Abstract
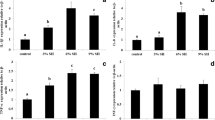
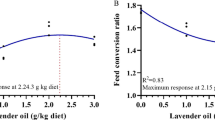
This study investigates the impact of different levels of hydroalcoholic extract of the marine red alga (Hypnea cornua) on growth performance, hematological indices, antioxidant capacity, immune response, and expression of growth-related genes in beluga sturgeon (Huso huso). A total of 120 juvenile beluga sturgeon (425.62 ± 26.32 g) were randomly divided into four treatments with three replicates and reared for 8 weeks. The fish were fed diets incorporating varying amounts of the algal extract (0 [control group], 5, 10, and 20 g kg-1). The inclusion of the dietary algal extract significantly improved final weight, weight gain, and specific growth rate (P < 0.05), while reducing the feed conversion ratio. The red blood cell count, hematocrit level, total protein level, and lysozyme activity were significantly increased (P < 0.05) in the fish group treated with 10 g algal extract kg-1 compared to the control and other treatments. The highest superoxide dismutase activity was observed in fish fed a diet with 10 g algal extract kg-1. The serum catalase activity was significantly higher in all fish treated with algal extract compared to those fed with the control diet (P < 0.05). The serum glutathione activity was markedly higher in the fish fed diets containing 10 and 20 g kg-1 compared to those fed with the control diet (P < 0.05). The malondialdehyde level was lower in the treated fish compared to those fed with the control diet (P < 0.05). The highest mRNA levels of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 were observed in the fish fed a diet containing 10 g algal extract kg-1 (P < 0.05). These findings suggest that an optimal dietary inclusion level of 11.22 g kg-1 of the marine red algal extract is recommended for improving growth performance, feed utilization, and overall well-being of beluga sturgeon.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Abdulrahman NM, Abid SH, Koyun M (2019) Effect of microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa as feed additive on common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) nutritional performance, proximate composition and organoleptic evaluation. Biol Appl Env Res 3:118–126
Abtahi B, Yousefi M, Kenari AA (2013) Influence of dietary nucleotides supplementation on growth, body composition and fatty acid profile of Beluga sturgeon juveniles (Huso huso). Aquacult Res 44:254–260
Adel M, Yeganeh S, Dadar M, Sakai M, Dawood MA (2016) Effects of dietary Spirulina platensis on growth performance, humoral and mucosal immune responses and disease resistance in juvenile great sturgeon (Huso huso Linnaeus, 1754). Fish Shellfish Immunol 56:436–444
Ahmadifar E, Pourmohammadi Fallah H, Yousefi M, Dawood MA, Hoseinifar SH, Adineh H, Yilmaz S, Paolucci M, Doan HV (2021) The gene regulatory roles of herbal extracts on the growth, immune system, and reproduction of fish. Animals 11:2167
Amrkolaie AK, Yansari AT, Khalesi M (2013) Calculation of protein and energy requirements in beluga sturgeon (Huso huso) using a factorial approach. Journal of Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 97:485–494
Banavreh A, Soltani M, Kamali A, Yazdani-Sadati MA, Shamsaie M (2019) Effects of olive pomace on growth performance, digestibility, body composition and fatty acid profile in yearling Siberian sturgeon, Acipenser baerii (Brandt 1896). Aquacult Nutr 25:333–342
Bernal J, Mendiola J, Ibáñez E, Cifuentes A (2011) Advanced analysis of nutraceuticals. J Pharmaceut Biomed Anal 55:758–774
Chandra G, Fopp-Bayat D (2021) Trends in aquaculture and conservation of sturgeons: A review of molecular and cytogenetic tools. Rev Aquacult 13:119–137
Council NR (2011) Nutrient requirements of fish and shrimp. National Academies Press, Washington DC
Daliri MK, Firouzbakhsh F, Deldar H (2020) Effect of oral administration of red alga (Laurencia caspica) hydroalcoholic extract on growth performance, hematological indices and serum biochemistry in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Vet Res 75:328–340 (in Persian)
Dawood MA, Basuini MFE, Yilmaz S, Abdel-Latif HM, Kari ZA, Abdul Razab MKA, Ahmed HA, Alagawany M, Gewaily MS (2021) Selenium nanoparticles as a natural antioxidant and metabolic regulator in aquaculture: a review. Antioxidants 10:1364
