Abstract
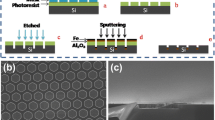
Vertically aligned carbon nanotubes having the advanced atomic configuration, structural properties, and electronic conductivity, which makes the CNTs as an eminent candidate for the electron field emission. In the present work, we have altered the morphology of the vertically aligned - CNT field emitters for improving the electron field emission parameters and temporal stability. The structural tuning and alteration of CNT field emitters was performed in the electron cyclotron resonance based chemical vapor deposition system via generating a dense resonating plasma of \({\text{N}\text{H}}_{3}\) gas. The as-synthesized pristine and resonating plasma treated VA-CNT field emitters were characterized by field emission scanning electron microscope for study the morphology, and Raman spectroscopy for the analysis of quality and structural defects. The horn type protrusions were formed after resonating plasma treatment. The electron field emission properties were drastically influenced by the time-based resonating plasma treatment. In terms of the reduction in the turn-on \(\left({E}_{to}\right)\) and threshold \(\left({E}_{th}\right)\) electric fields, improvement in the emission current density \(\left(J\right)\), increment in the conventional characteristics field enhancement factor \(\left(\gamma \right)\), and excellent temporal emission stability due to the incorporation of nitrogen species in the graphitic sheet of nanotubes, reduction in the screening effect, edge effect enhanced, and formation of defects in the graphitic sheet of VA-CNT. The calculated scaled barrier field values belong in the acceptable range and hence, orthodox emission hypothesis test qualified.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Iijima, T. Ichihashi, Single-shell carbon nanotubes of 1-nm diameter. Nature 363, 603 (1993)
W.A. De Heer, A. Chatelain, D. Ugarte, A carbon nanotube field-emission electron source. Science 270, 1179 (1995)
F. Giubileo, A. Di Bartolomeo, L. Iemmo, G. Luongo, F. Urban, Field emission from carbon nanostructures. Appl. Sci. 8, 526 (2018)
J.M. Bonard, M. Croci, C. Klinke, R. Kurt, O. Noury, N. Weiss, N., Carbon nanotube films as electron field emitters. Carbon 40, 1715 (2002)
W. Lei, Z. Zhu, C. Liu, X. Zhang, B. Wang, A. Nathan, High-current field-emission of carbon nanotubes and its application as a fast-imaging X-ray source. Carbon 94, 687 (2015)
M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Dresselhaus, J.C. Charlier, E. Hernandez, Electronic, thermal and mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 362, 2065 (2004)
H. Dai, E.W. Wong, C.M. Lieber, Probing electrical transport in nanomaterials: conductivity of individual carbon nanotubes. Science 272, 523 (1996)
M. Bockrath, D.H. Cobden, P.L. McEuen, N.G. Chopra, A. Zettl, A. Thess, R.E. Smalley, Single-electron transport in ropes of carbon nanotubes. Science 275, 1922 (1997)
J. Hone, M. Whitney, A. Zettl, Thermal conductivity of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Synth. Met. 103, 2498 (1999)
M. Yu, Strength and breaking mechanism of multiwalled carbon nanotubes under tensile load. Science 287, 637 (2000)
S. Sridhar, L. Ge, C.S. Tiwary, A.C. Hart, S. Ozden, K. Kalaga, S. Lei, S.V. Sridhar, R.K. Sinha, H. Harsh, K. Kordas, Enhanced field emission properties from CNT arrays synthesized on inconel superalloy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 1986 (2014)
W. Lei, Z. Zhu, C. Liu, X. Zhang, B. Wang, A. Nathan, High-current field-emission of carbon nanotubes and its application as a fast-imaging X-ray source. Carbon 94, 687 (2015)
J.W. Jeong, J.W. Kim, J.T. Kang, S. Choi, S. Ahn, Y.H. Song, A vacuum-sealed compact x-ray tube based on focused carbon nanotube field-emission electrons. Nanotechnology 24, 085201 (2013)
H.S. Kim, E.J.D. Castro, C.H. Lee, Optimum design for the carbon nanotube based micro-focus X-ray tube. Vacuum 111, 142 (2015)
R.H. Baughman, A.A. Zakhidov, W.A. De Heer, Carbon nanotubes--the route toward applications. Science 297, 787 (2002)
W.I. Milne, K.B.K. Teo, E. Minoux, O. Groening, L. Gangloff, L. Hudanski, J.P. Schnell, D. Dieumegard, F. Peauger, I.Y.Y. Bu, M.S. Bell, Aligned carbon nanotubes/fibers for applications in vacuum microwave amplifiers. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B: Microelectronics and Nanometer Structures Processing, Measurement, and Phenomena 24, 345 (2006)
X. Chen, T. Jiang, Z. Sun, W. Ou-Yang, Field emission device driven by self powered contact-electrification: Simulation and experimental analysis, Appl. Phys. Lett. 107, (2015).
