Abstract
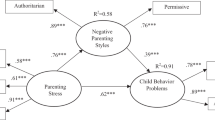
Existing literature has outlined how parental emotional regulation could affect children’s adjustment and parenting behaviors. Family studies also showed how the negative mood created by negative co-parenting interactions might spill over into the parent-child relationship, resulting in high levels of parenting stress and coercive and authoritarian parenting behaviors, strictly associated with children’s psychological maladjustment. The present study explored families’ pathways by which high levels of parental emotional dysregulation could affect children’s psychological adjustment by considering the mediating role of co-parenting, parenting stress, and authoritarian style. Mediation analyses were performed using a sample of 143 Italian father-mother dyads. Results showed that parental emotional dysregulation was linked to a negative co-parenting relationship. Moreover, the data indicated that parental emotional dysregulation was linked to children’s adjustment through the serial mediation of negative co-parenting and parenting stress. The results are discussed in terms of clinical and research implications.
Highlights
-
The exploration of families’ pathways by which high levels of parents’ emotional dysregulation could affect children’s psychological adjustment is an area worthy of further exploration.
-
The current study explored how coparenting relationships and parenting behaviors (parenting stress and authoritarian style) could serially mediate the associations between parents’ emotional dysregulation and children’s adjustment.
-
The results showed that both parents’ emotional dysregulation was linked to children’s adjustment through the serial mediators of negative coparenting and parenting stress.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidin, R. R. (1995). Parenting stress index. (Psychological Assessment Resources.
Achenbach, T. M., & Rescorla, L. (2001). Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms and profiles. Research Center for Children, Youth, and Families, University of Vermont.
Anthony, L. G., Anthony, B. J., Glanville, D. N., Naiman, D. Q., Waanders, C., & Shaffer, S. (2005). The relationships between parenting stress, parenting behaviour and preschoolers’ social competence and behaviour problems in the classroom. Infant and Child Development, 14(2), 133–154. https://doi.org/10.1002/icd.385.
Baril, M. E., Crouter, A. C., & McHale, S. M. (2007). Processes linking adolescent well-being, marital love, and co-parenting. Journal of Family Psychology, 21(4), 645–654. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-3200.21.4.645.
Bonds, D. D., & Gondoli, D. M. (2007). Examining the process by which marital adjustment affects maternal warmth: The role of co-parenting support as a mediator. Journal of Family Psychology, 21(2), 288–296. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-3200.21.2.288.
Brandão, T., Matias, M., Ferreira, T., Vieira, J., Schulz, M. S., & Matos, P. M. (2019). Attachment, emotion regulation, and well‐being in couples: Intrapersonal and interpersonal associations. Journal of Personality, 88(4), 748–761. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopy.12523.
Broderick, C., & Smith, J. (1979). The general systems approach to the family: Contemporary theories about the family. New York, NY: Free Press.
Burgdorf, V., Szabó, M., & Abbott, M. J. (2019). The effect of mindfulness interventions for parents on parenting stress and youth psychological outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 1336 https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01336.
Cabrera, N. J., Fitzgerald, H. E., Bradley, R. H., & Roggman, L. (2014). The ecology of father–child relationships: An expanded model. Journal of Family Theory and Review, 6, 336–354. https://doi.org/10.1111/jftr.12054.
Cabrera, N. J., Volling, B. L., & Barr, R. (2018). Fathers are parents, too! Widening the lens on parenting for children’s development. Child Development Perspectives, 12(3), 152–157. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdep.12275.
Camisasca, E., Miragoli, S., & Covelli, V. (2021a). Dallo stress economico al malessere psicologico dei minori durante la pandemia da Covid-19: quale ruolo per il conflitto co-genitoriale e le pratiche educative autoritarie? Maltrattamento e Abuso all’Infanzia, 23(1), 13–27. https://doi.org/10.3280/MAL2021-001002.
Camisasca, E., & Di Blasio, P. (2014). Does parenting stress mediate the association between maternal mind-mindedness and children’s psychological adjustment? A pilot study. Psicologia Clinica dello Sviluppo, 18(3), 479–490.
Camisasca, E., & Di Blasio, P. (2019). Stress genitoriale materno e sintomatologia post-traumatica in bambini esposti al conflitto genitoriale: Un modello di mediazione. Maltrattamento e Abuso All’infanzia, 2, 79–94. https://doi.org/10.3280/mal2019-002006.
Camisasca, E., Miragoli, S., & Di Blasio, P. (2021b). COVID-19 e funzionamento familiare. Maltrattamento e Abuso all’infanzia, 23(1), 7–11. https://doi.org/10.3280/MAL2021-001001.
