Abstract
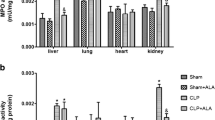
Sepsis progression is linked to the imbalance between reactive oxygen species and antioxidant enzymes. Sepsis affects multiple organs, but when associated with a chronic inflammatory disease, such as obesity, it may be exacerbated. We hypothesized that obesity could aggravate the oxidative damage to peripheral organs of rats submitted to an animal model of sepsis. Male Wistar rats aged 8 weeks received hypercaloric nutrition for 2 months to induce obesity. Sepsis was induced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) procedure, and sham-operated rats were considered as control group. The experimental groups were divided into sham + eutrophic, sham + obese, CLP + eutrophic, and CLP + obese. Twelve and 24 h after surgery, oxidative damage to lipids and proteins and superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities were evaluated in the liver, lung, kidney, and heart. The data indicate that obese rats subjected to sepsis present oxidative stress mainly in the lung and liver. This alteration reflected an oxidative damage to lipids and proteins and an imbalance of SOD and CAT levels, especially 24 h after sepsis. It follows that obesity due to its pro-inflammatory phenotype can aggravate sepsis-induced damage in peripheral organs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karapetsa, M., M. Pitsika, N. Goutzourelas, D. Stagos, A.T. Becker, et al. 2013. Oxidative status in ICU patients with septic shock. Food Chemistry and Toxicology 61: 106–111.
Kolyva, A.S., V. Zolota, D. Mpatsoulis, G. Skroubis, E.E. Solomou, I.G. Habeos, et al. 2014. The role of obesity in the immune response during sepsis. Nutrition and Diabetes 4(137): 1–7.
Rocha, M., R. Herance, S. Rovira, A. Hernández-Mijares, and V.M. Victor. 2012. Mitochondrial dysfunction and antioxidant therapy in sepsis. Infectious Disorder Drug Targets 12(2): 161–178.
Aziz, M., A. Jacob, W.L. Yang, A. Matsuda, and P. Wang. 2013. Current trends in inflammatory and immunomodulatory mediators in sepsis. Journal Leukocytes Biology 93(3): 329–342.
** review. Critical Care 19: 373.
Barichello, T., J.J. Fortunato, A.M. Vitali, G. Feier, A. Reinke, J.C. Moreira, et al. 2006. Oxidative variables in the rat brain after sepsis induced by cecal ligation and perforation. Critical Care Medicine 34(3): 886–889.
Andrades, M., C. Ritter, M.R. de Oliveira, E.L. Streck, J.C. Fonseca Moreira, and F. Dal-Pizzol. 2011. Antioxidant treatment reverses organ failure in rat model of sepsis: role of antioxidant enzymes imbalance, neutrophil infiltration, and oxidative stress. Journal of Surgical Research 167(2): e307–e313.
Ritter, C., M. Andrades, M.L. Frota Júnior, F. Bonatto, R.A. Pinho, M. Polydoro, et al. 2003. Oxidative parameters and mortality in sepsis induced by cecal ligation and perforation. Intensive Care Medicine 29(10): 1782–1789.
Zapelini, P.H., G.T. Rezin, M.R. Cardoso, C. Ritter, F. Klamt, J.C. Moreira, et al. 2008. Antioxidant treatment reverses mitochondrial dysfunction in a sepsis animal model. Mitochondrion 8(3): 211–218.
Matsuda, M., and I. Shimomura. 2013. Increased oxidative stress in obesity: implications for metabolic syndrome, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, and cancer. Obesity Research and Clinical Practice 7(5): e330–e341.
Murdolo, G.M., F. Piroddi, C. Luchetti, B. Tortoioli, C. Canonico, C. Zerbinati, et al. 2013. Oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation by-products at the crossroad between adipose organ dysregulation and obesity-linked insulin resistance. Biochimie 95(3): 585–594.
Genoni, G., F. Prodam, A. Marolda, E. Giglione, I. Demarchi, S. Bellone, et al. 2014. Obesity and infection: two sides of one coin. European Journal of Pediatrics 173(1): 25–32.
Huang, C.J., M.J. McAllister, A.L. Slusher, H.E. Webb, J.T. Mock, and E.O. Acevedo. 2015. Obesity-Related Oxidative Stress: the Impact of Physical Activity and Diet Manipulation. Sports Medicine – Open 1(1): 32.
