Abstract
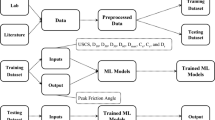
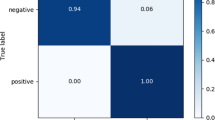
This study presents a comprehensive analysis of the capability of machine learning techniques in estimating the static liquefaction of sands containing plastic fines. In this regard, six methods, including backpropagation multi-layer perceptron, support vector regression (SVR), lazy K-star (LKS), decision table, random forest, and M5, are employed to predict the static liquefaction of saturated clayey sand. Static liquefaction susceptibility of soil is measured using the brittle index. The dataset includes 114 unconsolidated undrained triaxial shear tests performed on saturated sand containing various amounts of plastic fines. Results indicate that all employed models provide satisfactory predictions, with correlation coefficients ranging from 0.82 to 0.92 for testing set. Among all models, the SVR and LKS models make more accurate and reliable predictions. Furthermore, the significance of each input parameter is assessed through a series of sensitivity analyses, which shows that plasticity of fine particles, host sand gradation, and intergranular void ratio are more influential on static liquefaction. Additionally, some mathematical equations are presented for estimating the static liquefaction potential.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The dataset for this study is available upon request from the corresponding author.
References
Abedi M, Yasrobi SS (2010) Effects of plastic fines on the instability of sand. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 30:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2009.09.001
Al Bodour W, Hanandeh S, Hajij M, Murad Y (2022) Development of evaluation framework for the unconfined compressive strength of soils based on the fundamental soil parameters using gene expression programming and deep learning methods. J Mater Civ Eng 34:4021452. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0004087
Atangana Njock PG, Shen SL, Zhou A, Lyu HM (2020) Evaluation of soil liquefaction using AI technology incorporating a coupled ENN / t-SNE model. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 130:105988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.105988
Belkhatir M, Arab A, Della N et al (2010) Influence de l’indice des vides inter-granulaire sur la réponse monotone et cyclique non draine des sols sableux. Comptes Rendus-Mec 338:290–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crme.2010.04.002
Belkhatir M, Missoum H, Arab A et al (2011) Undrained shear strength of sand-silt mixture: effect of intergranular void ratio and other parameters. KSCE J Civ Eng 15:1335–1342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-011-1051-x
Bishop AW (1967) Progressive failure-with special reference to the mechanism causing it. Proc Geotech Conf Oslo 2:142–150
Bouferra R, Shahrour I (2004) Influence of fines on the resistance to liquefaction of a clayey sand. Gr Improv 8:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1680/grim.8.1.1.36366
Breiman L (1996) Bagging predictors. Mach Learn 24:123–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00058655
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Buscarnera G, Whittle AJ (2013) Model prediction of static liquefaction: influence of the initial state on potential instabilities. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 139:420–432. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gt.1943-5606.0000779
Chou J-S, Yang K-H, Lin J-Y (2016) Peak shear strength of discrete fiber-reinforced soils computed by machine learning and metaensemble methods. J Comput Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)cp.1943-5487.0000595
Cleary JG, Trigg LE (1995) K*: an instance-based learner using an entropic distance measure. In: machine learning proceedings 1995. Morgan Kaufmann, pp 108–114
Cover TM, Hart PE (1967) Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 13:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIT.1967.1053964
Das BM (2013) Principles of geotechnical engineering, 8th Editio
Derakhshandi M, Rathje EM, Hazirbaba K, Mirhosseini SM (2008) The effect of plastic fines on the pore pressure generation characteristics of saturated sands. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 28:376–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2007.07.002
Fu LM (1994) Rule generation from neural networks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 24:1114–1124. https://doi.org/10.1109/21.299696
Georgiannou VN, Burland JB, Hight DW (1990) The undrained behaviour of clayey sands in triaxial compression and extension. Geotechnique 40:431–449. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1990.40.3.431
Goodarzi S, Kashani HF, Chrismer S, Ho CL (2021) Using large datasets for finding the correlation between the rate of track settlement and changes in geometry indices. Transp Geotech 31:100665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2021.100665
Hanandeh SM, Al-Bodour WA, Hajij MM (2022) A comparative study of soil liquefaction assessment using machine learning models. Geotech Geol Eng 40:4721–4734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02180-z
Ishihara K (1993) Liquefaction and flow failure during earthquakes. Geotechnique 43:351–451. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1993.43.3.351
Keramatikerman M, Chegenizadeh A, Nikraz H, Sabbar AS (2018) Effect of flyash on liquefaction behaviour of sand-bentonite mixture. Soils Found 58:1288–1296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2018.07.004
Khan SZ, Suman S, Pavani M, Das SK (2016) Prediction of the residual strength of clay using functional networks. Geosci Front 7:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2014.12.008
Kohavi R (1995) The power of decision tables. Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 174–189
Kohestani VR, Hassanlourad M, Ardakani A (2015) Evaluation of liquefaction potential based on CPT data using random forest. Nat Hazards 79:1079–1089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1893-5
Kumar D, Samui P, Kim D, Singh A (2021) A novel methodology to classify soil liquefaction using deep learning. Geotech Geol Eng 39:1049–1058. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01544-7
Lade PV, Yamamuro JA (2011) Evaluation of static liquefaction potential of silty sand slopes. Can Geotech J. https://doi.org/10.1139/T10-063
Lagunas AI (1992) Comportamiento de una arena con caolín ensayado en un sistema automático. National autonomous university of Mexico
Li M, Vitányi P (1993) An introduction to Kolmogorov complexity and its applications. Springer
Macedo J, Vergaray L (2022) Properties of mine tailings for static liquefaction assessment. Can Geotech J. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2020-0600
McCulloch WS, Pitts W (1943) A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys 5:115–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478259