Camisasca, E., Miragoli, S., Caravita, S., & Di Blasio, P. (2015). The parenting alliance measure: The first contribution to the validation of the measure in Italian mothers and fathers. TPM: Testing, Psychometrics, Methodology in Applied Psychology, 22(1), 71–95. https://doi.org/10.1037/t47039-000.
Camisasca, E., Miragoli, S., & Di Blasio, P. (2013). L’attaccamento modera le reazioni dei bambini esposti al conflitto genitoriale? Verifica di un modello integrato [Does attachment moderate the reactions of children exposed to marital conflict? Evidence for an integrated model]. Psicologia Clinica Dello Sviluppo, 17(3), 479–500.
Camisasca, E., Miragoli, S., & Di Blasio, P. (2014). Is the relationship between marital adjustment and parenting stress mediated or moderated by parenting alliance? Europe’s Journal of Psychology, 10(2), 235–254. https://doi.org/10.5964/ejop.v10i2.724.
Camisasca, E., Miragoli, S., & Di Blasio, P. (2016b). Families with distinct levels of marital conflict and child adjustment: Which role for maternal and paternal stress? Journal of Child and Family Studies, 25(3), 733–745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-015-0261-0.
Camisasca, E., Miragoli, S., & Di Blasio, P. (2016c). Conflittualità genitoriale e sintomatologia da stress post-traumatico nei figli: Uno studio esplorativo. Maltrattamento e Abuso All’infanzia, 18(2), 139–149. https://doi.org/10.3280/mal2016-002008.
Camisasca, E., Miragoli, S., & Di Blasio, P. (2019a). Children’s triangulation during inter-parental conflict: Which role for maternal and paternal parenting stress? Journal of Child and Family Studies, 28(6), 1623–1634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-019-01380-1.
Camisasca, E., Miragoli, S., Di Blasio, P., & Feinberg, M. (2019b). Co-parenting mediates the influence of marital satisfaction on child adjustment: The conditional indirect effect by parental empathy. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 28(2), 519–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-018-1271-5.
Camisasca, E., Miragoli, S., Milani, L., & Di Blasio, P. (2016a). Adattamento di coppia, cogenitorialità e benessere psicologico dei figli: Uno studio esplorativo. Psicologia Della Salute, 2, 127–141. https://doi.org/10.3280/pds2016-002007.
Cheche Hoover, R., & Jackson, J. B. (2019). Insecure attachment, emotion dysregulation, and psychological aggression in couples. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 088626051987793. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260519877939
Choi, J. K., & Becher, E. H. (2019). Supportive co-parenting, parenting stress, harsh parenting, and child behavior problems in nonmarital families. Family Process, 58(2), 404–417. https://doi.org/10.1111/famp.12373.
Confaloneri, E., Giuliani, C., & Tagliabue, S. (2009). Authoritative and authoritian parenting style and their dimensions: First contribution to the italian adaptation of a self report instrument. Bollettino di Psicologia Applicata, 258, 51–61.
Davies, P., & Cummings, E. M. (1994). Marital conflict and childadjustment: An emotional security hypothesis. Psychological Bulletin, 116(3), 387–411.
Deater-Deckard, K., Li, M., & Bell, M. A. (2016). Multifaceted emotion regulation, stress and affect in mothers of young children. Cognition and Emotion, 30(3), 444–457. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699931.2015.1013087.
Denham, S. A., Workman, E., Cole, P. M., Weissbrod, C., Kendziora, K. T., & Zahn–Waxler, C. (2000). Prediction of externalizing behavior problems from early to middle childhood: The role of parental socialization and emotion expression. Development and Psychopathology, 12(1), 23–45. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579400001024.
English, T., & Eldesouky, L. (2020). We’re not alone: Understanding the social consequences of intrinsic emotion regulation. Emotion, 20(1), 43–47. https://doi.org/10.1037/emo0000661.
English, T., & John, O. P. (2013). Understanding the social effects of emotion regulation: The mediating role of authenticity for individual differences in suppression. Emotion, 13(2), 314–329. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0029847.
English, T., John, O. P., Srivastava, S., & Gross, J. J. (2012). Emotion regulation and peer-rated social functioning: A 4-year longitudinal study. Journal of Research in Personality, 46(6), 780–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2012.09.006.
Erel, O., & Burman, B. (1995). Interrelatedness of marital relations and parent-child relations: A meta-analytic review. Psychological Bulletin, 118(1), 108–132. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.118.1.108.
Feinberg, M. E. (2003). The internal structure and ecological context of co-parenting: A framework for research and intervention. Parenting, 3(2), 95–131. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327922par0302_01.
Feinberg, M. E., Brown, L. D., & Kan, M. L. (2012). A multi-domain self-report measure of co-parenting. Parenting, 12(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15295192.2012.638870.
