Abstract
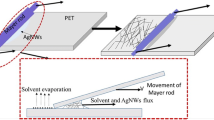
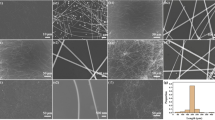
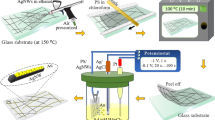
Silver nanowires (AgNWs) are considered as an ideal material to substitute indium tin oxide (ITO) owing to their outstanding characteristics, such as excellent electrical conductivity, transmittance, and bending properties. Ultrasonic spraying method is used to fabricate AgNWs films because of its high efficiency, controllability, and high uniformity of coating. In this work, high-purity AgNWs with an average diameter of 45 nm and an average length of 20 μm were prepared via acetone settling and ethanol washing of the products obtained by a simple solvothermal method. Subsequently, flexible transparent conductive films with sheet resistance non-uniformity less than 8% were prepared through Ultrasonic spraying AgNWs and modified poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS) upon polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate successively, and the surface roughness of the films was lessened by mechanical hot pressing. Finally, PET/AgNWs/PEDOT:PSS films were obtained with a transmittance at 550 nm of 85.06%, a sheet resistance of 45 Ω/sq, a haze of 3%, and a root mean square roughness of 14.1 nm. After being placed in air under normal temperature for two months and mechanical bending for 1000 times, respectively, the sheet resistance of the films showed only a slight change, which suggested that it was an excellent material to displace the conventional transparent conductive films.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available in this paper and on a request from the corresponding author.
References
Z.-R. Zhu, W. Geng, Q. Zhu et al., Nanotechnology (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/abb906
T. Wang, L.-C. **g, Q. Zhu et al., Appl. Surf. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143997
J. Kwon, H. Cho, H. Eom et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 11575 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b12714
H.S. Kang, J. Choi, W. Cho et al., J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 9834 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6tc03817d
M.A. Shinde, K. Mallikarjuna, J. Noh, H. Kim, Thin Solid Films 660, 447 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2018.06.054
Y. Zhang, S.-W. Ng, X. Lu, Z. Zheng, Chem. Rev. 120, 2049 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00483
S. Yu, X. Liu, H. Dong, X. Wang, L. Li, Ceram. Int. 47, 20379 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.04.046
M. Wu, H. Zheng, X. Li, S. Yu, Ceram. Int. 46, 4344 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.10.157
S. Ye, A.R. Rathmell, Z. Chen, I.E. Stewart, B.J. Wiley, Adv. Mater. 26, 6670 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201402710
J.P. Thomas, M.A. Rahman, S. Srivastava et al., ACS Nano 12, 9495 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b04848
B. Wang, M. Baeuscher, X. Hu et al., Micromachines (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11050474
K.A. Sierros, D.S. Hecht, D.A. Banerjee et al., Thin Solid Films 518, 6977 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2010.07.026
H. Sun, X. Li, Y. Li et al., Chem. Mater. 29, 7808 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b02348
P. Lee, J. Lee, H. Lee et al., Adv. Mater. 24, 3326 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201200359
J. Liu, Y. Zhang, W. Cheng et al., J. Colloid Interface Sci. 608, 2493 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.10.171
B. Zheng, Q. Zhu, Y. Zhao, J. Mater. Sci. Technol 71, 221 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2020.07.021
S. Fahad, H. Yu, W. Li et al., Mater. Chem. Phys. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.124643
L. Zhang, F. Jiang, B. Wu, C. Lv, M. Wu, Nanotechnology (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/abce7a
J. Xu, J. Hu, C. Peng, H. Liu, Y. Hu, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 298, 689 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.12.047
R.M. Mutiso, M.C. Sherrott, A.R. Rathmell, B.J. Wiley, K.I. Winey, ACS Nano 7, 7654 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn403324t
B. Li, S. Ye, I.E. Stewart, S. Alvarez, B.J. Wiley, Nano Lett. 15, 6722 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02582
Y. Li, X. Yuan, H. Yang, Y. Chao, S. Guo, C. Wang, Materials (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030401
Z. Niu, F. Cui, E. Kuttner et al., Nano Lett. 18, 5329 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b02479
Y. Li, Y. Li, Z. Fan, H. Yang, X. Yuan, C. Wang, RSC Adv. 10, 21369 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra03140b
G. Naz, H. Asghar, M. Ramzan et al., Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 12, 624 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.12.51
D. Shin, T. Kim, B.T. Ahn, S.M. Han, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 13557 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b02989
S. Duan, L. Zhang, Z. Wang, C. Li, RSC Adv. 5, 95280 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra19148c
D. Li, L. Wang, W. Ji et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 1735 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c16066
R. Xue, X. Wang, X. Chen, M. Zhang, S. Qi, J. Mater. Sci. 51, 7211 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0002-9
Z. Wang, K. Sun, H. Wu et al., J. Mater. Sci. 55, 15481 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05126-z
T.C. Hauger, S.M.I. Al-Rafia, J.M. Buriak, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 12663 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/am403986f
L. Hu, H.S. Kim, J.-Y. Lee, P. Peumans, Y. Cui, ACS Nano 4, 2955 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1005232
X.-Y. Zeng, Q.-K. Zhang, R.-M. Yu, C.-Z. Lu, Adv. Mater. 22, 4484 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201001811
S. Kim, S.Y. Kim, J. Kim, J.H. Kim, J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 5636 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4tc00686k
S. Zhang, X. Liu, T. Lin, P. He, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 18702 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02223-x
Y. Zhang, S. Bai, T. Chen, H. Yang, X. Guo, Mater. Res. Express. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab6262
Y. Wang, X. Wu, K. Wang et al., Int. J. Mol. Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147719
X. Wu, S. Wang, Z. Luo et al., Nanomaterials (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061571
R. Banica, D. Ursu, P. Svera et al., Part. Sci. Technol. 34, 217 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2015.1066473
W. Lee, K.D. Kihm, W. Lee et al., Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 134, 547 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.01.052
K. Lang, M. Klein, G. Domann, P. Loebmann, J. Solgel Sci. Technol. 96, 121 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05330-y
I. Verboven, J. Silvano, K. Elen et al., Adv. Eng. Mater. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.202100808
Y.-H. Ko, J.-W. Lee, W.-K. Choi, S.-R. Kim, Chem. Lett. 43, 1242 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.140220
W. Zhou, A. Hu, S. Bai, Y. Ma, D. Bridges, RSC Adv. 5, 39103 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra04214c
S. Kang, T. Kim, S. Cho et al., Nano Lett. 15, 7933 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b03019
Funding
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51672201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Experimental design, data collection, and analysis were performed by XF. Material preparation and experimental guidance were performed by XW. BZ, JG, CX, and SZ jointly reviewed and checked the experimental procedures and results. The first draft of the manuscript was written by XF and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, X., Wang, X., Zhang, B. et al. Flexible transparent conductive films based on silver nanowires by ultrasonic spraying process. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 25939–25949 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09284-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09284-5