Abstract
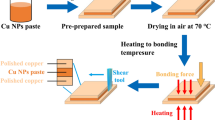
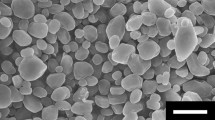
Wide bandgap (WBG) power devices have been attracting increasing attention for next-generation electronic applications. Cu–Cu bonding has been developed to accommodate the high temperature and current characteristics encountered in WBG semiconductors service conditions. In this study, we demonstrate and optimize a pressureless Cu–Cu bonding method by reductively sintering preoxidized Cu microparticles in a formic-acid atmosphere, and provide information on the bonding mechanism and relationship between behaviors of Cu microparticles and bonding quality. The transformation of Cu microparticles was examined at different preoxidation intervals, which were followed by a reduction reaction. The Cu oxide produced by preoxidation is critical for reliable Cu–Cu bonding because it forms linkages between Cu microparticles during the process; additionally, it fills the gaps between the individual particles to increase bonding density. In both thermal aging and cycling test, it was found that the Cu–Cu bonding exhibited similar microstructures and oxidation behavior, but followed different degradation and failure modes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.G. Neudeck, R.S. Okojie, L.-Y. Chen, High-temperature electronics-a role for wide bandgap semiconductors? Proc. IEEE 90, 1065 (2002)
H.S. Chin, K.Y. Cheong, A.B. Ismail, A review on die attach materials for SiC-based high-temperature power devices. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 41, 824 (2010)
V.R. Manikam, K.Y. Cheong, Die attach materials for high temperature applications: a review. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 1, 457 (2011)
T. Hu, H. Chen, M. Li, Die attach materials with high remelting temperatures created by bonding Cu@ Sn microparticles at lower temperatures. Mater. Des. 108, 383 (2016)
F.P. McCluskey, M. Dash, Z. Wang, D. Huff, Reliability of high temperature solder alternatives. Microelectron. Reliab. 46, 1910 (2006)
J. Cho, R. Sheikhi, S. Mallampati, L. Yin, D. Shaddock, Bismuth-based transient liquid phase (TLP) bonding as high-temperature lead-free solder alternatives, in 2017 IEEE 67th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC)IEEE (2017)
M.M. Hou, T.W. Eagar, Low temperature transient liquid phase (LTTLP) bonding for Au/Cu and Cu/Cu interconnections. J. Electron. Packag. 114(4), 443–447 (1992)
X. Liu, S. Zhou, H. Nishikawa, Thermal stability of low-temperature sintered joint using Sn-coated Cu particles during isothermal aging at 250 °C. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 12606 (2017)
K.S. Siow, Die-Attach Materials for High Temperature Applications in Microelectronics Packaging, 1st edn. (Springer, Berlin, 2019), pp. 9–10
H. Nishikawa, T. Hirano, T. Takemoto, N. Terada, Effects of joining conditions on joint strength of Cu/Cu joint using Cu nanoparticle paste. Open Surf. Sci. J. 3, 60 (2011)
A. Zinn, R. Stoltenberg, A. Fried et al., nanoCopper based solder-free electronic assembly material. Nanotech 2, 71 (2012)
T. Yamakawa, T. Takemoto, M. Shimoda, H. Nishikawa, K. Shiokawa, N. Terada, Influence of joining conditions on bonding strength of joints: efficacy of low-temperature bonding using Cu nanoparticle paste. J. Electron. Mater. 42, 1260 (2013)
J. Li, X. Yu, T. Shi et al., Low-temperature and low-pressure Cu–Cu bonding by highly sinterable Cu nanoparticle paste. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12, 255 (2017)
X. Wang, Y. Mei, X. Li, M. Wang, Z. Cui, G.-Q. Lu, Pressureless sintering of nanosilver paste as die attachment on substrates with ENIG finish for semiconductor applications. J. Alloys Compd. 777, 578 (2019)
Y. Morisada, T. Nagaoka, M. Fukusumi, Y. Kashiwagi, M. Yamamoto, M. Nakamoto, A low-temperature bonding process using mixed Cu–Ag nanoparticles. J. Electron. Mater. 39, 1283 (2010)
C. Chen, S. Noh, H. Zhang et al., Bonding technology based on solid porous Ag for large area chips. Scr. Mater. 146, 123 (2018)
A.K. Panigrahi, T. Ghosh, S.R.K. Vanjari, S.G. Singh, Demonstration of sub 150° C Cu-Cu thermocompression bonding for 3D IC applications, utilizing an ultra-thin layer of Manganin alloy as an effective surface passivation layer. Mater. Lett. 194, 86 (2017)
