Abstract
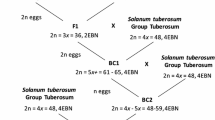
The genomic relationship between Mexican wild diploid species and South American wild and cultivated potato species is ambiguous because these species are reproductively isolated from each other. Previously, we successfully obtained triploid interspecific hybrids between a chromosome-doubled clone of the Mexican wild diploid species Solanum pinnatisectum (2n = 2x = 24) and a cultivated diploid species (A-genome species); these hybrids were then chromosome-doubled and backcrossed to tetraploid potatoes. In this study, we conducted a genomic in situ hybridization (GISH) analysis to reveal the chromosome behaviors of the S. pinnatisectum chromosomes in the hybrid progenies. Due to the high specificity of the A-genome probe for A-genome chromosomes, the chromosomes of the two species were differentially painted. In the triploid hybrid, bivalents with two S. pinnatisectum chromosomes and univalents with cultivated species chromosomes were exclusively observed at meiosis. However, in the hexaploid hybrid, 20% of the S. pinnatisectum chromosomes showed allosyndetic pairing with A-genome chromosomes and formed bivalents and multivalents. From the BC1 to BC4 plants, the number of S. pinnatisectum chromosomes was drastically reduced from 24 to an average of 0.9, and translocation chromosomes were observed. Therefore, we conclude that the S. pinnatisectum germplasm was actually introgressed by recombination into the S. tuberosum genome, which was demonstrated by the presence of an S. pinnatisectum-derived late blight resistance gene (Rpi-blb3) in BC4 plants whose chromosomes were all painted with the A-genome probe.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are included in the manuscript. Plant materials are available upon request.
References
Alonso LC, Kimber G (1981) The analysis of meiosis in hybrids. II. Triploid hybrids. Can J Genet Cytol 23:221–234
Bamberg J, Kielar A, del Rio A, Douches D (2021) Making hybrids with the wild potato Solanum jamesii. Am J Potato Res 98:187–193
Barone A, Sebastiano A, Carputo D, della Rocca F, Frusciante L, (2001) Molecular marker-assisted introgression of the wild Solanum commersonii genome into the cultivated S. tuberosum gene pool. Theor Appl Genet 102:900–907
Black W, Gallegly ME (1957) Screening of Solanum species for resistance to physiologic races of Phytophthora infestans. Am Potato J 34:273–281
Cai D, Rodríguez F, Teng Y, Ané C, Bonierbale M, Mueller LA, Spooner DM (2012) Single copy nuclear gene analysis of polyploidy in wild potatoes (Solanum section Petota). BMC Evol Biol 12:70
Chen Q, Kawchuk LM, Lynch DR, Goettel S, Fujimoto DK (2003) Identification of late blight, Colorado potato beetle and blackleg resistance in three Mexican and two South American wild 2x (1EBN) Solanum species. Am Potato J 80:9–19
Choudhary A, Wright L, Ponce O, Chen J, Prashar A, Sanchez-Moran E, Luo Z, Compton L (2020) Varietal variation and chromosome behaviour during meiosis in Solanum tuberosum. Heredity 125:212–226
Colton LM, Groza HI, Wielgus SM, Jiang J (2006) Marker-assisted selection for the broad-spectrum potato late blight resistance conferred by gene RB derived from a wild potato species. Crop Sci 46:589–594
De Koeyer D, Chen H, Gustafson V (2011) Molecular breeding for potato improvement. In: Bradeen JM, Kole C (eds) Genetics. Genomics and Breeding of Potato, Science Publishers, Enfield, pp 41–67
Dinu II, Hayes RJ, Kynast RG, Phillips RL, Thill CA (2005) Novel inter-series hybrids in Solanum, section Petota. Theor Appl Genet 110:403–415
Dionne LA (1963) Studies on the use of Solanum acaule as a bridge between Solanum tuberosum and species in the series Bulbocastana, Cardiophylla and Pinnatisecta. Euphytica 12:263–269