J. Xu, P. Xu, P. Guo, W. Ou-Yang, Y. Chen, T. Feng, X. Piao, M. Wang, Z. Sun, All carbon nanotube based flexible field emission devices prepared through a film transfer method. RSC Adv. 5, 21755 (2015).
Y. Saito, S. Uemura, S., Field emission from carbon nanotubes and its application to electron sources. Carbon 38, 169 (2000)
A.V. Melechko, V.I. Merkulov, T.E. McKnight, M.A. Guillorn, K.L. Klein, D.H. Lowndes, M.L. Simpson, Vertically aligned carbon nanofibers and related structures: Controlled synthesis and directed assembly. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 3 (2005)
P.H. Lin, C.L. Sie, C.A. Chen, H.A. Chang, Y.T. Shih, H.Y. Chang, W.J. Su, K.Y. Lee, Field emission characteristics of the structure of vertically aligned carbon nanotube bundles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 10, 1 (2015)
V. Semet, V.T. Binh, P. Vincent, D. Guillot, K.B.K. Teo, M. Chhowalla, G.A.J. Amaratunga, W.I. Milne, P. Legagneux, D. Pribat, Field electron emission from individual carbon nanotubes of a vertically aligned array. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 343 (2002)
A.G. Rinzler, J.H. Hafner, P. Nikolaev, P. Nordlander, D.T. Colbert, R.E. Smalley, L. Lou, S.G. Kim, D. Tománek, Unraveling nanotubes: field emission from an atomic wire. Science 269, 1550 (1995)
J.L. Silan, D.L. Niemann, B.P. Ribaya, M. Rahman, M. Meyyappan, C.V. Nguyen, Carbon nanotube pillar arrays for achieving high emission current densities. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 133111 (2009)
B.K. Gupta, G. Kedawat, A.K. Gangwar, K. Nagpal, P.K. Kashyap, S. Srivastava, S. Singh, P. Kumar, S.R. Suryawanshi, D.M. Seo, P. Tripathi, High-performance field emission device utilizing vertically aligned carbon nanotubes-based pillar architectures. AIP Adv. 8, 015117 (2018)
A. Thapa, K.L. Jungjohann, X. Wang, W. Li, Improving field emission properties of vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays through a structure modification. J. Mater. Sci. 55, 2101 (2020)
A. Thapa, J. Guo, K.L. Jungjohann, X. Wang, W. Li, Density control of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes and its effect on field emission properties. Mater. Today Commun. 22, 100761 (2020)
M. Kumari, S. Gautam, P.V. Shah, S. Pal, U.S. Ojha, A. Kumar et al., Improving the field emission of carbon nanotubes by lanthanum-hexaboride nano-particles decoration. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 123113 (2012)
S. Sridhar, C. Tiwary, S. Vinod, J.J. Taha-Tijerina, S. Sridhar, K. Kalaga, B. Sirota, A.H. Hart, S. Ozden, R.K. Sinha, R. Vajtai, Field emission with ultralow turn on voltage from metal decorated carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano 8, 7763 (2014)
L.A. Gautier, V. Le Borgne, N. Delegan, R. Pandiyan, M.A. El, Khakani, Field electron emission enhancement of graphenated MWCNTs emitters following their decoration with Au nanoparticles by a pulsed laser ablation process. Nanotechnology 26, 045706 (2015)
Y.W. Son, S. Han, J. Ihm, Electronic structure and the field emission mechanism of MgO-coated carbon nanotubes. New J. Phys. 5, 152 (2003) 151(
M.K. Tabatabaei, H.G. Fard, J. Koohsorkhi, Low-temperature preparation of a carbon nanotube–ZnO hybrid on glass substrate for field emission applications. Nano 10, 1550040 (2015)
J. Svensson, N.M. Bulgakova, O.A. Nerushev, E.E. Campbell, Field emission induced deformations in SiO2 during CVD growth of carbon nanotubes. Physica Status Solidi (b) 243, 3524 (2006)
M.M.H. Raza, M. Sadiq, S. Khan, M. Sarvar, S. Parveen, S.M. Aalam, M. Zulfequar, S. Husain, J. Ali, Surface modification via silver nanoparticles attachment: An ex-situ approach for enhancing the electron field emission properties of CNT field emitters. Materials Today: Proceedings, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.03.449
