Abstract
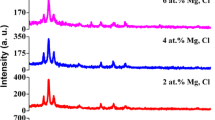
Ga doped CdS thin films were deposited on Soda Lime Glass substrates by Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD) method while concentrations of Gallium was varied during do**. X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy, Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Atomic Force Microscope (AFM), UV/VIS/NIR Lambda 9/19 double beam Spectrophotometer and Hall Effect Measurements system were used to analyse structural, surface morphology, optical and electrical properties of the films. XRD analysis revealed that deposited Ga doped CdS thin films had polycrystalline hexagonal phase, with preferred orientation along the (002) planes. An increase in Raman spectral intensity was observed for the doped films as compared to undoped CdS films. AFM and SEM analysis showed that grains were uniformly distributed on the substrate and were spherical in shape. The grain size and roughness increased with an increase in do** concentration as featured in the AFM and SEM images. Ga do** showed a strong effect to increase the transmittance of the films, with a maximum average transmittance of about 76% for film doped with 0.002 M of Ga concentration. Optical band gap for both undoped and doped films was in the range of 2.28 eV–2.44 eV. Electrical resistivity of the films decreased with an increase in dopant concentration, however beyond 0.002 M the resistivity increased.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
V. Narasimman, V.S. Nagarethinam, K. Usharani, A.R. Balu, Structural, morphological, optical and electrical properties of spray deposited ternary CdAgS thin films towards optoelectronic applications. Mater. Res. Innov. 22, 79–84 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/14328917.2016.1264857
D. Hariskos, S. Spiering, M. Powalla, Buffer layers in Cu(in,Ga)Se2 solar cells and modules. Thin Solid Films 480–481, 99–109 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2004.11.118
S. Sinha, D.K. Nandi, S.H. Kim, J. Heo, Atomic-layer-deposited buffer layers for thin film solar cells using earth-abundant absorber materials: a review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 176, 49–68 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOLMAT.2017.09.044
S.A. Khalate, R.S. Kate, R.J. Deokate, A review on energy economics and the recent research and development in energy and the Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) solar cells: a focus towards efficiency. Sol. Energy 169, 616–633 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.05.036
M.A. Contreras, M.J. Romero, B. To, F. Hasoon, R. Noufi, S. Ward, K. Ramanathan, Optimization of CBD CdS process in high-efficiency Cu(in, Ga)Se2-based solar cells. Thin Solid Films 403, 204–211 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090%2801%2901538-3
T. Gershon, T. Gokmen, O. Gunawan, R. Haight, S. Guha, B. Shin, Understanding the relationship between Cu2ZnSn(S, Se)4 material properties and device performance. MRS Commun. 4, 159–170 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2014.34
L. Ma, X. Ai, X. Wu, Effect of substrate and zn do** on the structural, optical and electrical properties of CdS thin films prepared by CBD method. J. Alloys Compd. 691, 399–406 (2016)
S. Alhammadi, H. Jung, S. Kwon, H. Park, J. Shim, C.M. Hwan, M. Lee, J.S. Kim, W.K. Kim, Effect of Gallium do** on CdS thin film properties and corresponding Cu(InGa)Se2/CdS:Ga solar cell performance. Thin Solid Films 660, 207–212 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2018.06.014
L. Soussi, A. Rmili et al., Structural, optical and electrical properties of spray pyrolysis deposited CdS:Fe thin films. In: 2018 6th International Renewable and Sustainable Energy Conference (IRSEC), Rabat, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/IRSEC.2018.8702936
F.J. Willars-Rodríguez, I.R. Chávez-Urbiola, M.A. HernándezLandaverde, R. Ramírez Bon, Y.V. Vorobiev, Effects of tin-do** on cadmium sulfide (CdS:sn) thin-films grown by light-assisted chemical bath deposition process for solar photovoltaic cell. Thin Solid Films 653, 341–349 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2018.03.046
H. Khallaf, Chemical bath deposition of group II–VI semiconductor thin films for solar cells applications. In: Electronic Thesis and Dissertations. 3941. (2009) https://stars.library.ucf.edu/etd/3941
O.K. Echendu, S.Z. Werta, F.B. Dejene, A.A. Ojo, I.M. Dharmadasa, Ga do** of nanocrystalline CdS thin films by electrodeposition method for solar cell application: the influence of dopant precursor concentration. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 4977–4989 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00794-3
E. Soto, F. Vaquero, N. Mota, S. Fateixa, T. Trindade, R.M. Navarro, J.L.G. Fierro, Structure and photoactivity for hydrogen production of CdS nanorods modified with In, Ga, Ag-In and Ag-Ga and prepared by solvothermal method. Mater. Today Energy 9, 345–358 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2018.06.009