Dong F, Novy RG, Helgeson JP, Jiang J (1999) Cytological characterization of potato-Solanum etuberosum somatic hybrids and their backcross progenies by genomic in situ hybridization. Genome 42:987–992
Dong F, McGrath JM, Helgeson JP, Jiang J (2001) The genetic identity of alien chromosomes in potato breeding lines revealed by sequential GISH and FISH analyses using chromosome-specific cytogenetic DNA markers. Genome 44:729–734
Gaiero P, Mazzella C, Vilaró F, Speranza P, de Jong H (2017) Pairing analysis and in situ hybridization reveal autopolyploid-like behaviour in Solanum commersonii × S. tuberosum (potato) interspecific hybrids. Euphytica 213:137
Gaiero P, Speranza P, de Jong H (2018) Introgressive hybridization in potato revealed by novel cytogenetic and genomic technologies. Am J Potato Res 95:607–621
Gaiero P, Vaio M, Peters SA, Schranz ME, de Jong H, Speranza PR (2019) Comparative analysis of repetitive sequences among species from the potato and the tomato clades. Ann Bot 123:521–532
Gavrilenko T, Thieme R, Heimbach U, Thieme T (2003) Fertile somatic hybrids of Solanum etuberosum (+) dihaploid Solanum tuberosum and their backcrossing progenies: relationships of genome dosage with tuber development and resistance to potato virus Y. Euphytica 131:323–332
Gong Z, Wu Y, Koblížková A, Torres GA, Wang K, Iovene M, Neumann P, Zhang W, Novák P, Buell CR, Macas J, Jiang J (2012) Repeatless and repeat-based centromeres in potato: implications for centromere evolution. Plant Cell 24:3559–3574
Greplová M, Polzerová H, Vlastníková H (2008) Electrofusion of protoplasts from Solanum tuberosum, S. bulbocastanum and S. pinnatisectum. Acta Physiol Plant 30:787–796
Hardigan MA, Bamberg J, Buell CR, Douches DS (2015) Taxonomy and genetic differentiation among wild and cultivated germplasm of Solanum sect. Petota. The Plant Genome 8:1
Hawkes JG (1958) Significance of wild species and primitive forms for potato breeding. Euphytica 7:257–270
Hawkes JG (1990) The potato: evolution, biodiversity and genetic resources. Belhaven Press, London
He L, Liu J, Torres GA, Zhang H, Jiang J, **e C (2012) Interstitial telomeric repeats are enriched in the centromeres of chromosomes in Solanum species. Chromosome Res 21:5–13
He L, Braz GT, Torres GA, Jiang J (2018) Chromosome painting in meiosis reveals pairing of specific chromosomes in polyploid Solanum species. Chromosoma 127:505–513
Helgeson JP, Pohlman JD, Austin S, Haberlach GT, Wielgus SM, Ronis D, Zambolim L, Tooley P, McGrath JM, James RV, Stevenson WR (1998) Somatic hybrids between Solanum bulbocastanum and potato: a new source of resistance to late blight. Theor Appl Genet 96:738–742
Hermsen JGTh, Ramanna MS (1969) Meiosis in different F1-hybrids of Solanum acaule Bitt. × S. bulbocastanum Dun. and its bearing on genomic relationship, fertility and breeding behaviour. Euphytica 18:27–35
Hermsen JGTh, Ramanna MS (1976) Barriers to hybridization of Solanum bulbocastanum Dun. and S. verrucosum Schlechtd. and structural hybridity in their F1 plants. Euphytica 25:1–10
Hosaka K, Hanneman RE Jr (1998) Genetics of self-compatibility in a self-incompatible wild diploid potato species Solanum chacoense. 2. Localization of an S locus inhibitor (Sli) gene on the potato genome using DNA markers. Euphytica 103:265–271
Howard HW, Swaminathan MS (1952) Species differentiation in the section Tuberarium of Solanum with particular reference to the use of interspecific hybridisation in breeding. Euphytica 1:20–28
Huang B, Ruess H, Liang Q, Colleoni C, Spooner DM (2019) Analyses of 202 plastid genomes elucidate the phylogeny of Solanum section Petota. Sci Rept 9:4454
Iovene M, Barone A, Frusciante L, Monti L, Carputo D (2004) Selection for aneuploid potato hybrids combining a low wild genome content and resistance traits from Solanum commersonii. Theor Appl Genet 109:1139–1146
