang C, Chen Y, Xu Y et al (2020) Aggregation-induced room-temperature phosphorescence obtained from water-dispersible carbon dot-based composite materials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(9):10791–10800
Long R, Tang C, Li T et al (2020) Dual-emissive carbon dots for dual-channel ratiometric fluorometric determination of pH and mercury ion and intracellular imaging. Microchim Acta 187(5):307
Luo X, Bai P, Wang X et al (2019) Preparation of nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots and its application as a fluorescent probe for Cr (VI) ion detection. New J Chem 43(14):5488–5494
Funding
This research was found by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21964016), **njiang National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (2022D01E37) Key programs of **njiang Natural Science Foundation(2022B02051), and Tianshan Innovation Team Program of **njiang Uygur Autonomous Region (2020D14038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors’ Contributions Conceptualization and supervision: Zhaofeng Wu, Changwu Lv; major contributor in the experimental analysis and writing the manuscript: Jierong **e; review: Jun Sun, Qihua Sun.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not Applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
**e, J., Wu, Z., Sun, J. et al. Green Synthesis of Carbon Quantum dots Derived from Lycium barbarum for Effective Fluorescence Detection of Cr (VI) Sensing. J Fluoresc 34, 571–578 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03300-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03300-5