Abstract
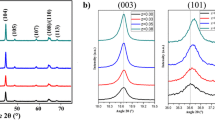
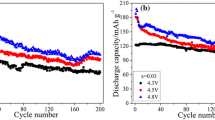
A LiNiO2 cathode material was cosubstituted with Mg and Al to obtain LiNi0.90Mg0.05Al0.05O2 via solid-state sintering of a mixture containing stoichiometric amounts of Ni(OH)2 precursor, LiOH·H2O, MgO, and Al2O3. The number of Li/Ni anti-site defects shown by X-ray diffraction was significantly reduced after cosubstitution of Mg and Al, and a 2–3 nm spinel-like structure was directly observed on the surface of LiNi0.90Mg0.05Al0.05O2 by Cs-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy. This cosubstitution-induced structural modification enhanced the stability of the material during cycling. The LiNi0.90Mg0.05Al0.05O2 half-cell showed an initial capacity of 210.8 mAh/g at 0.1 C (2.75–4.3 V) and excellent capacity retention of ~ 93.1% after 300 subsequent cycles at 1 C. In contrast, the bare LiNiO2 half-cell exhibited a capacity retention of only ~ 23.4% under the same cycling conditions, despite a high initial specific capacity of 238.1 mAh/g. Furthermore, the LiNi0.90Mg0.05Al0.05O2 half-cell also showed a much better rate performance than its bare LiNiO2 counterpart, with capacity retention levels at 5 C of 68.1% for the former and only 5.2% for the latter.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
M. Armand, J.M. Tarascon, Building better batteries. Nature 451, 652–657 (2008)
M.S. Whittingham, Lithium batteries: 50 years of advances to address the next 20 years of climate issues. Nano Lett. 20, 8435–8437 (2020)
A. Ueda, T. Ohzuku, Solid-state redox reactions of LiNi1/2Co1/2O2 (R-3m) for 4-volt secondary lithium cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 141, 2010–2014 (1994)
J.R. Dahn, U. Vonsacken, M.W. Juzkow, H. Aljanaby, Rechargeable LiNiO2 carbon cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 138, 2207–2211 (1991)
K.K. Cheralathan, N.Y. Kang, H.S. Park, Y.J. Lee, W.C. Choi, Y.S. Ko, Y.K. Park, Preparation of spherical LiNi0.80Co0.15Mn0.05O2 lithium-ion cathode material by continuous co-precipitation. J. Power Sources 195, 1486–1494 (2010)
T. Ohzuku, A. Ueda, M. Nagayama, Electrochemistry and structural chemistry of LiNiO2 (R-3m) for 4 volt secondary lithium cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 140, 1862–1870 (1993)
N. Zhang, N. Zaker, H.Y. Li, A. Liu, J. Inglis, L. **g, J. Li, Y. Li, G.A. Botton, J.R. Dahn, Cobalt-free nickel-rich positive electrode materials with a core-shell structure. Chem. Mater. 31, 10150–10160 (2019)
Y.K. Sun, Z.H. Chen, H.J. Noh, D.J. Lee, H.G. Jung, Y. Ren, S. Wang, C.S. Yoon, S.T. Myung, K. Amine, Nanostructured high-energy cathode materials for advanced lithium batteries. Nat. Mater. 11, 942–947 (2012)
W.M. Seong, A. Manthiram, Complementary effects of Mg and Cu incorporation in stabilizing the cobalt-free LiNiO2 cathode for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 43653–43664 (2020)
A. Konarov, S.T. Myung, Y.K. Sun, Cathode materials for future electric vehicles and energy storage systems. ACS Energy Lett. 2, 703–708 (2017)
B. Huang, Z.Y. Zhao, Y.Z. Sun, M. Wang, L. Chen, Y.J. Gu, Lithium-ion conductor LiAlO2 coated LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2 as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Solid State Ion. 338, 31–38 (2019)
H.Y. Li, A.R. Liu, N. Zhang, Y.Q. Wang, S. Yin, H.H. Wu, J.R. Dahn, An unavoidable challenge for ni-rich positive electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Mater. 31, 7574–7583 (2019)
L.Q. Mu, W.H. Kan, C.G. Kuai, Z.J. Yang, L.X. Li, C.J. Sun, S. Sainio, M. Avdeev, D. Nordlund, F. Lin, Structural and electrochemical impacts of Mg/Mn dual dopants on the LiNiO2 cathode in Li-metal batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 12874–12882 (2020)