A. Kumar, S. Husain, J. Ali, M. Husain, M. Husain, Field emission study of carbon nanotubes forest and array grown on Si using Fe as catalyst deposited by electro-chemical method. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 12, 2829 (2012)
C.J. Shearer, A. Fahy, M. Barr, P.C. Dastoor, J.G. Shapter, Improved field emission stability from single-walled carbon nanotubes chemically attached to silicon. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 1 (2012)
K.S. Kim, J.H. Ryu, C.S. Lee, J. Jang, K.C. Park, Enhanced and stable electron emission of carbon nanotube emitter arrays by post-growth hydrofluoric acid treatment. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 20, 120 (2009). DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-007-9463-6
Y.D. Lim, Q. Kong, S. Wang, C.W. Tan, B.K. Tay, S. Aditya, Enhanced field emission properties of carbon nanotube films using densification technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 477, 211 (2019). DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.005
K.Y. Wang, C.H. Chou, C.Y. Liao, Y.R. Li, H.C. Cheng, Densification effects of the carbon nanotube pillar array on field-emission properties. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 55, 06GF12 (2016). DOI:https://doi.org/10.7567/JJAP.55.06GF12
K.Y. Wang, C.Y. Liao, H.C. Cheng, Field-emission characteristics of the densified carbon nanotube pillars array. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 5, M99 (2016). DOI:https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0301609jss
J. Ali, A. Kumar, S. Husain, S. Parveen, R. Choithrani, M. Zulfequar, M. Husain, Enhancement of Field Emission Properties of Carbon Nanotubes by ECR-Plasma Treatment. J. Nanosci. (2014)
A. Kumar, S. Parveen, S. Husain, J. Ali, M. Zulfequar, M. Harsh, Husain, Effect of oxygen plasma on field emission characteristics of single-wall carbon nanotubes grown by plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition system. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 084308 (2014)
B.B. Wang, Q.J. Cheng, X. Chen, K. Ostrikov, Enhancement of electron field emission of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes by nitrogen plasma treatment. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 9329 (2011)
P.M. Koinkar, D. Yonekura, R.I. Murakami, T. Moriga, M.A. More, Field electron emission characteristics of plasma treated carbon nanotubes. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 29, 1540030 (2015)
G. Chen, S. Neupane, W. Li, L. Chen, J. Zhang, An increase in the field emission from vertically aligned multiwalled carbon nanotubes caused by NH3 plasma treatment. Carbon 52, 468 (2013)
J.Y. Kim, T. Jeong, C.W. Baik, S.H. Park, I. Han, G.H. Kim, S. Yu, Field-emission performance and structural change mechanism of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by oxygen plasma treatment. Thin Solid Films 547, 202 (2013)
Y.W. Zhu, A.M. Moo, T. Yu, X.J. Xu, X.Y. Gao, Y.J. Liu, C.T. Lim, Z.X. Shen, C.K. Ong, A.T.S. Wee, J.T.L. Thong, Enhanced field emission from O2 and CF4 plasma-treated CuO nanowires. Chem. Phys. Lett. 419, 458 (2006)
C.Y. Zhi, X.D. Bai, E.G. Wang, Enhanced field emission from carbon nanotubes by hydrogen plasma treatment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 1690 (2002)
A. Gohel, K.C. Chin, Y.W. Zhu, C.H. Sow, A.T.S. Wee, Field emission properties of N2 and Ar plasma-treated multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Carbon 43, 2530 (2005)
S.F. Lee, Y.P. Chang, L.Y. Lee, Plasma treatment effects on surface morphology and field emission characteristics of carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 20, 851 (2009)
S.T. Lim, G.H. Kim, G.H. Jeong, Field emission characteristics of cone-shaped carbon-nanotube bundles fabricated using an oxygen plasma. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 61, 1083 (2012)