Feinberg, M. E., & Jones, D. E. (2018). Experimental support for a family systems approach to child development: Multiple mediators of intervention effects across the transition to parenthood. Couple and Family Psychology: Research and Practice, 7(2), 63–75. https://doi.org/10.1037/cfp0000100.
Frigerio, A. (2001). Manual for the child behavior checklist 4-18. IRCCS Eugenio Medea, Editore Ghedini Libraio.
Fosco, G. M., & Grych, J. H. (2008). Emotional, cognitive, and family systems mediators of children’s adjustment to interparental conflict. Journal of Family Psychology, 22(6), 843 https://doi.org/10.1037/a0013809.
Gratz, K. L., & Roemer, L. (2004). Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation and dysregulation: development, factor structure, and initial validation of the difficulties in emotion regulation scale. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 26(1), 41–54. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:joba.0000007455.08539.94.
Gross, J. J. (2007). Handbook of emotion regulation (Editor). New York: Guilford.
Guarino, A., Di Blasio, P., D’Alessio, M., Camisasca, E., & Serantoni, M. (2008). Parenting stress index short form: Adattamento italiano. Giunti: Organizzazioni Speciali.
Grych, J. H., Seid, M., & Fincham, F. D. (1992). Assessing marital conflict from the child's perspective: The Children’s Perception of Interparental Conflict Scale. Child Development, 63(3), 558–572.
Han, Z. R., Lei, X., Qian, J., Li, P., Wang, H., & Zhang, X. (2016). Parent and child psychopathological symptoms: the mediating role of parental emotion dysregulation. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 21(3), 161–168. https://doi.org/10.1111/camh.12169.
Hayes, A. F. (2018). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach. Guilford Press.
Impett, E. A., Kogan, A., English, T., John, O., Oveis, C., Gordon, A. M., & Keltner, D. (2012). Suppression sours sacrifice. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 38(6), 707–720. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167212437249.
Jahromi, L. B., Zeiders, K. H., Updegraff, K. A., Umaña-Taylor, A. J., & Bayless, S. D. (2018). Co-parenting conflict and academic readiness in children of teen mothers: Effortful control as a mediator. Family Process, 57(2), 462–476. https://doi.org/10.1111/famp.12290.
Kabat-Zinn, J., Massion, A. O., Kristeller, J., Peterson, L. G., Fletcher, K. E., & Pbert, L., et al. (1992). Effectiveness of a meditation-based stress reduction program in the treatment of anxiety disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry, 149, 936. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.149.7.936.
Kang, S. K., Choi, H. J., & Chung, M. R. (2020). Coparenting and parenting stress of middle-class mothers during the first year: Bidirectional and unidirectional effects. Journal of Family Studies, 1-18. https://doi.org/10.1080/13229400.2020.1744472
Kim, H. K., Pears, K. C., Capaldi, D. M., & Owen, L. D. (2009). Emotion dysregulation in the intergenerational transmission of romantic relationship conflict. Journal of Family Psychology, 23(4), 585. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0015935.
Lau, E. Y. H., & Power, T. G. (2019). Co-parenting, parenting stress, and authoritative parenting among Hong Kong Chinese mothers and fathers. Parenting, 20(3), 167–176. https://doi.org/10.1080/15295192.2019.1694831.
Li, D., Li, D., Wu, N., & Wang, Z. (2019). Intergenerational transmission of emotion regulation through parents’ reactions to children’s negative emotions: Tests of unique, actor, partner, and mediating effects. Children and Youth Services Review, 101, 113–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2019.03.038.
Lindsey, E. W., Caldera, Y., & Colwell, M. (2005). Correlates of co-parenting during infancy*. Family Relations, 54(3), 346–359. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-3729.2005.00322.x.
McHale, J. P. (1995). Co-parenting and triadic interactions during infancy: The roles of marital distress and child gender. Developmental Psychology, 31(6), 985–996. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.31.6.985.
McHale, J. P., Kuersten-Hogan, R., Lauretti, A., & Rasmussen, J. L. (2000). Parental reports of co-parenting and observed co-parenting behavior during the toddler period. Journal of Family Psychology, 14(2), 220–236. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-3200.14.2.220.
McHale, J. P., & Lindahl, K. M. (2011). Co-parenting: A conceptual and clinical examination of family systems. American Psychological Association.
McNulty, J. K., & Hellmuth, J. C. (2008). Emotion regulation and intimate partner violence in newlyweds. Journal of Family Psychology, 22(5), 794–797. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0013516.
Minuchin, P. (1985). Families and individual development: Provocations from the field of family therapy. Child Development, 56(2), 289–302. https://doi.org/10.2307/1129720.