N. Voronina, Y.K. Sun, S.T. Myung, Co-free layered cathode materials for high energy density lithium-ion batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 5, 1814–1824 (2020)
K. Wang, J.J. Wan, Y.X. **ang, J.P. Zhu, Q.Y. Leng, M. Wang, L.M. Xu, Y. Yang, Recent advances and historical developments of high voltage lithium cobalt oxide materials for rechargeable Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 460, 228062 (2020)
Y.K. Sun, D.J. Lee, Y.J. Lee, Z. Chen, S.T. Myung, Cobalt-free nickel rich layered oxide cathodes for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 11434–11440 (2013)
N. Yabuuchi, Y.T. Kim, H.H. Li, Y. Shao-Horn, Thermal instability of cycled LixNi0.5Mn0.5O2 electrodes: an in situ synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction study. Chem. Mater. 20, 4936–4951 (2008)
J. Xu, F. Lin, M.M. Doeff, W. Tong, A review of Ni-based layered oxides for rechargeable Li-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 874–901 (2017)
P.K. Nayak, E.M. Erickson, F. Schipper, T.R. Penki, N. Munichandraiah, P. Adelhelm, H. Sclar, F. Amalraj, B. Markovsky, D. Aurbach, Review on challenges and recent advances in the electrochemical performance of high capacity Li- and Mn-rich cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1702397 (2018)
A. Aishova, G.-T. Park, C.S. Yoon, Y.-K. Sun, Cobalt-free high-capacity Ni-rich layered Li Ni0.9Mn0.1O2 cathode. Adv. Energy Mater. 10, 1903179 (2020)
J.T. Zhang, X.H. Tan, L.M. Guo, Y. Jiang, S.N. Liu, H.F. Wang, X.H. Kang, W.G. Chu, Origin of performance differences of nickel-rich LiNi0.9Mn0.1O2 cathode materials synthesized in oxygen and air. Energy Technol.-Ger 7, 1800752 (2019)
H.X. Ji, L.B. Ben, H.L. Yu, R.H. Qiao, W.W. Zhao, X.J. Huang, Electrolyzed Ni(OH)2 precursor sintered with LiOH/LiNiO3 mixed salt for structurally and electrochemically stable cobalt-free LiNiO2 cathode materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 50965–50974 (2021)
F. Tian, L. Ben, H. Yu, H. Ji, W. Zhao, Z. Liu, R. Monteiro, R.M. Ribas, Y. Zhu, X. Huang, Understanding high-temperature cycling-induced crack evolution and associated atomic-scale structure in a Ni-rich LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O layered cathode material. Nano Energy 98, 107222 (2022)
A.M. Wang, N. Bai, Improved electrochemical cycling performance of high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials by coating with spinel MgAl2O4. Solid State Ion. 336, 19–25 (2019)
N. Bai, Y.-J. Ma, A.-M. Wang, X. Luo, Effects of MoO3 coating on the structure and electrochemical performance of high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. Ionics 27, 469–478 (2021)
T. Rao, P. Gao, Z. Zhu, S. Wang, L. Ben, Y. Zhu, Structural, electrochemical, and Li-ion diffusion properties of Mg&Mn dual doped LiNiO2 cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ion. 376, 115860 (2022)
T. Rao, P. Gao, Z.M. Zhu, S. Wang, L.B. Ben, Y.M. Zhu, Structural, electrochemical, and Li-ion diffusion properties of Mg&Mn dual doped LiNiO2 cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ion. 376, 115860 (2022)
D. Weber, J. Lin, A. Pokle, K. Volz, J. Janek, T. Brezesinski, M. Bianchini, Tracing low amounts of Mg in the doped cathode active material LiNiO2. J. Electrochem. Soc. 169, 030540 (2022)
L. ** strategy to enhance the structural stability and long cycle life of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 cathode material. Ionics 28, 3101–3112 (2022)
H.B. Zhang, Y. Zhang, T.T. Du, X. Cheng, B.B. Zhao, W.J. Qiang, Enhanced cycle stability of Ni-rich LiNi0.83Co0.12Mn0.05O2 with Mg and La co-modification. J. Solid State Electrochem. 26, 1085–1095 (2022)
A. Liu, N. Zhang, H. Li, J. Inglis, Y. Wang, S. Yin, H. Wu, J.R. Dahn, Investigating the effects of magnesium do** in various Ni-rich positive electrode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 166, A4025–A4033 (2019)
