Abstract
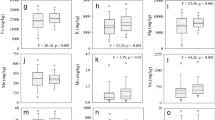
A detailed field study was carried out to monitor (i) the arsenic contents in irrigation groundwater and paddy soil and (ii) the accumulation of arsenic in the roots and grains of different paddy varieties grown in the arsenic-contaminated middle Indo-Gangetic Plains of Northern India. Results showed the highest arsenic contamination in the irrigation groundwater (312 μg l−1) and in paddy soil (35 mg kg−1) values that were significantly exceeded the recommended threshold values of 100 μg l−1 (EU) and 20 mg kg−1 (FAO), respectively. The paddy soil arsenic content ranged from 3 to 35 mg kg−1 with a mean value of 15 mg kg−1. The soil arsenic content was found to be influenced by the soil texture, carbon, macronutrients, phosphorus, sulfur, hydrolases, and oxidoreductases properties of the paddy soils as revealed in the principal component analyses. Higher root accumulation (>10 mg kg−1) of arsenic was observed in 6 of the 17 paddy varieties grown in the study area. The range of arsenic content accumulated in the paddy roots was 4.1 to 16.2 mg kg−1 dry weight (dw) and in the grains 0.179 to 0.932 mg kg−1 dw. Out of 17 paddy varieties, eight had 0 > .55 mg kg−1 grain arsenic content and were found unsafe for subsistence maximum daily tolerable dietary intake (MTDI) by human beings according to the regulatory standards.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedin, M. J., Feldmann, J., & Meharg, A. A. (2002). Uptake kinetics of arsenic species in rice plants. Plant Physiology, 128, 1120–1128.
Ahamed, S., et al. (2006). Arsenic groundwater contamination and its health effects in the state of Uttar Pradesh (UP) in upper and middle Ganga plain. India: a severe danger. Science of the Total Environment, 370, 310–322. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.06.015.
Alam, M., Rahman, M. (2003). Accumulation of arsenic in rice plant from arsenic contaminated irrigation water and effect on nutrient content. Paper presented at the BUET-UNU International symposium of fate of arsenic in the environment, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Banerjee, M., et al. (2013). High arsenic in rice is associated with elevated genotoxic effects in humans. Science Reports, 3, 2195.
Bhattacharya, P., Welch, A. H., Stollenwerk, K. G., McLaughlin, M. J., Bundschuh, J., & Panaullah, G. (2007). Arsenic in the environment: Biology and Chemistry. Science of the Total Environment, 379, 109–120. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.02.037.
Bhattacharyya, P., Tripathy, S., Kim, K., & Kim, S. H. (2008). Arsenic fractions and enzyme activities in arsenic-contaminated soils by groundwater irrigation in West Bengal. Ecotoxicology and Environment Safety, 71, 149–156. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.08.015.
Black, C. A. (ed) (1965) Method of Soil Analysis. Part 2, Chemical and Microbiological Properties. American Society of Agronomy, Inc, Publisher, Madison, Wisconsin USA.
Brammer, H., & Ravenscroft, P. (2009). Arsenic in groundwater: a threat to sustainable agriculture in South and South-east Asia. Environmental International, 35, 647–654. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2008.10.004.
Bundschuh, J., et al. (2012). Arsenic in the human food chain: the Latin American perspective. Science of the Total Environment, 429, 92–106. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.09.069.
Casentini, B., Hug, S. J., & Nikolaidis, N. P. (2011). Arsenic accumulation in irrigated agricultural soils in Northern Greece. Science of the Total Environment, 409, 4802–4810. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.07.064.
Chakraborti, D., et al. (2004). Groundwater arsenic contamination and its health effects in the Ganga-Meghna-Brahmaputra plain. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 6, 74–83.
Das, H. K., Mitra, A. K., Sengupta, P. K., Hossain, A., Islam, F., & Rabbani, G. H. (2004). Arsenic concentrations in rice, vegetables, and fish in Bangladesh: a preliminary study. Environmental International, 30, 383–387. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2003.09.005.
Das, S., Jean, S. H., Kar, S., & Chakraborty, S. (2013). Effect of arsenic contamination on bacterial and fungal biomass and enzyme activities in tropical arsenic-contaminated soils. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 49, 757–765.
Dick, R. P. (ed) (2011) Methods of Soil Enzymology. Issue 9 of Soil Science Society of America book series. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, USA.
Fernandez, P., Sommer, I., Cram, S., Rosas, I., & Gutierrez, M. (2005). The influence of water-soluble As(III) and As(V) on dehydrogenase activity in soils affected by mine tailings. Science of the Total Environment, 348, 231–243. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.12.065.
Ghosh, A. K., Bhattacharyya, P., & Pal, R. (2004). Effect of arsenic contamination on microbial biomass and its activities in arsenic contaminated soils of Gangetic West Bengal. India Environmental International, 30, 491–499. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2003.10.002.