Fleurence J, Morançais M, Dumay J (2018) Seaweed proteins. In: Yada Y (ed) Proteins in food processing, 2nd edn. Woodhead Publishing, Duxford, pp 245–262
Ghiasi S, Falahatkar B, Arslan M, Dabrowski K (2017) Physiological changes and reproductive performance of Sterlet sturgeon Acipenser ruthenus injected with thiamine. Animal Reprod Sci 178:23–30
Holdt S, Kraan S (2011) Bioactive compounds in seaweed: Functional food applications seaweed Ulva rigida C. Agardh. Int Immunopharmacol 7:879–888
Hoseinifar SH, Mirvaghefi A, Merrifield DL, Amiri BM, Yelghi S, Bastami KD (2011a) The study of some haematological and serum biochemical parameters of juvenile beluga (Huso huso) fed oligofructose. Fish Physiol Biochem 37:91–96
Hoseinifar SH, Mirvaghefi A, Mojazi Amiri B, Rostami HK, Merrifield D (2011b) The effects of oligofructose on growth performance, survival and autochthonous intestinal microbiota of beluga (Huso huso) juveniles. Aquacult Nutr 17:498–504
Jiménez-González C, Agrasar AMT, Mallo F, Rúa ML, Fuciños C (2023) Red seaweed proteins: Valuable marine-origin compounds with encouraging applications. Algal Res 75:103262
Khanzadeh M, Hoseinifar SH, Beikzadeh B (2024) Investigating the effect of hydroalcoholic extract of red algae (Laurencia caspica) on growth performance, mucosal immunity, digestive enzyme activity and resistance to Streptococcus iniae and Aeromonas hydrophila in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquacult Rep 35:101984
Kiadaliri M, Firouzbakhsh F, Deldar H (2020) Effects of feeding with red algae (Laurencia caspica) hydroalcoholic extract on antioxidant defense, immune responses, and immune gene expression of kidney in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquaculture 526:735361
Magnadóttir B (2006) Innate immunity of fish (overview). Fish Shellfish Immunol 20:137–151
Magouz FI, Radwan IA, Soltan HO, El-Keredy A (2023) Synbiotic Lactic Dry enhanced the growth performance, growth-related genes, intestinal health, and immunity of Nile tilapia reared in inland brackish groundwater. Ann Anim Sci 23:495–504
Mendes R, Cardoso C, Pestana C (2009) Measurement of malondialdehyde in fish: A comparison study between HPLC methods and the traditional spectrophotometric test. Food Chem 112:1038–1045
Mohseni M, Hamidoghli A, Bai SC (2021) Organic and inorganic dietary zinc in beluga sturgeon (Huso huso): Effects on growth, hematology, tissue concertation and oxidative capacity. Aquaculture 539:736672
Mzengereza K, Ishikawa M, Koshio S, Yokoyama S, Yukun Z, Shadrack RS, Seo S, Duy Khoa TN, Moss A, Dossou S (2021) Effect of substituting fish oil with camelina oil on growth performance, fatty acid profile, digestibility, liver histology, and antioxidative status of red seabream (Pagrus major). Animals 11:1990
Pourkazemi M (2006) Caspian Sea sturgeon Conservation and fisheries: Past present and future. J Appl Ichthyol 22:12–16
Prabu DL, Sahu NP, Pal AK, Dasgupta S, Narendra A (2016) Immunomodulation and interferon gamma gene expression in sutchi cat fish, Pangasianodon hypophthalmus: effect of dietary fucoidan rich seaweed extract (FRSE) on pre and post challenge period. Aquacult Res 47:199–218
Sa**a K, Sahu NP, Varghese T, Jain KK (2019) Fucoidan-rich Sargassum wightii extract supplemented with α-amylase improve growth and immune responses of Labeo rohita (Hamilton, 1822) fingerlings. J Appl Phycol 31:2469–2480
Saleh HA, Gaber HS, El-Khayat HMM, Abdel-Motleb A, Mohammed WA-A, Okasha H (2021) Influences of dietary supplementation of Chlorella vulgaris and Spirulina platensis on growth-related genes expression and antioxidant enzymes in Oreochromis niloticus fish exposed to heavy metals. Aquacult Stud 22:793
Sargazi F, Sheidai M, Riahi H (2014) The ecology and morphological variation of Hypnea (Red Algae) species in Iran. J Bio Environ Sci 5:312–317
Sattanathan G, Liu W-C, Padmapriya S, Pushparaj K, Sureshkumar S, Lee J-W, Balasubramanian B, Kim IH (2022) Effects of dietary blend of algae extract supplementation on growth, biochemical, haemato-immunological response, and immune gene expression in Labeo rohita with Aeromonas hydrophila post-challenges. Fishes 8:7
Saurabh S, Sahoo P (2008) Lysozyme: an important defence molecule of fish innate immune system. Aquacult Res 39:223–239
Schmittgen TD (2007) Quantitative gene expression by real-time PCR: a complete protocol. In: Dorak M (ed) Real-time PCR. Taylor & Francis, London, pp 155–166
