Abstract
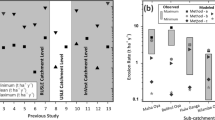
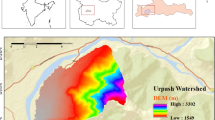
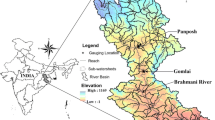
This paper integrates the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) with a GIS model to investigate the spatial distribution of annual soil loss and identify areas of soil erosion risk in the Uluabat sub-watershed, an important agricultural site in Bursa Province, Turkey. The total soil loss from water erosion was 473,274 Mg year−1. Accordingly, 60.3 % of the surveyed area was classified into a very low erosion risk class while 25.7 % was found to be in high and severe erosion risk classes. Soil loss had a close relationship with land use and topography. The most severe erosion risk typically occurs on ridges and steep slopes where agriculture, degraded forest, and shrubs are the main land uses and cover types. Another goal of this study was to use GIS to reveal the multi-year urbanization status caused by rapid urbanization that constitutes another soil erosion risk in this area. Urbanization has increased by 57.7 % and the most areal change was determined in class I lands at a rate of 80 % over 25 years. Urbanization was identified as one of the causes of excessive soil loss in the study area.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, C. L., Jr., & Gibbons, C. J. (1996). Impervious surface coverage: the emergence of a key environmental indicator. Journal of the American Planning Association, 62(2), 243–258.
Arnoldus, H. M. J. (1980). An approximation of the rainfall factor in the universal soil loss equation. In M. De Boodt & D. Gabriels (Eds.), Assessment of erosion (pp. 127–132). Chichester, England: John Wiley and Sons.
Bayramin, I., Basaran, M., Erpul, G., & Canga, M. R. (2008). Assessing the effects of land use changes on soil sensitivity to erosion in a highland ecosystem of semi-arid Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 140, 249–265.
Boggs, G., Devonport, C., Evans, K., & Puig, P. (2001). GIS-based rapid assessment of erosion risk in a small catchment in the wet/dry tropics of Australia. Land Degradation and Development, 12, 417–434.
CEM. (2014). Desertification and erosion in Turkey. General directorate of combating desertification and erosion, Republic of Turkey ministry of forestry and water affairs (CEM). http://www.cem.gov.tr/erozyon/Files/yayinlarimiz/CEMxBROSxINGxMAIL.pdf. Accessed 6 June 2014.
Desmet, P. J. J., & Govers, G. (1996). A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE-LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 51(5), 427–435.
Eswaran, H., Lal, R., & Reich, P. F. (2001). Land degradation: an overview. In E. M. Bridges, I. D. Hannam, L. R. Oldeman, F. W. T. de Vries Pening, S. J. Scherr, & S. Sompatpanit (Eds.), Response to land degradation. Proceeding 2nd International conference on land degradation and desertification, Khon Kaen, Thailand (p. 510). New Delhi, India: Oxford Press.
Grace, J. M. (2000). Forest road side slopes and soil conservation techniques. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 55, 96–101.
Herrick, J. E., Weltz, M. A., Reeder, J. D., Schuman, G. E., & Simanton, J. R. (1999). Rangeland soil erosion and soil quality: role of soil resistance, resilience, and disturbance regime. Ch.13. In R. Lal (Ed.), Soil quality and soil erosion (pp. 209–233). Boca Raton, FL: CRC press.
Hickey, R. (2000). Slope angle and slope length solutions for GIS. Cartography, 29, 1–8.
Holme, A. M. R., Burnside, D. G., & Mitchell, A. A. (1987). The development of a system for monitoring trend in range condition in the arid shrublands of Western Australia. Rangeland Journal, 9, 14–20.
Kinnel, P. I. A. (2001). Slope length factor for applying the USLE-M to erosion in grid cells. Soil and Tillage Research, 58, 11–17.
Kouli, M., Soupios, P., & Vallianatos, F. (2009). Soil erosion prediction using the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) in a GIS framework, Chania, Northwestern Crete Greece. Environmental Geology, 57, 483–497.
Lal, R. (2001). Soil degradation by erosion. Land Degradation and Development, 12, 519–539.