Miragoli, S., Balzarotti, S., Camisasca, E., & Di Blasio, P. (2018). Parents’ perception of child behavior, parenting stress, and child abuse potential: Individual and partner influences. Child Abuse & Neglect, 84, 146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2018.07.034.
Morrill, M. I., Hines, D. A., Mahmood, S., & CÓRdova, J. V. (2010). Pathways between marriage and parenting for wives and husbands: The role of co-parenting. Family Process, 49(1), 59–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1545-5300.2010.01308.x.
Parkes, A., Green, M., & Mitchell, K. (2019). Co-parenting and parenting pathways from the couple relationship to children’s behavior problems. Journal of Family Psychology, 33(2), 215–225. https://doi.org/10.1037/fam0000492.
Pinquart, M. (2017). Associations of parenting dimensions and styles with externalizing problems of children and adolescents: An updated meta-analysis. Developmental Psychology, 53(5), 873–932. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000295.
Quetsch, L. B., Wallace, N. M., McNeil, C. B., & Gentzler, A. L. (2018). Emotion regulation in families of children with behavior problems and nonclinical comparisons. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 27(8), 2467–2480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-018-1081-9.
Roberts, T. (1990). A systems perspective of parenting: The family’s responsibility in misbehaving. Family Science Review, 2, 139–151.
Robinson, C. C., Mandleco, B., Olsen, S. F., & Hart, C. H. (1995). Authoritative, authoritarian, and permissive parenting practices: Development of a new measure. Psychological Reports, 77(3), 819–830. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.1995.77.3.819.
Rose, J., Roman, N., Mwaba, K., & Ismail, K. (2018). The relationship between parenting and internalizing behaviours of children: A systematic review. Early Child Development and Care, 188(10), 1468–1486. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004430.2016.1269762.
Rutherford, H. J. V., Wallace, N. S., Laurent, H. K., & Mayes, L. C. (2015). Emotion regulation in parenthood. Developmental Review, 36, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dr.2014.12.008.
Shorey, R., McNulty, J., Moore, T., & Stuart, G. (2015). Emotion regulation moderates the association between proximal negative affect and intimate partner violence perpetration. Prevention Science, 16(6), 873–880. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-015-0568-5.
Shaw, Z. A., & Starr, L. R. (2019). Intergenerational transmission of emotion dysregulation: The role of authoritarian parenting style and family chronic stress. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 28(12), 3508–3518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-019-01534-1.
Sighinolfi, C., Norcini Pala, A., Chiri, L., Marchetti, I., & Sica, C. (2010). Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale (DERS): The Italian translation and adaptation. Psicoterapia Cognitiva Comportamentale, 16, 141–170.
Solmeyer, A. R., & Feinberg, M. E. (2011). Mother and father adjustment during early parenthood: The roles of infant temperament and co-parenting relationship quality. Infant Behavior and Development, 34(4), 504–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infbeh.2011.07.006.
Solmeyer, A. R., Feinberg, M. E., Coffman, D. L., & Jones, D. E. (2014). The effects of the family foundations prevention program on co-parenting and child adjustment: A mediation analysis. Prevention Science, 15(2), 213–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-013-0366-x.
Stroud, C. B., Meyers, K. M., Wilson, S., & Durbin, C. E. (2015). Marital quality spillover and young children’s adjustment: Evidence for dyadic and triadic parenting as mechanisms. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 44(5), 800–813. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2014.900720.
Teubert, D., & Pinquart, M. (2010). The association between co-parenting and child adjustment: A meta-analysis. Parenting, 10(4), 286–307. https://doi.org/10.1080/15295192.2010.492040.
Velotti, P., Balzarotti, S., Tagliabue, S., English, T., Zavattini, G. C., & Gross, J. J. (2016). Emotional suppression in early marriage: Actor, partner, and similarity effects on marital quality. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 33(3), 277–302. https://doi.org/10.1177/0265407515574466.
von Bertalanffy, L. (1968). General system theory: foundations, development, applications. George Braziller.
Zou, S., Wu, X., & Li, X. (2020). Co-parenting behavior, parent–adolescent attachment, and peer attachment: An examination of gender differences. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 49(1), 178–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-019-01068-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
In the treatment of the subjects, we have complied with APA and AIP (Associazione Italiana di Psicologia), ethical standards and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the Catholic University of Milan in April 2013.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Camisasca, E., Miragoli, S., Di Blasio, P. et al. Pathways Among Negative Co-parenting, Parenting Stress, Authoritarian Parenting Style, and Child Adjustment: The Emotional Dysregulation Driven Model. J Child Fam Stud 31, 3085–3096 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-022-02408-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-022-02408-9