Abstract
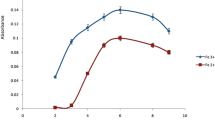
This study reports the synthesis of water soluble iron(II) phthalocyanine and a facile method for spectrophotometric determination of Hg(II) in environmental water samples by ionic liquid based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (IL-DLLME). In the method, 1-heptyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate (250 µL) as extraction solvent, acetonitrile (750 µL) as dispersive solvent and Triton X-100 (200 µL) as anti-sticking agent were used. After the extraction of the Hg(II) complex (Hg(II):q-Fe(II)-Pc) into thin droplets of ionic liquid, the sample was centrifuged for 4 min at 2000 rpm. The upper aqueous phase was removed and the residue diluted to 250 µL with methanol and transferred to a 250 µL cell for spectrophotometric detection at 280 nm. The linear range of the method is 0.05–1 µg/mL. The limits of detection and quantification is 0.01 and 0.03 µg/mL, respectively. The RSD for the developed method was calculated as 0.78% at 0.50 µg/mL Hg(II).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pacyna, E.G., Pacyna, J.M., Sundseth, K., Munthe, J., Kindbom, K., Wilson, S., Steenhuisen, F., Maxson, P.: Global emission of mercury to the atmosphere from anthrophojenic sources in 2005 and projections to 2020. Atmos. Environ. 44, 2487–2499 (2010)
Nuttal, K.L.: Interpreting mercury in blood and urine of individual patients. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 34, 235–250 (2004)
World Health Organization, http://www.who.int/foossafety/publications/risk-mercury-exposure/en/
Atkins, P., Jones, L.: Chemical Principles: The Quest for Insight. W.H. Freeman and Company Press, New York (2010)
Bast-Pettersen, R., Ellingsen, D.G., Efskind, J., Jordskogen, R., Thomassen, Y.: A neurobehavioral study of chloralkali workers after the cessation of exposure to Hg vapor. Neuro Toxicology 26, 427–437 (2005)
Langworth, S., Almkvist, O., Soderman, E., Wikstrom, B.O.: Effects of occupational exposure to Hg vapour on the central nervous system. Br. J. Ind. Met. 49, 545–555 (1992)
Nam, D.H., Yates, D., Ardapple, P., Evers, D.C., Schmerfeld, J., Basu, N.: Elevated Hg exposure and neurochemical alterations in little browns bats (Myotis lucifigus) from a site with historical Hg contamination. Ecotoxicology 21, 1094–1101 (2012)
Hopkins, W., Bodinof, C., Budischak, S., Perkins, C.: Nondestructive indicates of Hg exposure in three species of turtles occupying different trophic niches downstream from a former chloralkali facility. Ecotoxicology 22, 22–32 (2013)
Neghab, M., Choobineh, A., Hassan Zadeh, J., Ghaderi, E.: Symptoms of intoxication in dentists associated with exposure to low levels of Hg. Ind. Health 49, 249–254 (2011)
Shirkhanloo, H., Golbabaei, F., Hassani, H., Eftekhar, F., Kian, M.J.: Occupational exposure to mercury: air exposure assessment and biological monitoring based on dispersive ionic liquid–liquid microextraction. Iran. J. Public Health 43, 793–799 (2014)
Sarafraz-Yazdi, A., Amiri, A.: Liquid phase microextraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 29, 1–14 (2010)
Armenta, S., Garrigues, S., de la Guardia, M.: The role of green extraction techniques in green analytical chemistry. Trends Anal. Chem. 71, 2–8 (2015)
Pena-Pereira, F., Lavilla, I., Bendicho, C., Vidal, L., Canals, A.: Speciation of mercury by ionic-liquid based single drop microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array detection. Talanta 78, 537–541 (2009)
Kogelnig, D., Stojanovik, A., Galanski, M., Groessl, M., Jirsa, F., Krachler, R., Keppler, B.K.: Greener synthesis of new ammonium ionic liquids and their potential as extracting agents. Tetrahedron 49, 2782–2785 (2008)
Ojeda, C.B., Rojas, F.S.: Seperation preconcentration by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction procedure: a review. Chromatographia 69, 1149–1159 (2009)
Rezaee, M., Yamini, Y., Faraji, M.: Evolution of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method. J. Chromatogr. A. 1217, 2342–2357 (2010)
Cruz-Vera, M., Lucena, R., Cardenas, S., Valcercel, M.: Sample treatments based on dispersive (micro) extraction. Anal. Methods 3, 1719–1728 (2011)
Lu, Y., Lin, Q., Luo, G., Dai, Y.: Directly suspended droplet microextraction. Anal. Chim. Acta. 566, 259–264 (2006)
Rezaee, M., Assadi, Y., Milani Hosseini, M.R., Aghaee, E., Ahmadi, F., Berijani, S.: Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A. 1116, 1–9 (2006)
Bidari, A., Zeini Jahromi, E., Assadi, Y., Milani Hosseini, M.R.: Monitoring of selenium in water samples using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by iridium-modified tube graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem. J. 87, 6–12 (2007)
Gharehbaghi, M., Shemirani, F., Baghdadi, M.: Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and spectrophotometric determination of cobalt in water samples. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 88, 513–523 (2008)
Liang, P., Sang, H.: Determination of trace lead in biological and water samples with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction preconcentration. Anal. Biochem. 380, 21–25 (2008)
Liang, P., Peng, L., Yan, P.: Speciation of As(III) and As(V) in water samples by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction separation and determination by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchim. Acta. 166, 47–52 (2009)