Iovene M, Savarese S, Cardi T, Frusciante L, Scotti N, Simon PW, Carputo D (2007) Nuclear and cytoplasmic genome composition of Solanum bulbocastanum (+) S. tuberosum somatic hybrids. Genome 450:443–450
Irikura Y (1976) Cytogenetic studies on the haploid plants of tuber-bearing Solanum species. 2. Cytological investigations on haploid plants and interspecific hybrids by utilizing haploidy (in Japanese). Res Bull Hokkaido Natl Agric Exp Stn 115:1–80
Jansky S, Hamernik A (2009) The introgression of 2x 1EBN Solanum species into the cultivated potato using Solanum verrucosum as a bridge. Genet Resour Crop Evol 56:1107–1115
Kato A, Lamb JC, Birchler JA (2004) Chromosome painting using repetitive DNA sequences as probes for somatic chromosome identification in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13554–13559
Kuhl JC, Hanneman RE Jr, Havey MJ, (2001) Characterization and map** of Rpi1, a late-blight resistance locus from diploid (1EBN) Mexican Solanum pinnatisectum. Mol Genet Genomics 265:977–985
Li Y, Colleoni C, Zhang J, Liang Q, Hu Y, Ruess H, Simon R, Liu Y, Liu H, Yu G, Schmitt E, Ponitzki C, Liu G, Huang H, Zhan F, Chen L, Huang Y, Spooner D, Huang B (2018) Genomic analyses yield markers for identifying agronomically important genes in potato. Mol Plant 11:473–484
Lokossou AA, Rietman H, Wang M, Krenek P, van der Schoot H, Henken B, Hoekstra R, Vleeshouwers GAA, van der Vossen EAG, Visser RGF, Jacobsen E, Vosman B (2010) Diversity, distribution, and evolution of Solanum bulbocastanum late blight resistance genes. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 23:1206–1216
Marks GE (1955) Cytogenetic studies in tuberous Solanum species. I. Genomic differentiation in the group Demissa. J Genet 53:262–269
Marks GE (1965) Cytogenetic studies in tuberous Solanum species. III. Species relationships in some South and Central American species. New Phytol 64:293–306
Matsubayashi M (1955) Studies on the species differentiation in the section Tuberarium of Solanum. III. Behavior of meiotic chromosomes in F1 hybrid between S. longipedicellatum and S. schickii, in relation to its parent species. Sci Rept Hyogo Univ Agri 2:25–31
Matsubayashi M (1982) Species differentiation in Solanum, sect. Petota. XI Genomic relationships between S. acaule and certain diploid Commersoniana species. Sci Rept Fac Agr Kobe Univ 15:23–33
Matsubayashi M (1991) Phylogenetic relationships in the potato and its related species. In: Tsuchiya T, Gupta PK (eds) Chromosome engineering in plants: genetics, breeding, evolution, Part B. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 93–118
Matsubayashi M, Misoo S (1977) Species differentiation in Solanum, sect. Tuberarium. IX. Genomic relationships between three Mexican diploid species. Japan J Breed 27:241–250
Menke U, Schilde-Rentschler L, Ruoss B, Zanke C, Hemleben V, Ninnemann H (1996) Somatic hybrids between the cultivated potato Solanum tuberosum L. and the 1EBN wild species Solanum pinnatisectum Dun.: morphological and molecular characterization. Theor Appl Genet 92:617–626
Muakrong N, Kikuchi S, Fukuhara S, Tanya P, Srinives P (2018) Two jatropha karyotypes constructed from meiotic pachytene chromosomes: Pericentric distribution of heterochromatin and variation in repetitive DNAs. PLoS ONE 13:e0208549
Naess SK, Bradeen JM, Wielgus SM, Haberlach GT, McGrath JM, Helgeson JP (2001) Analysis of the introgression of Solanum bulbocastanum DNA into potato breeding lines. Mol Gen Genom 265:694–704
Niederhauser JS, Mills WR (1953) Resistance of Solanum species to Phytophthora infestans in Mexico. Phytopath 43:456–457
Niederhauser JS, Cervantes J, Servin L (1954) Late blight in Mexico and its implications. Phytopath 44:406–408