Lambin, E. F., Turner, B. L., Geist, H. J., Agbola, S. B., Angelsen, A., Bruce, J. W., Coomes, O. T., Dirzo, R., Fischer, G., Folke, C., George, P. S., Homewood, K., Imbernon, J., Leemans, R., Li, X., Moran, E. F., Mortimore, M., Ramakrishnan, P. S., Richards, J. F., Skanes, H., Steffen, W., Stone, G. D., Svedin, U., Veldkamp, T. A., Vogel, C., & Xu, J. (2001). The causes of land-use and land-cover change: moving beyond the myths. Global Environmental Change, 11, 261–269.
Lu, D., Li, G., Valladares, G. S., & Batistella, M. (2004). Map** soil erosion risk in Rondonia, Brazilian Amazonia: using RUSLE, remote sensing and GIS. Land Degradation and Development, 15, 499–512.
Moore, I. D., & Burch, G. J. (1986). Physical basis of the length slope factor in the universal soil loss equation. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 50(5), 1294–1298.
Morgan, R. P. (1995). Soil erosion and conservation (2nd ed.). Cranfield: Longman group. 412p.
Nearing, M. A., Pruski, F. F., & O’Neal, M. R. (2004). Expected climate change impacts on soil erosion rates: a review. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 59(1), 43–50.
Oldeman, L. R. (1992). Global extent of soil degradation. Bio-annual report. (pp. 19–36) Waganingen, the Netherlands: International Soil Reference and Information Center.
Onori, F., Bonis, P. D., & Grauso, S. (2006). Soil erosion prediction at the basin scale using the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) in a catchment of Sicily (southern Italy). Environmental Geology, 50, 1129–1140.
Ozsoy, G., Aksoy, E., Dirim, M. S., & Tumsavas, Z. (2012). Determination of soil erosion risk in the Mustafakemalpasa river basin, Turkey, using the revised universal soil loss equation, geographic information system, and remote sensing. Environmental Management, 50(4), 679–694.
Ozsoy, G., Aksoy, E., & Karaata, E. U. (2013). Estimating soil loss of Doganci Dam watershed, northwest Turkey and lifetime analyze of Doganci Dam using multi-year remotely sensed data and GIS techniques. Soil-Water Journal, 2(1), 927–934.
Paul, M. J., & Meyer, J. L. (2001). Streams in the urban landscape. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 32, 333–365.
Renard, K. G., & Freimund, J. R. (1994). Using monthly precipitation data to estimate the R-factor in the revised USLE. Journal of Hydrology, 157, 287–306.
Renard, K. G., Foster, G. R., Weesies, G. A., McCool, D. K., Yoder, D. C. (1997). Predicting soil erosion by water: A guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agriculture Handbook No 703, p 404.
Shalaby, A., Aboel, G. M., & Tateishi, R. (2004). Desertification impact assessment in Egypt using low resolution satellite data and GIS. The International Journal of Environmental Studies, 61(4), 375–384.
Troeh, F. R., Hobbs, J. A., & Donahue, R. L. (2003). Soil and water conservation for productivity and environmental protection (4th ed.). New Jersey, USA: Prentice Hall. 656p.
Van der Kniff, J. M, Jones, R. J. A., Montanarella, L. (2000). Soil erosion risk assessment in Italy. European commission directorate general, joint research centre space applications institute and European soil bureau (p. 52) Italy: EUR 19022EN.
Wischmeier, W. H., & Smith, D. D. (1978). Predicting rainfall erosion losses: a guide to conservation (Agricultural handbook No: 537. Planning, science and education administration). Washington, DC, USA: US Dep. of Agriculture. 58p.
Yu, B., & Rosewell, C. J. (1996). A robust estimator of the R-factor for the universal soil loss equation. Transactions of the ASAE, 39(2), 559–561.
Zhou, P., Luukkanen, O., Tokola, T., & Nieminen, J. (2008). Effect of vegetation cover on soil erosion in a mountainous watershed. Catena, 75, 319–325.
Acknowledgments
The Scientific Research Projects Unit of Uludag University (Grant No. YDP (Z)-2010/5) supported this research. Some parts of this research were carried out at Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA with funds provided by Uludag University. The results of this study provide useful data to decision makers of the Bursa, Turkey metropolitan area.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 47.2 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozsoy, G., Aksoy, E. Estimation of soil erosion risk within an important agricultural sub-watershed in Bursa, Turkey, in relation to rapid urbanization. Environ Monit Assess 187, 419 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4653-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4653-9