Abstract
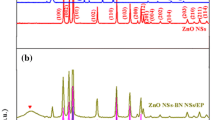
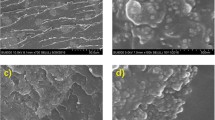
The effects of nano-particles on the electrical properties of the epoxy/ZnO nano-composites are studied and the nonlinear conduction characteristics of the nano-composites are discussed. The morphology structure, relative permittivity, DC breakdown strength and DC conductivity of the nano-composites are measured. Micro-structure analysis shows that the ZnO nano-particles were well dispersed in the epoxy matrix. Experimental results show that the relative permittivity and DC conductivity of epoxy nano-composite with the filler loading of 0.5 wt% are lower than those of pure epoxy and the other nano-composites, but the 0.5 wt% has the highest breakdown strength among the epoxy/ZnO nano-composites. In addition, when the filler loading is larger than 0.5 wt%, the epoxy/ZnO nano-composite exhibits a distinct nonlinear conduction character, namely, that the DC conductivity is greatly dependent on the applied electric field. The variation of the electrical properties and the nonlinear conduction character against the filler loading may be attributed to the interaction zone around the nano-particles.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
V.A. Zakrevskii, N.T. Sudar, A. Zaopo, Y.A. Dubitsky, Mechanism of electrical degradation and breakdown of insulating polymers. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 2135–2140 (2003)
J.M. Yang, X. Wang, H. Zhao, W.L. Zhang, M.Z. Xu, Influence of moisture absorption on the DC conduction and space charge property of MgO/LDPE nanocomposite. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 21, 1957–1964 (2014)
H. Hama, T. Hikosaka, S. Okabe, H. Okubo, Cross-equipment study on charging phenomena of solid insulators in high voltage equipment. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 14, 508–519 (2007)
D.-E.A. Mansour, H. Kojima, N. Hayakawa, F. Endo, H. Okubo, Surface charge accumulation and partial discharge activity for small gaps of electrode/epoxy interface. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 16, 1150–1157 (2009)
T. Tanaka, G.C. Montanari, R. Mulhaupt, Polymer nanocomposites as dielectrics and electrical insulation-perspectives for processing technologies, material characterization and future applications. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 11, 763–784 (2004)
T. Takada, Y. Hayase, Y. Tanaka, T. Okamoto, Space charge trap** in electrical potential well caused by permanent and induced dipoles for LDPE/MgO nanocomposite. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 15, 152–160 (2008)
B.Y. Zhang, W.Q. Gao, P.F. Chu, Z. Zhang, G.X. Zhang, Trap-modulated carrier transport tailors the dielectric properties of alumina/epoxy nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 1964–1974 (2018)
B.X. Du, J.W. Zhang, Y. Gao, Effects of TiO2 particles on surface charge of epoxy nanocomposites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 19, 755–762 (2012)
F.Q. Tian, Q.Q. Lei, X. Wang, Y. Wang, Investigation of electrical properties of LDPE/ZnO nanocomposite dielectrics. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 19, 763–769 (2012)
K. Tavernier, B.R. Varlow, D.W. Auckland, M. Ugur, Improvement in electrical insulators by nonlinear fillers. IEEE Proc. Sci. Meas. Technol. 146, 88–94 (1999)
K.P. Donnelly, B.R. Varlow, Nonlinear dc and ac conductivity in electrically insulating composites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 10, 610–614 (2003)
X. Wang, J.K. Nelson, L.S. Schadler, H. Hillborg, Mechanisms leading to nonlinear electrical response of a nano p-SiC/silicone rubber composite. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 17, 1687–1696 (2010)
T. Christen, L. Donzel, F. Greuter, Nonlinear resistive electric field grading part 1: theory and simulation. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 26, 47–59 (2011)
S.M. Lebedev, O.S. Gefle, A.E. Strizhkov, Novel polymeric composites with nonlinear current-voltage characteristic. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 20, 289–295 (2013)
J.I. Hong, L.S. Schadler, R.W. Siegel, E. Martensson, Rescaled electrical properties of ZnO/low density polyethylene nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 1956–1958 (2003)
J.I. Hong, P. Winberg, L.S. Schadler, R.W. Siegel, Dielectric properties of zinc oxide/low density polyethylene nanocomposites. Mater. Lett. 59, 473–476 (2005)
S.C. Tjong, G.D. Liang, Electrical properties of low density polyethylene/ZnO nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 100, 1–5 (2006)
S. Singha, M.J. Thomas, Influence of filler loading on dielectric properties of epoxy-ZnO nanocomposites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 16, 531–542 (2009)
N.S. Jyothi, T.S. Ramu, M. Mandlik, Temperature distribution in resin impregnated paper insulation for transformer bushings. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 17, 931–938 (2010)
D.-E.A. Mansour, H. Kojima, N. Hayakawa, F. Endo, H. Okubo, Partial discharges and associated mechanisms for micro gap delamination at epoxy spacer in GIS. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 17, 855–861 (2010)
K. Fukunaga, T. Maeno, K. Okamoto, Three-dimensional space charge observation of ion migration in a metal-base printed circuit board. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 10, 458–462 (2003)
S. Singha, M.J. Thomas, Dielectric properties of epoxy nanocomposites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 15, 12–23 (2008)
M. Roy, J.K. Nelson, R.K. MacCrone, L.S. Schadler, C.W. Reed, R. Keefe, W. Zenger, Polymer nanocomposite dielectrics—the role of the interface. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 12, 629–643 (2005)
Y.S. Han, S.T. Li, D.M. Min, Nonlinear conduction and surface potential decay of epoxy/SiC nanocomposites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 24, 3154–3164 (2017)
S.T. Li, G.L. Yin, G. Chen, J.Y. Li, S.N. Bai, L.S. Zhong, Y.X. Zhang, Q.Q. Lei, Short-term breakdown and long-term failure in nanodielectrics: a review. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 17, 1523–1535 (2010)
S.T. Li, G.L. Yin, S. Bai, J.Y. Li, A new potential barrier model in epoxy resin nanodielectrics. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 18, 1535–1543 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51677046, 51407051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Chen, Q., Yang, H. et al. Electrical properties of epoxy/ZnO nano-composite. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 12765–12770 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9394-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9394-4