Oosumi T, Rockhold DR, Maccree MM, Deahl KL, McCue KF, Belknap WR (2009) Gene Rpi-bt1 from Solanum bulbocastanum confers resistance to late blight in transgenic potatoes. Am J Potato Res 86:456–465
Park TH, Gros J, Sikkema A, Vleeshouwers VGAA, Muskens M, Allefs S, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF, van der Vossen EAG (2005a) The late blight resistance locus Rpi-blb3 from Solanum bulbocastanum belongs to a major late blight R gene cluster on chromosome 4 of potato. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18:722–729
Park TH, Vleeshouwers VGAA, Hutten RCB, van Eck HJ, van der Vossen E, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF (2005b) High-resolution map** and analysis of the resistance locus Rpi-abpt against Phytophthora infestans in potato. Mol Breed 16:33–43
Pendinen G, Gavrilenko T, Jiang J, Spooner DM (2008) Allopolyploid speciation of the Mexican tetraploid potato species Solanum stoloniferum and S. hjertingii revealed by genomic in situ hybridization. Genome 51:714–720
Pendinen G, Spooner DM, Jiang J, Gavrilenko T (2012) Genomic in situ hybridization reveals both autopolyploid and allopolyploid origins of different North and Central American hexaploid potato (Solanum sect. Petota) species. Genome 55:407–415
Phumichai C, Ikeguchi-Samitsu Y, Fujimatsu M, Kitanishi S, Kobayashi A, Mori M, Hosaka K (2006) Expression of S locus inhibitor gene (Sli) in various diploid potatoes. Euphytica 148:227–234
Plaisted RL, Hoopes RW (1989) The past record and future prospects for the use of exotic potato germplasm. Am Potato J 66:603–627
Prakken R, Swaminathan MS (1952) Cytological behaviour of some inter-specific hybrids in the genus Solanum sect. Tuberarium. Genetica 26:77–101
Propach H (1937) Cytogenetische Untersuchungen in der Gattung Solanum, Sect. Tuberarium. II. Triploide und tetraploide Artbastarde. Z Induktive Abstammungs- Vererbungslehre 73:143–154
Rakosy-Tican E, Thieme R, König J, Nachtigall M, Hammann T, Denes T-E, Kruppa K, Molnár-Láng M (2020) Introgression of two broad-spectrum late blight resistance genes, Rpi-blb1and Rpi-blb3, from Solanum bulbocastanum Dun plus race-specific R genes into potato pre-breeding lines. Front Plant Sci 11:699
Ramanna MS, Hermsen JGTh (1981) Structural hybridity in the series Etuberosa of the genus Solanum and its bearing on crossability. Euphytica 30:15–31
Ramanna MS, Hermsen JGTh (1982) Gene transfer from non-tuberous to tuberous Solanum species: evidence from meiosis in hybrids. Euphytica 31:565–572
Rodríguez F, Spooner DM (2009) Nitrate reductase phylogeny of potato (Solanum sect. Petota) genomes with emphasis on the origins of the polyploid species. Syst Bot 34:207–219
Ross H (1986) Potato breeding - problems and perspectives. Verlag Paul Parey, Berlin and Hamburg
Sanetomo R, Hosaka K (2013) A recombination-derived mitochondrial genome retained stoichiometrically only among Solanum verrucosum Schltdl. and Mexican polyploid wild potato species. Genet Resour Crop Evol 60:2391–2404
Sanetomo R, Akino S, Suzuki N, Hosaka K (2014) Breakdown of a hybridization barrier between Solanum pinnatisectum Dunal and potato using the S locus inhibitor gene (Sli). Euphytica 197:119–132
Sanetomo R, Habe I, Hosaka K (2019) Sexual introgression of the late blight resistance gene Rpi-blb3 from a Mexican wild diploid species Solanum pinnatisectum Dunal into potato varieties. Mol Breed 39:13
Spooner DM, Sytsma KJ, Conti E (1991) Chloroplast DNA evidence for genome differentiation in wild potatoes Solanum sect. Petota: Solanaceae). Am J Bot 78:1354–1366
Spooner DM, van den Berg RG, Rodríguez A, Bamberg J, Hijmans RJ, Cabrera SIL (2004) Wild potatoes (Solanum section Petota: Solanaceae) of North and Central America. Syst Bot Monogr 68:1–209
Spooner DM, Rodríguez F, Polgár Z, Ballard HEJr, Jansky SH, (2008) Genomic origins of potato polyploids: GBSSI gene sequencing data. Crop Sci 48(S1):S27–S36