Biyiklioğlu, Z.: New water soluble and amphiphilic titanium(IV) phthalocyanines and investigation of electropolymerization properties. J. Organomet. Chem. 752, 59–66 (2014)
Sun, J.-N., Chen, J., Shi, Y.-P.: Multiple functional ionic liquids based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high performance chromatography for the determination of phenolic compounds in water samples. Talanta 125, 329–335 (2014)
Zhou, Q., Bai, H., **e, G., **ao, J.: Temprature-controlled Ionic liquid dispersive liquid phase micro-extractin. J. Choromatogr. A. 1177, 43–49 (2008)
Li, Y., Zhang, J., Peng, B., Li, S., Gao, H., Zhou, W.: Determination of triazole pesticides in rat blood by the combination of ultrasound-enhanced temprature-controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid mcroextraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Methods 5, 2241–2248 (2013)
Gharehbaghi, M., Shemirani, F., Bagdadi, M.: Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on ionic liquid and spectrophotometric determination of mercury in water samples. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 89, 21–33 (2009)
Sanagi, M.M., Abbas, H.H., İbrahim, W.A.W., Aboul-Enien, H.Y.: Determination of triazine herbicides using membrane-protected carbon nanotubes solid phase membrane tip extraction prior to micro-liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 133, 557–562 (2012)
Kocúrová, L., Balogh, I.S., Śandrejová, J., Andruch, V.: Recent advances in dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction using organic solvents lighter than water. A review. Microchem. J. 102, 11–17 (2012)
Farajzadeh, M.A., Bahram, M., Mehr, B.G., Jönsson, J.A.: Optimization of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of copper (II) by atomic absorption spectrometry as its oxinate chelate: application to determination of copper in different water samples. Talanta 75, 832–840 (2008)
Kandhro, G.A., Soylak, M., Kazi, T.G., Yilmaz, E., Afridi, H.I.: Room temperature ionic liquid-based microextraction for pre-concentration of cadmium and copper from biological samples and determination by FAAS. At. Spectrosc. 33, 166–172 (2012)
Lemos, V.A., Dos Santoz, L.O., Dos Santoz Silva, E., Dos Santoz Vieira, E.V. : Spectrophotometric determination of mercury in water samples after preconcentration using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J. AOAC Int. 95, 227–231 (2012)
Gao, Z., Ma, X.: Speciation analysis of mercury in water samples using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta. 702, 50–55 (2011)
Hossien-poor-Zaryabi, M., Chamsaz, M., Heidari, T., Zavar, M.H.A., Behbahani, M., Salarian, M.: Application of dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extraction using mean centering of ratio spectra method for trace determination of mercury in food and environmental samples. Food Anal. Methods 7, 352–359 (2014)
Mohammadi, S.Z., Afzali, D., Baghelani, Y.M.: Ligandless-dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of trace amount of copper ions. Anal. Chim. Acta. 653, 173–177 (2009)
Shokoufi, N., Shemirani, F., Assadi, Y.: Fiber optic linear array detection spectrophotometry in combination with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for simultaneous preconcentration and determination of palladium and cobalt. Anal. Chim. Acta. 597, 349–356 (2007)
Citak, D.M.: Tuzen Seperation and determination of copper in bottled water samples by combination of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and microsample introduction flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J. AOAC Int. 96, 1435–1444 (2013)
Asghari, A., Ghazaghi, M., Rajabi, M., Behzad, M., Ghaedi, M.: Ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography-UV detection for simultaneous preconcentration and determination of Ni, Co, Cu and Zn in water samples. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 79, 63–76 (2014)
Baghdadi, M., Shemirani, F.: Cold-induced aggregation microextraction: a novel sample preparation technique based on ionic liquids. Anal. Chim. Acta. 613, 56–63 (2008)
Çağlar, Y., Gümrükçüoğlu, N., Saka, E.T., Ocak, M., Kantekin, H., Ocak, Ü: Phthalocyanine based fluorescent chemosensor for the sensing of Zn(II) in dimethyl sulfoxide-acetonitrile. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 72, 443–447 (2012)
Günsel, A., Bilgiçli, A.T., Kandaz, M., Orman, E.B., Özkaya, A.Z.: Ag(I) and Pd(II) sensing, H- or J-aggregation and redox propertiesof metal-free, manganase(III) and gallium(III) phthalocyanines. Dyes Pigments 102, 169–179 (2014)
Çağlar, Y., Saka, E.T., Alp, H., Kantekin, H., Ocak, Ü, Ocak, M.: A simple spectrofluorimetric method based on Qquenching of a nickel(II)-phthalocyanine complex to determine Iron (III). J. Fluoresc. 26, 1381–1389 (2016)
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the financial support of the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK). Grant Number: 115Z076.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çağlar, Y., Biyiklioglu, Z. Spectrophotometric determination of Hg(II) in water samples by dispersive liquid liquid microextraction with use ionic liquid after derivatization with a water soluble Fe(II) phthalocyanine. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 90, 331–339 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-018-0780-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-018-0780-6