A. Rmili, F. Ouachtari, A. Bouaoud, A. Louardi, T. Chtouki, B. Elidrissi, H. Erguig, Structural, optical and electrical properties of Ni-doped CdS thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. J. Alloys Compd. 557, 53–59 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.12.136
P. Scherrer, Bestimmung der Grösse und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgenstrahlen. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen 26, 98 (1918)
J.I. Langford, A.J.C. Wilson, Scherrer after sixty years: a survey and some new results in determination of crystallite size. J. Appl. Cryst. 11, 102–113 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889878012844
V. Uvarov, I. Popov, Metrological characterization of X-ray diffraction methods at different acquisition geometries for determination of crystallite size in nano-scale materials. Mater. Charac. 85, 111–123 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2013.09.002
P.Q. Zhao, L.Z. Liu, H.T. Xue, X.L. Wu, J.C. Shen, P.K. Chu, Resonant Raman scattering from CdS nanocrystals enhanced by interstitial mn. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 061910 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4792512
J. Trajić, M. Gilić, N. Romčević, M. Romčević, G. Stanišić, B. Hadžić, M. Petrović, Y.S. Yahia, Raman spectroscopy of optical properties in CdS thin films. Sci. Sinter. 47, 145–152 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2298/SOS1502145T
J. Díaz-Reyes, J.I. Contreras-Rascón, M. Galván-Arellano, J.S. Arias-Cerón, J.E.M. Gutiérrez-Arias, J.E. Flores-Mena, Morín-Castillo, physical property characterization of Pb2+ doped CdS nanofilms deposited by chemical-bath deposition at low temperature. Braz J. Phys. 46, 612–620 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-016-0445-0
S. Yilmaz, I. Polat, M.A. Olgar, M. Tomakin, S.B. Töreli, E. Bacaksiz, Physical properties of CdS:Ga thin films synthesized by spray pyrolysis technique. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 3191–3199 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5908-0
E. Akbarnejad, Z. Ghorannevis, F. Abbasi, M. Ghoranneviss, Investigation of annealing temperature effect on magnetron sputtered cadmium sulfide thin film properties. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 11, 45–49 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40094-016-0237-5
R. Olvera-Rivas, F. De moure-flores, S.A. Mayén-hernández, J. Quiñones-galvan, A. Centeno, A. Sosa-domínguez, Santos-cruz, effect of indium do** on structural, optical and electrical properties of cadmium sulfide thin films. Chalcogenide Lett. 17(7), 329–336 (2020)
X. Liu, Q. Zhang, J.N. Yip, Q. **ong, T.C. Sum, Wavelength tunable single nanowire lasers based on surface plasmon polariton enhanced Burstein–Moss effect. Nano Lett. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl402836x
L. Pholds, M.E. Samiji, N.R. Mlyuka, B.S. Richards, R.T. Kivaisi, Boron doped zinc oxide films grown by dc reactive magnetron sputtering. In: 28th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition (28th EU PVSEC) Paris, 30 September–04 October, pp. 2311–2315 (2013)
J. Cai, J. Jie, P. Jiang, D. Wu, C. ** and their nano-optoelectronic applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13, 14663–14667 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21104H
S. Yilmaz, I. Polat, M. Tomakin, T. Küçükömeroğlu, S.B. Töreli, E. Bacaksiz, Sm-doped CdS thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis: a structural, optical and electrical examination. Appl. Phys. A 124, 502 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1922-9
A. Fernández-Perez, C. Navarrete, P. Valenzuela, W. Gacitúa, E. Mosquera, H. Fernández, Characterization of chemically deposited aluminum-doped CdS thin films with post-deposition thermal annealing. Thin Solid Films 623, 127–134 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2016.12.036
S. Yilmaz, I. Polat, M. Tomakin, T. Küçükömeroğlu, S.B. Töreli, E. Bacaksiz, Optical and electrical optimization of dysprosium doped CdS thin films. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 14774–14782 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9613-z
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank the University of Dar es Salaam, The World Academy of Sciences, and International Science Programme for financial support.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: GS; Methodology: GS; Formal analysis and investigation: GS and ETS; Writing - original draft preparation: GS; Writing - review and editing: GS, MES, NRM and ETS; Funding acquisition: MES and NRM; Resources: GS, MES and NRM; Supervision: MES and NRM.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sungi, G., Samiji, M.E., Mlyuka, N.R. et al. Effect of Ga do** on optical transmittance and electrical conductivity of CdS thin films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 768 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10185-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10185-4