Milner, J.J., and M.A. Beck. 2012. The impact of obesity on the immune response to infection. The Proceedings of the Nutritional Society 71(2): 298–306.
Wurzinger, B., M.W. Dünser, C. Wohlmut, M.C. Deutinger, H. Ulmer, C. Torgersen, et al. 2010. The association between body-mass index and patient outcome in septic shock: a retrospective cohort study. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 122(1-2): 31–36.
Vieira, A.A., M. Michels, D. Florentino, D.Z. Nascimento, G.T. Rezin, D.D. Leffa, et al. 2015. Obesity promotes oxidative stress and exacerbates sepsis-induced brain damage. Current Neurovascular Research 12(2): 147–154.
Estadella, D., L.M. Oyama, A.R. Damaso, E.B. Ribeiro, and C.M. Oller Do Nascimento. 2004. Effect of palatable hyperlipidic diet on lipid metabolism of sedentary and exercised rats. Nutrition 20(2): 218–224.
Bernardis, L.L., and B.D. Patterson. 1968. Correlation between ‘Lee index’ and carcass fat content in weanling and adult female rats with hypothalamic lesions. Journal of Endocrinology 40(4): 527–528.
Hubbard, W.J., M. Choudhry, M.G. Schwacha, J.D. Kerby, L.W. Rue, K.I. Bland, et al. 2005. Cecal ligation and puncture. Shock 24(Suppl 1): 52–57.
Draper, H.H., and M. Hadley. 1990. Malondialdehyde determination as índex of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymology 186: 421–431.
Levine, R.L., D. Garland, C.N. Oliver, A. Amici, I. Climent, A.G. Lenz, et al. 1990. Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymology 186: 464–478.
Bannister, J.V., and L. Caberese. 1987. Assays for superoxide dismutase. Methods Biological Analytical 32: 231–279.
Aebi, H. 1984. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymology 105: 121–126.
Lowry, O.H., A.L. Rosebrough, A.L. Farr, and R.J. Randal. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. Journal of Biological and Chemistry 193(1): 265–275.
Vachharajani, V. 2008. Influence of obesity on sepsis. Pathophysiology 15(2): 123–134.
Zhou, L., and F. Liu. 2010. Autophagy: roles in obesity-induced ER stress and adiponectin downregulation in adipocytes. Autophagy 6(8): 1196–1197.
Wang, S., and R.J. Kaufman. 2014. How does protein misfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum affect lipid metabolism in the liver? Current Opinion Lipidology 25(2): 125–132.
Fu, S., S.M. Watkins, and G.S. Hotamisligil. 2012. The role of endoplasmic reticulum in hepatic lipid homeostasis and stress signaling. Cell Metabolism 15(5): 623–634.
Yang, L., P. Li, S. Fu, E.S. Calay, and G.S. Hotamisligil. 2010. Defective hepatic autophagy in obesity promotes ER stress and causes insulin resistance. Cell Metabolism 11(6): 467–478.
Chang, Y.C., S.W. Hee, M.L. Hsieh, Y.M. Jeng, and L.M. Chuang. 2015. The Role of Organelle Stresses in Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity: Implication for Treatment. Analytical Cellular Pathology (Amst) 2015: 972891.
Guo, B., and Z. Li. 2014. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatic steatosis and inflammatory bowel diseases. Frontiers in Genetics 5: 242.
Kume, S., T. Uzu, A. Shin-ichi, S. Toshiro, I. Keiji, C.K. Masami, et al. 2008. Role of altered renal lipid metabolism in the development of renal injury induced by a high-fat diet. Journal of American Society of Nephrology 18(10): 2715–2723.
Roza, N.A., L.F. Possignolo, A.C. Palanch, and J.A. Gontijo. 2016. Effect of long-term high-fat diet intake on peripheral insulin sensibility, blood pressure, and renal function in female rats. Food Nutrition Research 60: 28536.
Knight, S.F., J.E. Quigley, J. Yuan, S.S. Roy, A. Elmarakby, and J.D. Imig. 2008. Endothelial dysfunction and the development of renal injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats fed a high-fat diet. Hypertension 51(2): 352–359.