Y.Y. Dai, M.Z. Ng, P. Anantha, C.L. Gan, C.S. Tan, Enhanced copper micro/nano-particle mixed paste sintered at low temperature for 3D interconnects. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 26 (2016)
X. Liu, H. Nishikawa, Low-pressure Cu-Cu bonding using in-situ surface-modified microscale Cu particles for power device packaging. Scr. Mater. 120, 80 (2016)
X. Liu, H. Nishikawa, Improved joint strength with sintering bonding using microscale Cu particles by an oxidation-reduction process, in Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), 2016 IEEE 66thIEEE, (2016)
T. Yao, T. Matsuda, T. Sano et al., In situ study of reduction process of CuO paste and its effect on bondability of Cu-to-Cu joints. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 2193 (2018)
S. He, R. Gao, J. Li, Y.-A. Shen, H. Nishikawa, In-situ observation of fluxless soldering of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu/Cu under a formic acid atmosphere. Mater. Chem. Phys. 239, 1 (2020)
W. Lin, Y. Lee, Study of fluxless soldering using formic acid vapor. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 22, 592 (1999)
S. He, R. Gao, Y.-A. Shen, J. Li, H. Nishikawa, Wettability, interfacial reactions, and impact strength of Sn–30Ag–05Cu solder/ENIG substrate used for fluxless soldering under formic acid atmosphere. J. Mater. Sci. 55, 7 (2020)
J. Liu, H. Chen, H. Ji, M. Li, Highly conductive Cu–Cu joint formation by low-temperature sintering of formic acid-treated Cu nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 33289 (2016)
R. Gao, S. He, Y.-A. Shen, H. Nishikawa, Effect of substrates on fracture mechanism and process optimization of oxidation-reduction bonding with copper microparticles. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 2263 (2019)
S.T. Chua, K.S. Siow, Microstructural studies and bonding strength of pressureless sintered nano-silver joints on silver, direct bond copper (DBC) and copper substrates aged at 300 C. J. Alloy. Compd. 687, 486–498 (2016)
Y. Joliff, J. Absi, M. Huger, J.C. Glandus, Microcracks with unexpected characteristics induced by CTE mismatch in two-phase model materials. J. Mater. Sci. 43(1), 330–337 (2008)
N. Pilling, The oxidation of metals at high temperature. J. Inst. Met. 29, 529 (1923)
C. Xu, W. Gao, Pilling-Bedworth ratio for oxidation of alloys. Mater. Res. Innov. 3, 231 (2000)
C.H. Xu, C.H. Woo, S.Q. Shi, Formation of CuO nanowires on Cu foil. Chem. Phys. Lett. 399, 62 (2004)
M. Bowker, E. Rowbotham, F. Leibsle, S. Haq, The adsorption and decomposition of formic acid on Cu {110}. Surf. Sci. 349, 97 (1996)
A.K. Singh, S. Singh, A. Kumar, Hydrogen energy future with formic acid: a renewable chemical hydrogen storage system. Catal. Sci. Technol. 6, 12 (2016)
F. Conti, A. Hanss, C. Fischer, G. Elger, Thermogravimetric investigation on the interaction of formic acid with solder joint materials. New J. Chem. 40, 10482 (2016)
B. Hayden, K. Prince, D. Woodruff, A. Bradshaw, An IRAS study of formic acid and surface formate adsorbed on Cu (110). Surf. Sci. 133, 589 (1983)
T. Fujimoto, T. Ogura, T. Sano, M. Takahashi, A. Hirose, Joining of pure copper using Cu nanoparticles derived from CuO paste. Mater. Trans. 56, 992 (2015)
J. Li, X. Li, L. Wang, Y.-H. Mei, G.-Q. Lu, A novel multiscale silver paste for die bonding on bare copper by low-temperature pressure-free sintering in air. Mater. Des. 140, 64 (2018)
S. Hong, C.L. Fu, Theoretical study on cracking behavior in two-phase alloys Cr–Cr2X (X= Hf, Nb, Ta, Zr). Intermetallics 9(9), 799–805 (2001)
Acknowledgements
Runhua Gao thanks the China Scholarship Council for doctoral research assistantships (Support Number: 201706050096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, R., He, S., Li, J. et al. Interfacial transformation of preoxidized Cu microparticles in a formic-acid atmosphere for pressureless Cu–Cu bonding. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 14635–14644 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04026-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04026-x