U.-H. Kim, L.-Y. Kuo, P. Kaghazchi, C.S. Yoon, Y.-K. Sun, Quaternary layered Ni-Rich NCMA cathode for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 4, 576–582 (2019)
H.Y. Li, M. Cormier, N. Zhang, J. Inglis, J. Li, J.R. Dahn, Is cobalt needed in Ni-rich positive electrode materials for lithium ion batteries? J. Electrochem. Soc. 166, A429–A439 (2019)
S. Sun, D. Li, C. Yang, L. Fu, D. Kong, Y. Lu, Y. Guo, D. Liu, P. Guan, Z. Zhang, J. Chen, W. Ming, L. Wang, X. Han, Direct atomic-scale observation of ultrasmall Ag nanowires that exhibit fcc, bcc, and hcp structures under bending. Phys. Rev. Lett. 128, 015701 (2022)
L. Wang, Y. Zhang, Z. Zeng, H. Zhou, J. He, P. Liu, M. Chen, J. Han, D.J. Srolovitz, J. Teng, Y. Guo, G. Yang, D. Kong, E. Ma, Y. Hu, B. Yin, X. Huang, Z. Zhang, T. Zhu, X. Han, Tracking the sliding of grain boundaries at the atomic scale. Science 375, 1261–1265 (2022)
F. Tian, Y. Zhang, Z. Liu, R. de Souza Monteiro, R.M. Ribas, P. Gao, Y. Zhu, H. Yu, L. Ben, X. Huang, Investigation of structure and cycling performance of Nb5+ doped high-nickel ternary cathode materials. Solid State Ion. 359, 115520 (2021)
Q.Y. Lin, W.H. Guan, J. Meng, W. Huang, X. Wei, Y.W. Zeng, J.X. Li, Z. Zhang, A new insight into continuous performance decay mechanism of Ni-rich layered oxide cathode for high energy lithium ion batteries. Nano Energy 54, 313–321 (2018)
L. Ben, H. Yu, B. Chen, Y. Chen, Y. Gong, X. Yang, L. Gu, X. Huang, Unusual spinel-to-layered transformation in LiMn2O4 cathode explained by electrochemical and thermal stability investigation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 35463–35475 (2017)
L.B. Ben, H.L. Yu, Y.D. Wu, B. Chen, W.W. Zhao, X.J. Huang, Ta2O5 coating as an HF barrier for improving the electrochemical cycling performance of high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 at elevated temperatures. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 1, 5589–5598 (2018)
C.S. Yoon, H.-H. Ryu, G.-T. Park, J.-H. Kim, K.-H. Kim, Y.-K. Sun, Extracting maximum capacity from Ni-rich Li[Ni0.95Co0.025Mn0.025]O2 cathodes for high-energy-density lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 4126–4132 (2018)
G.G. Min, Y. Ko, T.H. Kim, H.K. Song, S.B. Kim, S.M. Park, Fourier transform electrochemical impedance spectroscopic studies on LiFePO4 nanoparticles of hollow sphere secondary structures. J. Electrochem. Soc. 158, A1267–A1274 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by YLU-DNL fund (Grant No. 2021002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to study conception and design. Material preparation was performed by NB, YQ, and DG. Data collection and analysis were performed by ZS. The first draft of the manuscript was written by GC and AW. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Final manuscript read and approved by all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work. There is no personal or financial conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Hereby, we declare that the manuscript is our original work and have not been published or under editorial considerations anywhere else. The stated authors of the work have read the content and approved for submission of this manuscript to Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics. There is no personal or financial conflict of interest. Further if our article has been accepted, we ensure that we will not publish it anywhere else in any form, in any language without getting consent of the publisher.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, N., Qi, Y., Sun, Z. et al. Effect of Mg and Al cosubstitution on the structure and electrochemical performance of a Co-free LiNiO2 cathode material. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 18533–18543 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08705-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08705-9