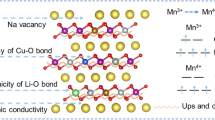
Abstract
Transition Metal Chalcogenides (TMC), due to their unique physicochemical properties, are studied in various fields and have potent applications in energy storage applications. This work is based on the synthesis and characterization of copper-doped manganese di-selenide and the effect of its do** on electrochemical performance as anode material for lithium-ion battery applications using the solvothermal method. The characterization techniques used are X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, field-emission scanning electron microscopy, XPS, UV–visible absorption spectroscopy, and electrochemical analysis. The XRD data confirms the formation of MnSe2 exhibiting Cubic crystal geometry. The FESEM images show the micro-cube-like structure with agglomerated nanocluster nanostructures on the surface with a dimension of 100–200 nm. The do** of the copper has decreased the band gap of the MnSe2, as studied by the UV–visible absorption spectrum. The electrochemical performance is analyzed as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. The charge/discharge measurements show a specific capacity of 706 mAh g−1 as the initial discharge capacity and 336 mAh g−1 as the initial charge capacity at 0.1 A g−1 current density. Meanwhile, 3% Copper-doped MnSe2 showed a better specific capacity of 878 mAh g−1 as the initial discharge capacity and 461 mAh g−1 as the initial charge capacity at 0.1 A g−1 current density. Cyclic stability, rate capability, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy were performed, and it shows that 3% copper-doped MnSe2 has good stability and better conductivity and charge kinetics, indicating copper do** has enhanced the electrochemical performance of pristine MnSe2.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
S. Dey, A. Sreenivasulu, G.T.N. Veerendra, K.V. Rao, P.S.S.A. Babu, Innov. Green Dev. 1, 100006 (2022)
H.A. Khayoon, M. Ismael, A. Al-nayili, H.A. Alshamsi, Inorg. Chem. Commun. 157, 111356 (2023)
A.K. Prajapati, A. Bhatnagar, J. Energy Chem. 83, 509 (2023)
G. Zu, G. Guo, H. Li, Y. Lu, R. Wang, Y. Hu, L. Wang, J. Wang, J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 6569 (2020)
Md.H. Hossain, M.A. Chowdhury, N. Hossain, Md.A. Islam, M.H. Mobarak, Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 16, 100569 (2023)
S. Joseph, J. Mohan, S. Lakshmy, S. Thomas, B. Chakraborty, S. Thomas, N. Kalarikkal, Mater. Chem. Phys. 297, 127332 (2023)
R.R. Chianelli, Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2, 127 (1982)
A. Sobhani, M. Salavati-Niasari, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 287, 102321 (2021)
J. Zheng, X. Li, C. He, C. Zhou, H. Zhang, B. Tang, Y. Rui, ChemElectroChem 7, 782 (2020)
J. Qian, S.P. Lau, Mater. Today Energy 10, 62 (2018)
H. Zhou, X. Li, Y. Li, M. Zheng, H. Pang, Nano-Micro Lett. 11, 40 (2019)
Z. Chang, X. Ju, P. Guo, X. Zhu, C. Liao, Y. Zong, X. Li, X. Zheng, J. Alloys Compd. 824, 153873 (2020)
B.D. Falola, L. Fan, T. Wiltowski, I.I. Suni, J. Electrochem. Soc. 164, D674 (2017)
X. Deng, W. Li, M. Zhu, D. **ong, M. He, Solid State Ionics 364, 115614 (2021)
Q. Chen, Z. Li, W. Chen, J. Alloys Compd. 872, 159655 (2021)
X. Shang, S. Li, K. Wang, X. Teng, X. Wang, Q. Li, J. Pang, J. Xu, D. Cao, S. Li, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 14, 6000 (2019)
A. Sobhani, M. Salavati-Niasari, J. Alloys Compd. 617, 93 (2014)
A.A. Kadhem, H.A. Alshamsi, Biomass Convers. Bioref. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-04501-5
K. Joshi, M. Rawat, S.K. Gautam, R.G. Singh, R.C. Ramola, F. Singh, J. Alloys Compd. 680, 252 (2016)
B. Balamuralitharan, S.N. Karthick, S.K. Balasingam, K.V. Hemalatha, S. Selvam, J.A. Raj, K. Prabakar, Y. Jun, H.-J. Kim, Energy Technol. 5, 1953 (2017)
M.S. Vidhya, R. Yuvakkumar, P.S. Kumar, G. Ravi, D. Velauthapillai, Top. Catal. 65, 615 (2022)
A. Sobhani, M. Salavati-Niasari, Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 3204 (2013)
Y. Wang, L. Cao, J. Li, L. Kou, J. Huang, Y. Feng, S. Chen, Chem. Eng. J. 391, 123597 (2020)
T. Alford, S. Das, J. Appl. Phys.Phys. 113(24), 244905 (2013)
M. Aftab, M.Z. Butt, D. Ali, F. Bashir, T.M. Khan, Opt. Mater. 119, 111369 (2021)
Acknowledgements
HSN acknowledges the DST-SERB Project Grant (No. SB/S2/CMP-105/2013) for providing financial support. Mukesh P would like to thank CSIR-UGC for its financial support.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mr. Mukesh P- design and implementation of the research, data collection, analysis and interpretation of results, and drafting manuscript; Mr. Lakshmisagar G.- data analysis and interpretation of results; Dr. Brijesh K- interpretation of results, manuscript correction; Mr. Sachin Kumawat- carried out the experiment, data collection; Mr. Akshay Prakash Hegde- helped in conducting experiment and data analysis; Mr. Arvind Kumar- helped in synthesis and conducting experiment; Prof. H S Nagaraja- supervised the findings of the work, helped in drafting manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mukesh, P., Sagar, G.L., Brijesh, K. et al. Impact of copper do** on the electrochemical response of MnSe2 as anode for lithium-ion battery. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 854 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12630-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12630-4