Hite, A. H. (2013). Arsenic and rice: a call for regulation. Nutrition, 29, 353–354. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2012.10.001.
Hossain, M. B., Jahiruddin, M., Panaullah, G. M., Loeppert, R. H., Islam, M. R., & Duxbury, J. M. (2008). Spatial variability of arsenic concentration in soils and plants, and its relationship with iron, manganese and phosphorus. Environmental Pollution, 156, 739–744. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2008.06.015.
Hua, B., Yan, W., Wang, J., Deng, B., & Yang, J. (2011). Arsenic accumulation in rice grains: effects of cultivars and water management practices. Environmental Engineering Science, 28, 591–596.
Islam, M. R., Salminen, R., & Lahermo, P. W. (2000). Arsenic and other toxic elemental contamination of groundwater, surface water and soil in Bangladesh and its possible effects on human health. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 22, 33–53.
Karaca, A., Cetin, S. C., Turgay, O. C., & Kizilkaya, R. (2010). Effects of heavy metals on soil enzyme activities. In I. Sherameti & A. Varma (Eds.), Soil heavy metals (pp. 237–262). Berlin, Germany: Springer.
Khan, M., Islam, M., Panaullah, G., Duxbury, J., Jahiruddin, M., & Loeppert, R. (2009). Fate of irrigation-water arsenic in rice soils of Bangladesh. Plant and Soil, 322, 263–277.
Koo, N., Lee, S., & Kim, J. (2012). Arsenic mobility in the amended mine tailings and its impact on soil enzyme activity. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 34, 337–348.
Lei, M., Tie, B., Zeng, M., Qing, P., Song, Z., Williams, P. N., & Huang, Y. (2012). An arsenic-contaminated field trial to assess the uptake and translocation of arsenic by genotypes of rice. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 35, 379–390.
Meharg, A. A., & Rahman, M. M. (2003). Arsenic contamination of Bangladesh paddy field soils: implications for rice contribution to arsenic consumption. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 229–234.
Mukherjee, A. B., Bhattacharya, P., Jacks,G., Banerjee, D. M., Ramanathan, A. L., Mahanta, C. (2006). Groundwater arsenic contamination in India: Extent and severity. In: R. Naidu ES, G. Owens, P. Bhattacharya, & P. Nadebaum (ed) Managing arsenic in the environment: From soil to human health CSRIO Publishing, Melbourne, pp 553–594.
Norton, G. J., et al. (2009a). Environmental and genetic control of arsenic accumulation and speciation in rice grain: comparing a range of common cultivars grown in contaminated sites across Bangladesh, China, and India. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 8381–8386. doi:10.1021/es901844q.
Norton, G. J., et al. (2009b). Identification of low inorganic and total grain arsenic rice cultivars from Bangladesh. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 6070–6075.
Norton, G. J., et al. (2010). Arsenic shoot-grain relationships in field grown rice cultivars. Environmental Science and Technology, 44, 1471–1477. doi:10.1021/es902992d.
Norton, G. J., et al. (2012). Variation in grain arsenic assessed in a diverse panel of rice (Oryza sativa) grown in multiple sites. New Phytologist, 193, 650–664. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03983.x.
Panaullah, G., et al. (2009). Arsenic toxicity to rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Bangladesh. Plant and Soil, 317, 31–39.
Patel, K. S., Shrivas, K., Brandt, R., Jakubowski, N., Corns, W., & Hoffmann, P. (2005). Arsenic contamination in water, soil, sediment and rice of central India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 27, 131–145. doi:10.1007/s10653-005-0120-9.
Rahman, M. A., Hasegawa, H., Rahman, M. M., & Miah, M. A. (2007). Accumulation of arsenic in tissues of rice plant (Oryza sativa L.) and its distribution in fractions of rice grain. Chemosphere, 69, 942–948. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.05.044.
Rahman, M. A., Hasegawa, H., Rahman, M. M., Miah, M. A. M., & Tasmin, A. (2008). Arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.): human exposure through food chain. Ecotoxicology and Environment Safety, 69, 317–324. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.01.005.
Rahman, M. M., Naidu, R., & Bhattacharya, P. (2009). Arsenic contamination in groundwater in the Southeast Asia region. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 31, 9–21. doi:10.1007/s10653-008-9233-2.
Sidhu, S. S., Brar, J. S., Biswas, A., Banger, K., & Saroa, G. S. (2012). Arsenic contamination in soil-water-plant (rice, Oryza sativa L.) continuum in central and sub-mountainous Punjab, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol, 89, 1046–1050. doi:10.1007/s00128-012-0799-0.
Singh, M., Singh, A. K., Srivastava, S. N., Singh, S., & Chowdhary, A. K. (2010). Arsenic mobility in fluvial environment of the Ganga Plain, Northern India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 59, 1703–1715.