Siwicki AK, Anderson DP (1993) Nonspecific defense mechanisms assay in fish II; Potential killing activity of neutrophils and monocytes, lysozyme activity in serum and organs and total immunoglobulin (Ig) level in serum. In: Siwicki AK, Anderson DP, Waluga J (eds) Fish Diseases Diagnosis and Prevention Methods. Wydawnictwo Instytutu Rybactwa Strodladowego, Olsztyn, pp 105–111
Soler-Vila A, Coughlan S, Guiry MD, Kraan S (2009) The red alga Porphyra dioica as a fish-feed ingredient for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): effects on growth, feed efficiency, and carcass composition. J Appl Phycol 21:617–624
Souza BW, Cerqueira MA, Martins JT, Quintas MA, Ferreira AC, Teixeira JA, Vicente AA (2011) Antioxidant potential of two red seaweeds from the Brazilian coasts. J Ag Food Chem 59:5589–5594
Thanigaivel S, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A, Thomas J (2016) Seaweeds as an alternative therapeutic source for aquatic disease management. Aquaculture 464:529–536
Thepot V, Campbell AH, Rimmer MA, Paul NA (2021) Meta-analysis of the use of seaweeds and their extracts as immunostimulants for fish: a systematic review. Rev Aquacult 13:907–933
Tulaby Dezfuly Z, Mesbah M, Peyghan R, Mohammadian T, Bita S (2017) Effect of feeding diets containing ethanol extract of algae, Sargassum angustifolium on some blood and immune factors in Macro (Labidochromis caeruleus). Iranian Vet J 13:68–77 (In Persian)
Van Muiswinkel WB, Nakao M (2014) A short history of research on immunity to infectious diseases in fish. Develop Comparat Immunol 43:130–150
Wan AH, Davies SJ, Soler-Vila A, Fitzgerald R, Johnson MP (2019) Macroalgae as a sustainable aquafeed ingredient. Rev Aquacult 11:458–492
Wan AH, Soler-Vila A, O’Keeffe D, Casburn P, Fitzgerald R, Johnson MP (2016) The inclusion of Palmaria palmata macroalgae in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) diets: effects on growth, haematology, immunity and liver function. J Appl Phycol 28:3091–3100
Wassef EA, El-Sayed A-FM, Sakr EM (2013) Pterocladia (Rhodophyta) and Ulva (Chlorophyta) as feed supplements for European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax L., fry. J Appl Phycol 25:1369–1376
Wood TL, Rogler LE, Czick ME, Schuller AG, Pintar JE (2000) Selective alterations in organ sizes in mice with a targeted disruption of the insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 gene. Mol Endocrinol 14:1472–1482
Xu X, Song F, Fan X, Fang N, Shi J (2009) A novel bromophenol from marine red alga Symphyocladia latiuscula. Chem Nat Comp 45:811–813
Younis E-SM, Al-Quffail AS, Al-Asgah NA, Abdel-Warith A-WA, Al-Hafedh YS (2018) Effect of dietary fish meal replacement by red algae, Gracilaria arcuata, on growth performance and body composition of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Saudi J Biol Sci 25:198–203
Yousefi M, Abtahi B, Kenari AA (2012) Hematological, serum biochemical parameters, and physiological responses to acute stress of Beluga sturgeon (Huso huso, Linnaeus 1785) juveniles fed dietary nucleotide. Comp Clin Pathol 21:1043–1048
Zhao J-G, Zhou L, ** J-Y, Zhao Z, Lan J, Zhang Y-B, Zhang Q-Y, Gui J-F (2009) Antimicrobial activity-specific to Gram-negative bacteria and immune modulation-mediated NF-κB and Sp1 of a medaka β-defensin. Develop Comp Immunol 33:624–637
Zhou H, Ko WK, Ho WK, Stojilkovic SS, Wong AO (2004) Novel aspects of growth hormone (GH) autoregulation: GH-induced GH gene expression in grass carp pituitary cells through autocrine/paracrine mechanisms. Endocrinology 145:4615–4628
Acknowledgements
We hereby thank Mazandaran Biotechnology Laboratory for hel** us in this research to perform the gene expression assay.
Funding
No funds, grants, or other financial support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.Gh.: Investigation, Writing—Original draft preparation. M.S.M.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Methodology, and Writing—Review & Editing. H.R.I and A.M.M.: Formal analysis and Writing—Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghanadi, A., Mehrgan, M.S., Rajabi Islami, H. et al. Exploring the potential of the marine red alga (Hypnea cornua) hydroalcoholic extract in beluga sturgeon (Huso huso) diet: Growth, immuno-antioxidant responses, and growth-related gene expression. J Appl Phycol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-024-03275-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-024-03275-1