Pinhal, C.S., A. Lopes, D.B. Torres, S.L. Felisbino, J.A. Rocha Gontijo, and P.A. Boer. 2013. Time-course morphological and functional disorders of the kidney induced by long-term high-fat diet intake in female rats. Nephrology Dialysis and Transplantation 28(10): 2464–2476.
Maithilikarpagaselvi, N., M.G. Sridhar, R.P. Swaminathan, and R. Sripradha. 2016. Preventive effect of curcumin on inflammation, oxidative stress and insulin resistance in high-fat fed obese rats. Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine 13(2): 137–143.
Rani, V., G. Deep, R.K. Singh, K. Palle, and U.C. Yadav. 2016. Oxidative stress and metabolic disorders: Pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Life Science 148: 83–93.
Abraham, E., and M. Singer. 2007. Mechanisms of sepsis-induced organ dysfunction. Crit Care Medicine 35(10): 2408–2416.
Van den Berghe, G. 2004. How does blood glucose control with insulin save lives in intensive care? Journal of Clinical Investigation 114(9): 1187–1195.
Rolo, A.P., J.S. Teodoro, and C.M. Palmeira. 2012. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Free Radical in Biology & Medicine 52(1): 59–69.
Zhang, L.N., J.J. Zheng, L. Zhang, X. Gong, H. Huang, C.D. Wang, et al. 2011. Protective effects of asiaticoside on septic lung injury in mice. Experimental Toxicology and Pathology 63(6): 519–525.
Kaplan, J.M., M. Nowell, P. Lahni, M.P. O’Connor, P.W. Hake, and B. Zingarelli. 2012. Short-term high fat feeding increases organ injury and mortality after polymicrobial sepsis. Obesity (Silver Spring) 20(10): 1995–2002.
Steinberg, J., J. Halter, H.J. Schiller, M. Dasilva, S. Landas, L.A. Gatto, et al. 2003. Metalloproteinase inhibition reduces lung injury and improves survival after cecal ligation and puncture in rats. Journal of Surgical Research 111(2): 185–195.
Cadirci, E., Z.A. Berrin, H. Zekai, O. Fehmi, M.H. Uyanik, C. Gundogdu, et al. 2010. α-lipoic acid as a potential target for the treatment of lung injury caused by cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis model in rats. Shock 33(5): 479–484.
Bacanlı, M., S. Aydın, G. Taner, H.G. Göktaş, T. Şahin, A.A. Başaran, et al. 2014. The protective role of ferulic acid on sepsis-induced oxidative damage in Wistar albino rats. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 38(3): 774–782.
Taner, G., S. Aydın, M. Bacanlı, Z. Sarıgöl, T. Sahin, A.A. Başaran, et al. 2014. Modulating effects of pycnogenol® on oxidative stress and DNA damage induced by sepsis in rats. Phytotherapy Research 28(11): 1692–1700.
Arvidsson, S., K. Falt, S. Marklund, and U. Haglund. 1985. Role of free oxygen radicals in the development of gastrointestinal mucosal damage in Escherichia coli sepsis. Circulatory Shock 16(4): 383–393.
**ao, F., S. Pardue, T.Y. Aw, and D.L. Carden. 2005. Obesity exacerbates sepsis-mediated pulmonary microvascular injury. Academic Emergency Medicine 12(5 suppl 1): 37–38.
Mruk, D.D., B. Silvestrini, M.Y. Mo, and C.Y. Cheng. 2002. Antioxidant superoxide dismutase—a review: its function, regulation in the testis, and role in male fertility. Contraception 65(4): 305–311.
Glorieux, C., M. Zamocky, J.M. Sandoval, J. Verrax, and P.B. Calderon. 2015. Regulation of catalase expression in healthy and cancerous cells. Free Radical in Biology & Medicine 87: 84–97.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Programa de Pós-graduação em Ciências da Saúde–UNISUL and the CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All studies were performed in compliance with the National Institutes of Health Guidelines and with the approval of the Animal Care and Experimentation Committee of UNISUL (protocol number 13.026.4.03.IV), Brazil.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petronilho, F., Giustina, A.D., Nascimento, D.Z. et al. Obesity Exacerbates Sepsis-Induced Oxidative Damage in Organs. Inflammation 39, 2062–2071 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0444-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0444-x