Sinha, B., & Bhattacharyya, K. (2011). Retention and release isotherm of arsenic in arsenic-humic/fulvic equilibrium study. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 47, 815–822.
Srivastava, P. K., Gupta, M., Upadhyay, R. K., Sharma, S., Shikha, S. N., Tewari, S. K., & Singh, B. (2012). Effects of combined application of vermicompost and mineral fertilizer on the growth of Allium cepa L. and soil fertility. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 175, 101–107.
Srivastava, P. K., Singh, M., Singh, N., & Tripathi, R. D. (2013). Soil arsenic pollution: a threat to crops. Journal of Bioremediation & Biodegradation, 4, 7.
Srivastava, P. K., Singh, P. C., Gupta, M., Sinha, A., Vaish, A., Shukla, A., Singh, N., & Tewari, S. K. (2011a). Influence of earthworm culture on fertilization potential and biological activities of vermicomposts prepared from different plant wastes. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 174, 420–429.
Srivastava, P. K., Vaish, A., Dwivedi, S., Chakrabarty, D., Singh, N., & Tripathi, R. D. (2011b). Biological removal of arsenic pollution by soil fungi. Science of the Total Environment, 409, 2430–2442. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.03.002.
Srivastava, S., & Sharma, Y. K. (2013). Arsenic occurrence and accumulation in soil and water of eastern districts of Uttar Pradesh, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 4995–5002.
Stroud, J. L., et al. (2011). The dynamics of arsenic in four paddy fields in the Bengal delta. Environmental Pollution, 159, 947–953. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2010.12.016.
Su, Y. H., McGrath, S. P., & Zhao, F. J. (2010). Rice is more efficient in arsenite uptake and translocation than wheat and barley. Plant and Soil, 328, 27–34.
Van Zwieten, L., Ayres, M. R., & Morris, S. G. (2003). Influence of arsenic co-contamination on DDT breakdown and microbial activity. Environmental Pollution, 124, 331–339.
WHO (2005). Water sanitation and health. Guidelines for drinking water quality. 3rd edn. World Health Organization.
Williams, P. N., Prince, A. H., Raab, A., Hossain, S. A., Feldmann, J., & Meharg, A. A. (2005). Variation in arsenic speciation and concentration in paddy rice related to dietary exposure. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 5531–5540.
Wu, C., Ye, Z. H., Shu, W. S., Zhu, Y. G., & Wong, M. H. (2011). Arsenic accumulation and speciation in rice are affected by root aeration and variation of genotypes. Journal of Experimental Botany, 62, 2889–2898. doi:10.1093/jxb/erq462.
Yan, W., Agrama, A. H., Slaton, A. N., & Gibbons, W. J. (2008). Soil and plant minerals associated with rice straighthead disorder induced by arsenic. Agronomy Journal, 100, 1655.
Zavala, Y. J., & Duxbury, J. M. (2008). Arsenic in rice: I. Estimating normal levels of total arsenic in rice grain. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 3856–3860.
Zhao, F. J., McGrath, S. P., & Meharg, A. A. (2010). Arsenic as a food chain contaminant: mechanisms of plant uptake and metabolism and mitigation strategies. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 61, 535–559.
Zheng, M. Z., et al. (2011). Spatial distribution of arsenic and temporal variation of its concentration in rice. New Phytologist, 189, 200–209. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03456.x.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support for this work from the Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India. Authors are also thankful to the Director, CSIR–National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow, India, for providing the institutional support. Ms. Manvi Singh, UGC-SRF (ref. no. 3185/NET-DEC-2011) is thankful to UGC for financial support to her as SRF. The contributions of Prof. R. S. Tripathi and Prof. S. A Ranade for required linguistic correction of the paper are also gratefully acknowledged.
Compliance with ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure S1
Correlations among soil, root and grain arsenic (As) contents of R&D based released paddy varieties grown in the middle IGP region. (DOC 54 kb)
Figure S2
Correlations among soil, root and grain arsenic (As) contents of traditional paddy varieties grown in the middle IGP region. (DOC 40 kb)
Figure S3
Correlations among soil, root and grain arsenic (As) contents of company hybrids paddy varieties grown in the middle IGP region. (DOC 44 kb)
Table S1
GPS details of all 18 blocks in different districts as project sites in the middle IGP region of the state of Uttar Pradesh, India. (DOC 41 kb)
Table S2
Different soil physical properties (Mean ± SE) of paddy soils in the middle IGP region. (DOC 54 kb)
Table S3
Different soil chemical properties (Mean ± SE) of paddy soils in the middle IGP region. (DOC 87 kb)
Table S4
Different soil enzyme activities (Mean ± SE) of paddy soils in the middle IGP region. (DOC 57 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, P.K., Singh, M., Gupta, M. et al. Map** of arsenic pollution with reference to paddy cultivation in the middle Indo-Gangetic Plains. Environ Monit Assess 187, 198 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4418-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4418-5