Abstract
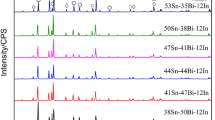
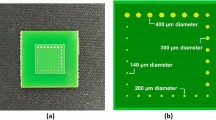
In pursuit of functionality and miniaturization in electronics, 3D integrated packaging requires low-temperature solders. This study explores a novel low-temperature lead-free SnBiIn solder. The solder has an ultimate tensile strength of 43.9 MPa, an elongation after break of 36.5%, and a low melting point of 91.8 °C. It is environmentally friendly with a homogeneous structure. Under controlled conditions of reflow at 150 °C for 5 min, the solder exhibited a solder/Cu(substrate) wetting angle of 32.6° and an average intermetallic compound (IMC) thickness of 2.3 μm—both meeting rigorous electronic industry standards. Furthermore, the Cu/SnBiIn/Cu joint demonstrated a substantial shear strength of 34.4 ± 1 MPa. These results highlight the potential of this lead-free, low-temperature solder for electronic packaging applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
H.R. Kotadia, P.D. Howes, S.H. Mannan, A review: on the development of low melting temperature Pb-free solders. Microelectron. Reliab. 54, 1253 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2014.02.025
H.-Y. Huang, C.-W. Yang, Y.-C. Peng, Effects on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn-0.7Cu lead-free solder with the addition of a small amount of magnesium. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 23, 641 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1515/secm-2014-0130
W.R. Osório, A. Garcia, Interrelation of wettability–microstructure–tensile strength of lead-free Sn–Ag and Sn–Bi solder alloys. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 21, 429 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2015.1124176
T. An, F. Qin, Effects of the intermetallic compound microstructure on the tensile behavior of Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu/Cu solder joint under various strain rates. Microelectron. Reliab. 54, 932 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2014.01.008
S.Q. Gu, Material innovation opportunities for 3D integrated circuits from a wireless application point of view. MRS Bull. 40, 233 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2015.9
H.F. Zou, Q.K. Zhang, Z.F. Zhang, Eliminating interfacial segregation and embrittlement of bismuth in SnBi/Cu joint by alloying Cu substrate. Scr. Mater. 61, 308 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2009.04.009
F. Wang, H. Chen, Y. Huang, L. Liu, Z. Zhang, Recent progress on the development of Sn–Bi based low-temperature Pb-free solders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 3222 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00701-w
D.L. Han, Y.-A. Shen, S. **, H. Nishikawa, Microstructure and mechanical properties of the In–48Sn–xAg low-temperature alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 55, 10824 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04691-7
S. Liu, S. Xue, P. Xue, D. Luo, Present status of Sn–Zn lead-free solders bearing alloying elements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 4389 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2659-7
M. Deshpande, R. Chaudhari, P. Ramesh Narayanan, H. Kale, Evaluation of shear properties of indium solder alloys for cryogenic applications. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30, 7958 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05983-y
K.-K. Xu, L. Zhang, L.-L. Gao, N. Jiang, L. Zhang, S.-J. Zhong, Review of microstructure and properties of low temperature lead-free solder in electronic packaging. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 21, 689 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/14686996.2020.1824255
B. Cantor, I.T.H. Chang, P. Knight, A.J.B. Vincent, Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.10.257
S. Wang, J. Feng, S. Wang, K. Wang, M. Yu, Y. Tian, Interfacial reaction between novel high entropy alloy SnPbInBiSb and Cu substrate. Mater. Lett. 325, 132901 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2022.132901
Y. Liu, L. Pu, Y. Yang, Q. He, Z. Zhou, C. Tan, X. Zhao, Q. Zhang, K.N. Tu, A high-entropy alloy as very low melting point solder for advanced electronic packaging. Mater. Today Adv. 7, 100101 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtadv.2020.100101
R.E. Villarreal-Loya, C.G. Garay-Reyes, A. Martínez-García, X. Atanacio-Sánchez, P.A. Guerrero-Seañez, I. Estrada-Guel, J.M. Mendoza-Duarte, Design of a Multicomponent Alloy for Application in Electronic Components Solder. Microsc Microanal 29, 578 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1093/micmic/ozad067.279
M.L. Huang, Q. Zhou, N. Zhao, L.D. Chen, Interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of In–Bi–Sn lead-free solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 2624 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1143-0
L. Pu, Y. Liu, Y. Yang, Q. He, Z. Zhou, X. Zhao, C. Tan, K.N. Tu, Effect of adding Ag to the medium entropy SnBiIn alloy on intermetallic compound formation. Mater. Lett. 272, 127891 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.127891
R.E. Villarreal-Loya, C.G. Garay-Reyes, J.M. Mendoza-Duarte, J.L. Hernández-Rivera, J.J. Cruz-Rivera, I. Estrada-Guel, R. Martínez-Sánchez, Ultra-low-temperature lead-free multicomponent alloy solder for application in heat-sensitive electronic components. Mater. Lett. 343, 134342 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2023.134342
Z. Wang, Q.K. Zhang, Y.X. Chen, Z.L. Song, Influences of Ag and in alloying on Sn-Bi Eutectic solder and SnBi/Cu solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 18524 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02206-y
R. Canyook, K. Fakpan, Effect of Cu and Ni Addition on microstructure and wettability of Sn-Zn solders. Key Eng. Mater. 728, 9 (2017)
I. Artaki, A. Jackson, P.T. Vianco, Evaluation of lead- free solder joints in electronic assemblies. J. Electron. Mater. 23, 757 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02651370
M.F. Arenas, V.L. Acoff, Contact angle measurements of Sn-Ag and Sn-Cu lead-free solders on copper substrates. J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1452 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-004-0086-x
M.A.A. Mohd Salleh, S.D. McDonald, H. Yasuda, A. Sugiyama, K. Nogita, Rapid Cu6Sn5 growth at liquid Sn/solid Cu interfaces. Scr. Mater. 100, 17 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.11.039
H. Ma, B. Zhao, G. Wu, Z. Li, Y. Gao, A SnBiAgIn solder alloy with exceptional mechanical properties by rapid quenching. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 8167 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05539-9
R. Sayyadi, H. Naffakh-Moosavy, The role of intermetallic compounds in controlling the microstructural, physical and mechanical properties of Cu-[Sn-Ag-Cu-Bi]-Cu solder joints. Sci. Rep. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44758-3
N. Javid, R. Sayyadi, F. Khodabakhshi, Lead-free Sn-based/MW-CNTs nanocomposite soldering: effects of reinforcing content, Ni-coating modification, and isothermal ageing treatment. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 4737 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00767-6
S. Phairote Sungkhaphaitoon, Chantaramanee, Effect of Aging temperature on the microstructure and shear strength of SAC0307-0.1Ni lead-free solders in copper joints. Russ. J. Non-ferr. Met. 61, 89 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/s1067821220010162
J. Zhou, Y. Sun, F. Xue, Properties of low melting point Sn–Zn–Bi solders. J. Alloys Compd. 397, 260 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2004.12.052
W.J. Tomlinson, A. Fullylove, Strength of tin-based soldered joints. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 5777 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01119737
Funding
This work was supported by Science and Technology Innovation 2025 Major Project of Ningbo (Grant No. 2022Z103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. SZ: Formal Analysis, Writing—Original Draft, Investigation. WL: Resources, Methodology. PL: Investigation, Validation. FL: Supervision, Validation. HX: Methodology, Funding Acquisition. TD: Data Curation, Writing—Review & Editing. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Long, W., Li, P. et al. Low-temperature lead-free SnBiIn solder for electronic packaging. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 690 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12405-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12405-x