Md. Rahman M (2009) Modelling the influence of fines on liquefaction behaviour. The University of New South Wales at Australian De
Mesri G (2007) Yield strength and critical strength of liquefiable sands in slo** ground. Géotechnique 57:309–311. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2007.57.3.309
Moraglio A, Di Chio C, Poli R (2007) Geometric particle swarm optimisation. Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Mróz Z, Boukpeti N, Drescher A (2003) Constitutive model for static liquefaction. Int J Geomech 3:133–144. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)1532-3641(2003)3:2(133)
Muduli PK, Das SK (2014) CPT-based seismic liquefaction potential evaluation using multi-gene genetic programming approach. Indian Geotech J 44:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-013-0048-4
Naeemifar O, Yasrobi SS (2012) Collapse surface characteristics of clayey sands. Proc Inst Civ Eng Geotech Eng 165:379–390. https://doi.org/10.1680/geng.9.00058
Olson SM, Stark TD (2002) Liquefied strength ratio from liquefaction flow failure case histories. Can Geotech J 39:629–647. https://doi.org/10.1139/t02-001
Olson SM, Stark TD (2003) Yield strength ratio and liquefaction analysis of slopes and embankments. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 129:727–737. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)1090-0241(2003)129:8(727)
Ovando-Shelley E, BP (1997) Undrained behaviour of clayey sands in load controlled triaxial tests. Geotechnique 47:97–111
Papadopoulou AI, Tika TM (2016) The effect of fines plasticity on monotonic undrained shear strength and liquefaction resistance of sands. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 88:191–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2016.04.015
Park SS, Byrne PM (2004) Practical constitutive model for soil liquefaction. In: numerical models in geomechanics—9th proceedings of the international symposium on numerical models in geomechanics, NUMOG 2004. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 181–186
Pitman TD, Robertson PK, Sego DC (1994) Influence of fines on the collapse of loose sands. Can Geotech J 31:728–739. https://doi.org/10.1139/t94-084
Quinlan JR (1992) Learning with continuous classes. Australian joint conference on artificial intelligence. World Scientific, Singapore, pp 343–348
Rahman MM, Lo S-CR (2008) Effect of sand gradation and fines type on liquefaction behaviour of sand-fines mixture. Am Soc Civil Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/40975(318)90
Rahman MM, Lo SR (2012) Predicting the onset of static liquefaction of loose sand with fines. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 138:1037–1041. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gt.1943-5606.0000661
Rumelhart DE, Hinton GE, Williams RJ (1986) Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 323:533–536. https://doi.org/10.1038/323533a0
Sabbar AS, Chegenizadeh A, Nikraz H (2019) Prediction of liquefaction susceptibility of clean sandy soils using artificial intelligence techniques. Indian Geotech J 49:58–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40098-017-0288-9
Sadrekarimi A (2020) Forewarning of static liquefaction landslides. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 146:4020090. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gt.1943-5606.0002320
Savvides A-A, Papadopoulos L (2022) A neural network model for estimation of failure stresses and strains in cohesive soils. Geotechnics. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics2040051
Savvides AA, Papadrakakis M (2021) A computational study on the uncertainty quantification of failure of clays with a modified Cam-Clay yield criterion. SN Appl Sci 3:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04631-3
Schober P, Schwarte LA (2018) Correlation coefficients: appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth Analg 126:1763–1768. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000002864
Shen SL, Elbaz K, Shaban WM, Zhou A (2022) Real-time prediction of shield moving trajectory during tunnelling. Acta Geotech 17:1533–1549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-022-01461-4
Sheskin DJ (2011) Handbook of parametric and nonparametric statistical procedures. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Fifth Edit
Smola AJ, Schölkopf B (2004) A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat Comput 14:199–222. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:STCO.0000035301.49549.88
Stark TD, Mesri G (1994) Undrained shear strength of liquefied sands for stability analysis. J Geotech Eng 120:1287. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1994)120:7(1287)
Talamkhani SSAN (2018) Effect of plastic fines on the undrained behavior of clayey sands. Int J Geotech Geol Eng 12:525–528. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1340402
Talamkhani S, Naeini SA (2021) The undrained shear behavior of reinforced clayey sand. Geotech Geol Eng 39:265–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01490-4
Thevanayagam S, Mohan S (2000) Intergranular state variables and stress-strain behaviour of silty sands. Geotechnique 50:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2000.50.1.1
Thevanayagam S (1998) Effect of fines and confining stress on undrained shear strength of silty sands. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)1090-0241(1999)125:11(1024)
Üstün B, Melssen WJ, Buydens LMC (2006) Facilitating the application of support vector regression by using a universal Pearson VII function based kernel. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 81:29–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2005.09.003
Vapnik VN (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Wang Y, Witten IH (1997) Induction of model trees for predicting continuous classes. In: Proceedings of the 9th European conference on machine learning poster papers. pp 128–137
Witten IH, Frank E (2002) Data mining: practical machine learning tools and techniques with Java implementations. Acm Sigmod Rec 31:76–77
Yan RX, Peng JB, Zhang JY, Wang SK (2020) Static liquefaction capacity of saturated undisturbed loess in South **gyang platform. Water 12:2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082298
Yang Y, Zhang Q (1997) A hierarchical analysis for rock engineering using artificial neural networks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 30:207–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01045717
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by ST. The first draft of the manuscript was written by ST and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Talamkhani, S., Naeini, S.A. & Ardakani, A. Prediction of Static Liquefaction Susceptibility of Sands Containing Plastic Fines Using Machine Learning Techniques. Geotech Geol Eng 41, 3057–3074 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02444-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02444-2