Spooner DM, Ghislain M, Simon R, Jansky SH, Gavrilenko T (2014) Systematics, diversity, genetics, and evolution of wild and cultivated potatoes. Bot Rev 80:283–383
Swaminathan MS (1954) Nature of polyploidy in some 48-chromosome species of the genus Solanum, section Tuberarium. Genetics 39:59–76
Szczerbakowa A, Bołtowicz D, Wielgat B (2003) Interspecific somatic hybrids Solanum bulbocastanum (+) S. tuberosum H-8105. Acta Physiol Plant 25:365–373
Tek AL, Stevenson WR, Helgeson JP, Jiang J (2004) Transfer of tuber soft rot and early blight resistances from Solanum brevidens into cultivated potato. Theor Appl Genet 109:249–254
Tiwari JK, Devi S, Ali N, Luthra SK, Kumar V, Bhardwaj V, Singh RK, Rawat S, Chakrabarti SK (2018) Progress in somatic hybridization in potato during the past 40 years. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 132:225–238
Tiwari JK, Rawat S, Luthra SK, Zinta R, Sahu S, Varshney S, Kumar V, Dalamu D, Mandadi N, Kumar M, Chakrabarti SK, Rao AR, Rai A (2021) Genome sequence analysis provides insights on genomic variation and late blight resistance genes in potato somatic hybrid (parents and progeny). Mol Biol Rept 48:623–635
Toxopeus HJ (1960) Studies on the resistance of tuber-bearing Solanaceae from Mexico to Phytophthora infestans. Euphytica 9:39–56
van der Vossen E, Sikkema A, Hekkert BtL, Gros J, Stevens P, Muskens M, Wouters D, Pereira A, Stiekema W, Allef S (2003) An ancient R gene from the wild potato species Solanum bulbocastanum confers broad-spectrum resistance to Phytophthora infestans in cultivated potato and tomato. Plant J 36:867–882
van der Vossen EAG, Gros J, Sikkema A, Muskens M, Wouters D, Wolters P, Pereira A, Allefs S (2005) The Rpi-blb2 gene from Solanum bulbocastanum is an Mi-1 gene homolog conferring broad-spectrum late blight resistance in potato. Plant J 44:208–222
Wang M, Allefs S, van den Berg RG, Vleeshouwers VGAA, van der Vossen EAG, Vosman B (2008) Allele mining in Solanum: conserved homologues of Rpi-blb1 are identified in Solanum stoloniferum. Theor Appl Genet 116:933–943
Wang L, Kikuchi S, Muto C, Naito K, Isemura T, Ishimoto M, Cheng X, Kaga A, Tomooka N (2015) Reciprocal translocation identified in Vigna angularis dominates the wild population in East Japan. J Plant Res 128:653–663
Yang L, Wang D, Xu Y, Zhao H, Wang L, Cao X, Chen Y, Chen Q (2017) A new resistance gene against potato late blight originating from Solanum pinnatisectum located on potato chromosome 7. Front Plant Sci 8:1729
Zhang H, Koblížková A, Wang K, Gong Z, Oliveira L, Torres GA, Wu Y, Zhang W, Novák P, Buell CR, Macas J, Jiang J (2014) Boom-bust turnovers of megabase-sized centromeric DNA in Solanum species: rapid evolution of DNA sequences associated with centromeres. Plant Cell 26:1436–1447
Acknowledgements
We thank the US Potato Genebank at Sturgeon Bay, Wis. for providing Solanum seeds. This research was supported partly by Calbee Inc., Hokkaido Potato Growers Association, Kewpie Corp., KENKO Mayonnaise Co., Ltd., and the Japan Snack Cereal Foods Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SK, RS and KH conceived and designed the experiment and interpreted the results. SK and HI carried out the chromosome observation and GISH analysis. RS prepared all plants and DNA materials. KH conducted the marker analysis. RS and SK wrote the manuscript with the help of KH who edited the final version. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kikuchi, S., Ishii, H., Hosaka, K. et al. Behavior of chromosomes from the Mexican wild diploid species Solanum pinnatisectum in the interspecific hybrid with cultivated potato and its backcross progenies. Euphytica 218, 56 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-03003-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-03003-1