M.M.H. Raza, M. Sadiq, S. Khan, M. Zulfequar, M. Husain, S. Husain, J. Ali, A single step in-situ process for improvement in electron emission properties of surface-modified carbon nanotubes (CNTs): Titanium dioxide nanoparticles attachment. Diam. Relat. Mater. 110, 108139 (2020)
M.M.H. Raza, S. Khan, M. Sadiq, M. Zulfequar, M. Husain, J. Ali, Enhancement of Electron Emission Properties of Carbon Nanotubes by the Decoration with Low Work Function Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 20, 6463 (2020)
A.C. Ferrari, Raman spectroscopy of graphene and graphite: Disorder, electron–phonon coupling, do** and nonadiabatic effects. Solid State Commun. 143, 47 (2007). DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2007.03.052
T.M.G. Mohiuddin, A. Lombardo, R.R. Nair, A. Bonetti, G. Savini, R. Jalil, N. Bonini, D.M. Basko, C. Galiotis, N. Marzari, K.S. Novoselov, Uniaxial strain in graphene by Raman spectroscopy: G peak splitting, Grüneisen parameters, and sample orientation. Phys. Rev. B 79, 205433 (2009). DOI:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.79.205433
R.G. Forbes, Development of a simple quantitative test for lack of field emission orthodoxy. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 469, 20130271(2013)
R.G. Forbes, Simple good approximations for the special elliptic functions in standard Fowler-Nordheim tunneling theory for a Schottky-Nordheim barrier. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 113122 (2006)
R.G. Forbes, J.H. Deane, Reformulation of the standard theory of Fowler–Nordheim tunnelling and cold field electron emission. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 463, 2907(2007)
R.H. Fowler, L. Nordheim, Electron emission in intense electric fields. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. A. Series, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character, 119, 173(1928)
R.G. Forbes, Comments on the continuing widespread and unnecessary use of a defective emission equation in field emission related literature. J. Appl. Phys. 126, 210901 (2019)
R. Patra, S. Ghosh, H. Sharma, V.D. Vankar, High stability field emission from zinc oxide coated multiwalled carbon nanotube film. Adv. Mater. Lett. 4, 849 (2013)
J. Derakhshandeh, Y. Abdi, S. Mohajerzadeh, H. Hosseinzadegan, E.A. Soleimani, H. Radamson, Fabrication of 100 nm gate length MOSFET’s using a novel carbon nanotube-based nano-lithography. Mater. Sci. Eng: B 124, 354–358 (2005)
K. Tang, C. Yuan, Y. **ong, H. Hu, M. Wu. Inverse-opal-structured hybrids of N, S-codoped-carbon-confined Co9S8 nanoparticles as bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst for on-chip all-solid-state rechargeable Zn-air batteries. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 260, 118209 (2020)
Z. Cao, H. Hu, M. Wu, K. Tang, T. Jiang, Planar all-solid-state rechargeable Zn–air batteries for compact wearable energy storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 7(29), 17581–17593 (2019)
Z.Q. Cao, M.Z. Wu, H.B. Hu, G.J. Liang, C.Y. Zhi. Monodisperse Co 9 S 8 nanoparticles in situ embedded within N, S-codoped honeycomb-structured porous carbon for bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst in a rechargeable Zn–air battery. NPG Asia Mater. 10(7), 670–684 (2018)
Acknowledgements
Author (J. Ali) thanks to University Grant Commission for providing financial assistance in the form of UGC-BSR Start-up Research Grant [Sanction No. F.30-359/2017 (BSR)]. FESEM was performed in the Centre for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, India. Raman spectroscopy was performed in the Central Instrumentation Facility, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raza, M.M.H., Aalam, S.M., Sadiq, M. et al. Time-dependent resonating plasma treatment of carbon nanotubes for enhancing the electron field emission properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 1211–1227 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07413-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07413-0